Varvara Guljajeva
Why Open Small AI Models Matter for Interactive Art
Nov 12, 2025
Abstract:This position paper argues for the importance of open small AI models in creative independence for interactive art practices. Deployable locally, these models offer artists vital control over infrastructure and code, unlike dominant large, closed-source corporate systems. Such centralized platforms function as opaque black boxes, imposing severe limitations on interactive artworks, including restrictive content filters, preservation issues, and technical challenges such as increased latency and limited interfaces. In contrast, small AI models empower creators with more autonomy, control, and sustainability for these artistic processes. They enable the ability to use a model as long as they want, create their own custom model, either by making code changes to integrate new interfaces, or via new datasets by re-training or fine-tuning the model. This fosters technological self-determination, offering greater ownership and reducing reliance on corporate AI ill-suited for interactive art's demands. Critically, this approach empowers the artist and supports long-term preservation and exhibition of artworks with AI components. This paper explores the practical applications and implications of using open small AI models in interactive art, contrasting them with closed-source alternatives.
Loading Ceramics: Visualising Possibilities of Robotics in Ceramics
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:This article introduces an artistic research project that utilises artist-in-residency and exhibition as methods for exploring the possibilities of robotic 3D printing and ceramics. The interdisciplinary project unites artists and architects to collaborate on a proposed curatorial concept and Do-It-With-Others (DIWO) technological development. Constraints include material, specifically local clay, production technique, namely 3D printing with a robotic arm, and kiln size, as well as an exhibition concept that is further elaborated in the next chapter. The pictorial presents four projects as case studies demonstrating how the creatives integrate these constraints into their processes. This integration leads to the subsequent refinement and customization of the robotic-ceramics interface, aligning with the practitioners' requirements through software development. The project's focus extends beyond artistic outcomes, aiming also to advance the pipeline of 3D robotic printing in clay, employing a digitally controlled material press that has been developed in-house, with its functionality refined through practice.
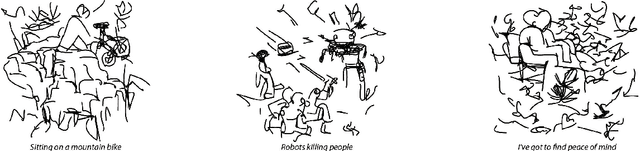
Visions of Destruction: Exploring a Potential of Generative AI in Interactive Art
Aug 26, 2024Abstract:This paper explores the potential of generative AI within interactive art, employing a practice-based research approach. It presents the interactive artwork "Visions of Destruction" as a detailed case study, highlighting its innovative use of generative AI to create a dynamic, audience-responsive experience. This artwork applies gaze-based interaction to dynamically alter digital landscapes, symbolizing the impact of human activities on the environment by generating contemporary collages created with AI, trained on data about human damage to nature, and guided by audience interaction. The transformation of pristine natural scenes into human-made and industrialized landscapes through viewer interaction serves as a stark reminder of environmental degradation. The paper thoroughly explores the technical challenges and artistic innovations involved in creating such an interactive art installation, emphasizing the potential of generative AI to revolutionize artistic expression, audience engagement, and especially the opportunities for the interactive art field. It offers insights into the conceptual framework behind the artwork, aiming to evoke a deeper understanding and reflection on the Anthropocene era and human-induced climate change. This study contributes significantly to the field of creative AI and interactive art, blending technology and environmental consciousness in a compelling, thought-provoking manner.
Explaining CLIP through Co-Creative Drawings and Interaction
Jun 12, 2023


Abstract:This paper analyses a visual archive of drawings produced by an interactive robotic art installation where audience members narrated their dreams into a system powered by CLIPdraw deep learning (DL) model that interpreted and transformed their dreams into images. The resulting archive of prompt-image pairs were examined and clustered based on concept representation accuracy. As a result of the analysis, the paper proposes four groupings for describing and explaining CLIP-generated results: clear concept, text-to-text as image, indeterminacy and confusion, and lost in translation. This article offers a glimpse into a collection of dreams interpreted, mediated and given form by Artificial Intelligence (AI), showcasing oftentimes unexpected, visually compelling or, indeed, the dream-like output of the system, with the emphasis on processes and results of translations between languages, sign-systems and various modules of the installation. In the end, the paper argues that proposed clusters support better understanding of the neural model.
Synthetic Books
Jan 24, 2022



Abstract:The article explores new ways of written language aided by AI technologies, like GPT-2 and GPT-3. The question that is stated in the paper is not about whether these novel technologies will eventually replace authored books, but how to relate to and contextualize such publications and what kind of new tools, processes, and ideas are behind them. For that purpose, a new concept of synthetic books is introduced in the article. It stands for the publications created by deploying AI technology, more precisely autoregressive language models that are able to generate human-like text. Supported by the case studies, the value and reasoning of the synthetic books are discussed. The paper emphasizes that artistic quality is an issue when it comes to AI-generated content. The article introduces projects that demonstrate an interactive input by an artist and/or audience combined with the deep-learning-based language models. In the end, the paper focuses on understanding the neural aesthetics of written language in the art context.
* 7 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge