Tamer Cavalcante
A New Algorithm of Speckle Filtering using Stochastic Distances
Aug 29, 2013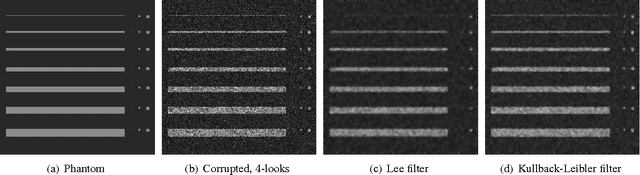
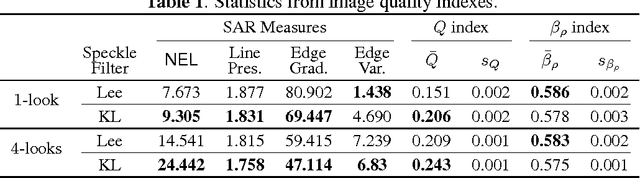
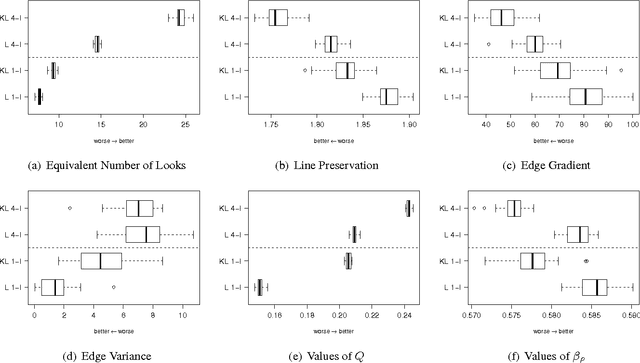
Abstract:This paper presents a new approach for filter design based on stochastic distances and tests between distributions. A window is defined around each pixel, overlapping samples are compared and only those which pass a goodness-of-fit test are used to compute the filtered value. The technique is applied to intensity SAR data with homogeneous regions using the Gamma model. The proposal is compared with the Lee's filter using a protocol based on Monte Carlo. Among the criteria used to quantify the quality of filters, we employ the equivalent number of looks, line and edge preservation. Moreover, we also assessed the filters by the Universal Image Quality Index and the Pearson's correlation on edges regions.
Speckle Reduction using Stochastic Distances
Jul 03, 2012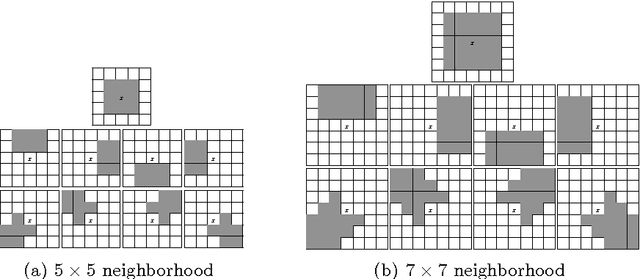
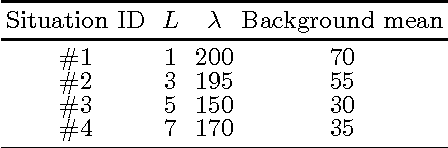
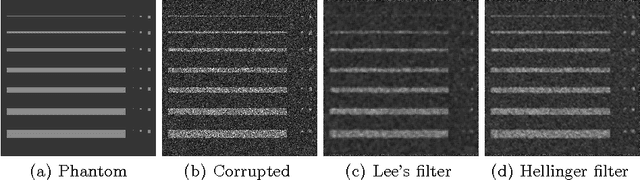
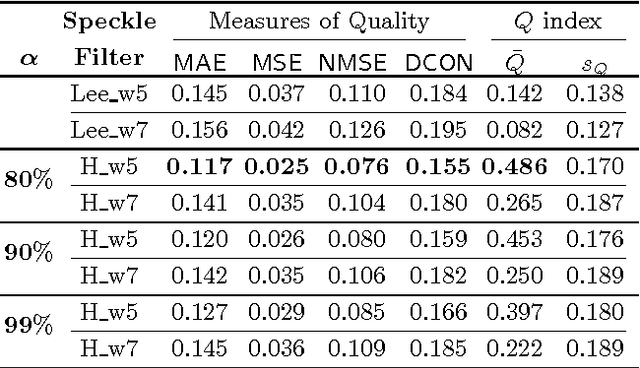
Abstract:This paper presents a new approach for filter design based on stochastic distances and tests between distributions. A window is defined around each pixel, samples are compared and only those which pass a goodness-of-fit test are used to compute the filtered value. The technique is applied to intensity Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data, using the Gamma model with varying number of looks allowing, thus, changes in heterogeneity. Modified Nagao-Matsuyama windows are used to define the samples. The proposal is compared with the Lee's filter which is considered a standard, using a protocol based on simulation. Among the criteria used to quantify the quality of filters, we employ the equivalent number of looks (related to the signal-to-noise ratio), line contrast, and edge preservation. Moreover, we also assessed the filters by the Universal Image Quality Index and the Pearson's correlation between edges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge