Travis Mandel
Reliable Multi-Object Tracking in the Presence of Unreliable Detections
Dec 15, 2021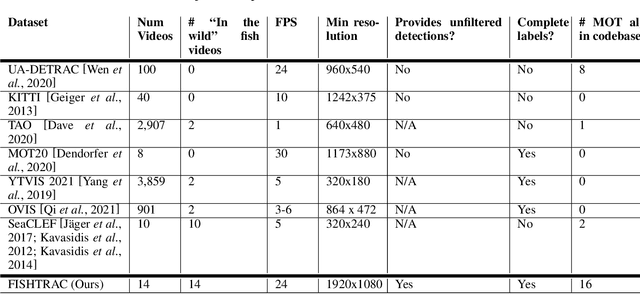
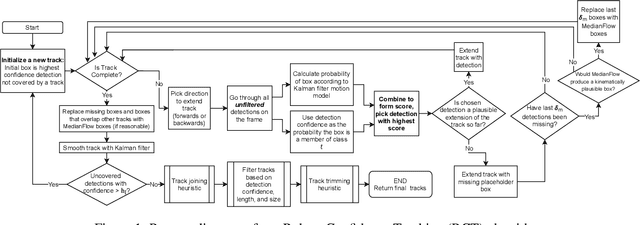
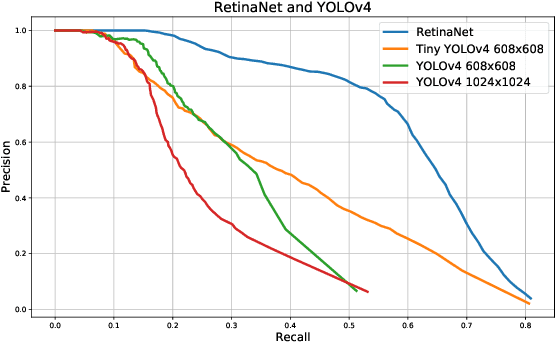
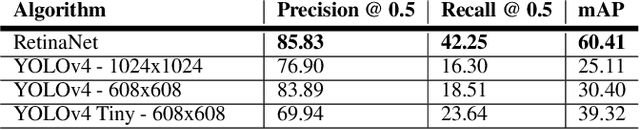
Abstract:Recent multi-object tracking (MOT) systems have leveraged highly accurate object detectors; however, training such detectors requires large amounts of labeled data. Although such data is widely available for humans and vehicles, it is significantly more scarce for other animal species. We present Robust Confidence Tracking (RCT), an algorithm designed to maintain robust performance even when detection quality is poor. In contrast to prior methods which discard detection confidence information, RCT takes a fundamentally different approach, relying on the exact detection confidence values to initialize tracks, extend tracks, and filter tracks. In particular, RCT is able to minimize identity switches by efficiently using low-confidence detections (along with a single object tracker) to keep continuous track of objects. To evaluate trackers in the presence of unreliable detections, we present a challenging real-world underwater fish tracking dataset, FISHTRAC. In an evaluation on FISHTRAC as well as the UA-DETRAC dataset, we find that RCT outperforms other algorithms when provided with imperfect detections, including state-of-the-art deep single and multi-object trackers as well as more classic approaches. Specifically, RCT has the best average HOTA across methods that successfully return results for all sequences, and has significantly less identity switches than other methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge