Xiuling Wang
Communication-efficient Federated Graph Classification via Generative Diffusion Modeling
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) unlock new ways of learning from graph-structured data, proving highly effective in capturing complex relationships and patterns. Federated GNNs (FGNNs) have emerged as a prominent distributed learning paradigm for training GNNs over decentralized data. However, FGNNs face two significant challenges: high communication overhead from multiple rounds of parameter exchanges and non-IID data characteristics across clients. To address these issues, we introduce CeFGC, a novel FGNN paradigm that facilitates efficient GNN training over non-IID data by limiting communication between the server and clients to three rounds only. The core idea of CeFGC is to leverage generative diffusion models to minimize direct client-server communication. Each client trains a generative diffusion model that captures its local graph distribution and shares this model with the server, which then redistributes it back to all clients. Using these generative models, clients generate synthetic graphs combined with their local graphs to train local GNN models. Finally, clients upload their model weights to the server for aggregation into a global GNN model. We theoretically analyze the I/O complexity of communication volume to show that CeFGC reduces to a constant of three communication rounds only. Extensive experiments on several real graph datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of CeFGC against state-of-the-art competitors, reflecting our superior performance on non-IID graphs by aligning local and global model objectives and enriching the training set with diverse graphs.
Inference Attacks Against Graph Generative Diffusion Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Graph generative diffusion models have recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for generating complex graph structures, effectively capturing intricate dependencies and relationships within graph data. However, the privacy risks associated with these models remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we investigate information leakage in such models through three types of black-box inference attacks. First, we design a graph reconstruction attack, which can reconstruct graphs structurally similar to those training graphs from the generated graphs. Second, we propose a property inference attack to infer the properties of the training graphs, such as the average graph density and the distribution of densities, from the generated graphs. Third, we develop two membership inference attacks to determine whether a given graph is present in the training set. Extensive experiments on three different types of graph generative diffusion models and six real-world graphs demonstrate the effectiveness of these attacks, significantly outperforming the baseline approaches. Finally, we propose two defense mechanisms that mitigate these inference attacks and achieve a better trade-off between defense strength and target model utility than existing methods. Our code is available at https://zenodo.org/records/17946102.
Feature-Aware One-Shot Federated Learning via Hierarchical Token Sequences
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:One-shot federated learning (OSFL) reduces the communication cost and privacy risks of iterative federated learning by constructing a global model with a single round of communication. However, most existing methods struggle to achieve robust performance on real-world domains such as medical imaging, or are inefficient when handling non-IID (Independent and Identically Distributed) data. To address these limitations, we introduce FALCON, a framework that enhances the effectiveness of OSFL over non-IID image data. The core idea of FALCON is to leverage the feature-aware hierarchical token sequences generation and knowledge distillation into OSFL. First, each client leverages a pretrained visual encoder with hierarchical scale encoding to compress images into hierarchical token sequences, which capture multi-scale semantics. Second, a multi-scale autoregressive transformer generator is used to model the distribution of these token sequences and generate the synthetic sequences. Third, clients upload the synthetic sequences along with the local classifier trained on the real token sequences to the server. Finally, the server incorporates knowledge distillation into global training to reduce reliance on precise distribution modeling. Experiments on medical and natural image datasets validate the effectiveness of FALCON in diverse non-IID scenarios, outperforming the best OSFL baselines by 9.58% in average accuracy.
Equipping Federated Graph Neural Networks with Structure-aware Group Fairness
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been widely used for various types of graph data processing and analytical tasks in different domains. Training GNNs over centralized graph data can be infeasible due to privacy concerns and regulatory restrictions. Thus, federated learning (FL) becomes a trending solution to address this challenge in a distributed learning paradigm. However, as GNNs may inherit historical bias from training data and lead to discriminatory predictions, the bias of local models can be easily propagated to the global model in distributed settings. This poses a new challenge in mitigating bias in federated GNNs. To address this challenge, we propose $\text{F}^2$GNN, a Fair Federated Graph Neural Network, that enhances group fairness of federated GNNs. As bias can be sourced from both data and learning algorithms, $\text{F}^2$GNN aims to mitigate both types of bias under federated settings. First, we provide theoretical insights on the connection between data bias in a training graph and statistical fairness metrics of the trained GNN models. Based on the theoretical analysis, we design $\text{F}^2$GNN which contains two key components: a fairness-aware local model update scheme that enhances group fairness of the local models on the client side, and a fairness-weighted global model update scheme that takes both data bias and fairness metrics of local models into consideration in the aggregation process. We evaluate $\text{F}^2$GNN empirically versus a number of baseline methods, and demonstrate that $\text{F}^2$GNN outperforms these baselines in terms of both fairness and model accuracy.
Group Property Inference Attacks Against Graph Neural Networks
Sep 02, 2022
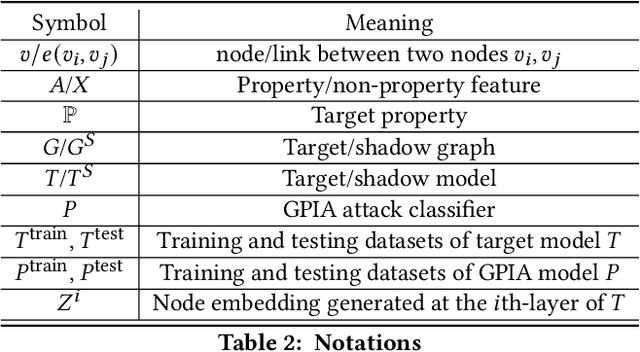
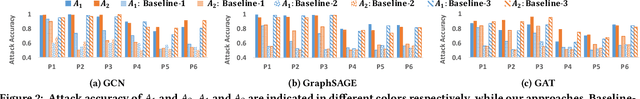

Abstract:With the fast adoption of machine learning (ML) techniques, sharing of ML models is becoming popular. However, ML models are vulnerable to privacy attacks that leak information about the training data. In this work, we focus on a particular type of privacy attacks named property inference attack (PIA) which infers the sensitive properties of the training data through the access to the target ML model. In particular, we consider Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) as the target model, and distribution of particular groups of nodes and links in the training graph as the target property. While the existing work has investigated PIAs that target at graph-level properties, no prior works have studied the inference of node and link properties at group level yet. In this work, we perform the first systematic study of group property inference attacks (GPIA) against GNNs. First, we consider a taxonomy of threat models under both black-box and white-box settings with various types of adversary knowledge, and design six different attacks for these settings. We evaluate the effectiveness of these attacks through extensive experiments on three representative GNN models and three real-world graphs. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of these attacks whose accuracy outperforms the baseline approaches. Second, we analyze the underlying factors that contribute to GPIA's success, and show that the target model trained on the graphs with or without the target property represents some dissimilarity in model parameters and/or model outputs, which enables the adversary to infer the existence of the property. Further, we design a set of defense mechanisms against the GPIA attacks, and demonstrate that these mechanisms can reduce attack accuracy effectively with small loss on GNN model accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge