Weitong Zhai
Cognitive-Driven Optimization of Sparse Array Transceiver for MIMO Radar Beamforming
Mar 04, 2021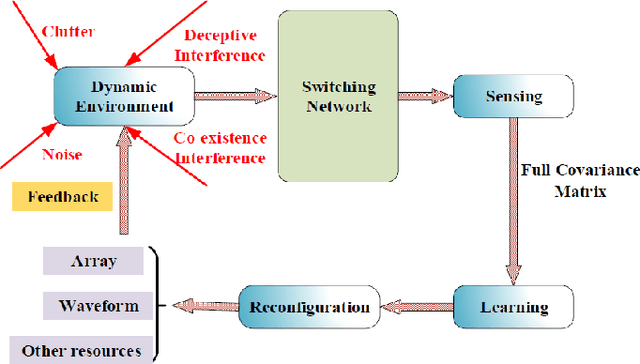

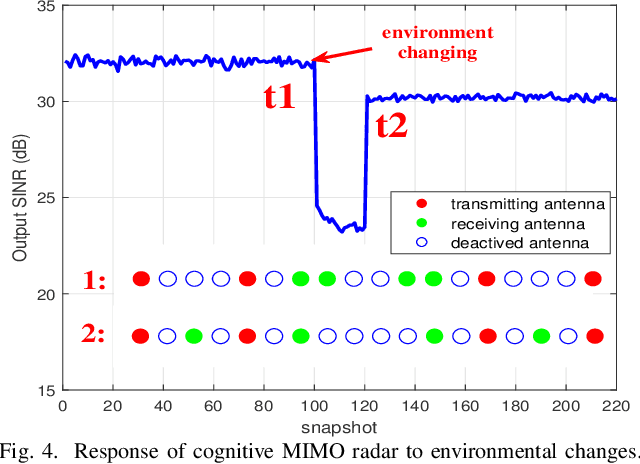
Abstract:Cognitive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar is capable of adjusting system parameters adaptively by sensing and learning in complex dynamic environment. Beamforming performance of MIMO radar is guided by both beamforming weight coefficients and the transceiver configuration. We propose a cognitive-driven MIMO array design where both the beamforming weights and the transceiver configuration are adaptively and concurrently optimized under different environmental conditions. The perception-action cycle involves data collection of full virtual array, covariance reconstruction and joint design of the transmit and receive arrays by antenna selection.The optimal transceiver array design is realized by promoting two-dimensional group sparsity via iteratively minimizing reweighted mixed L21-norm, with constraints imposed on transceiver antenna spacing for proper transmit/receive isolation. Simulations are provided to demonstrate the "perception-action" capability of the proposed cognitive sparse MIMO array in achieving enhanced beamforming and anti-jamming in dynamic target and interference environment.
Sparse Array Transceiver Design for Enhanced Adaptive Beamforming in MIMO Radar
Feb 20, 2021
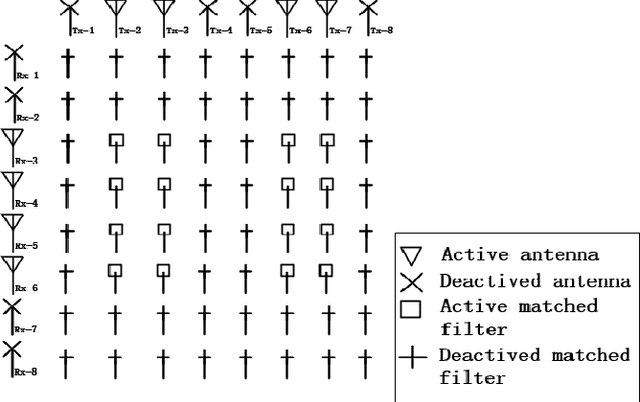

Abstract:Sparse array design aided by emerging fast sensor switching technologies can lower the overall system overhead by reducing the number of expensive transceiver chains. In this paper, we examine the active sparse array design enabling the maximum signal to interference plus noise ratio (MaxSINR) beamforming at the MIMO radar receiver. The proposed approach entails an entwined design, i.e., jointly selecting the optimum transmit and receive sensor locations for accomplishing MaxSINR receive beamforming. Specifically, we consider a co-located multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar platform with orthogonal transmitted waveforms, and examine antenna selections at the transmit and receive arrays. The optimum active sparse array transceiver design problem is formulated as successive convex approximation (SCA) alongside the two-dimensional group sparsity promoting regularization. Several examples are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in utilizing the given transmit/receive array aperture and degrees of freedom for achieving MaxSINR beamforming.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge