Suparna Biswas
Detection of Epilepsy Seizure using Different Dimensionality Reduction Techniques and Machine Learning on Transform Domain
Feb 17, 2023



Abstract:An Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive exam that records the electrical activity of the brain. This exam is used to help diagnose conditions such as different brain problems. EEG signals are taken for the purpose of epilepsy detection and with Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and machine learning classifier, they perform epilepsy detection. In Epilepsy seizure detection, mainly machine learning classifiers and statistical features are used. The hidden information in the EEG signal is useful for detecting diseases affecting the brain. Sometimes it is very difficult to identify the minimum changes in the EEG in time and frequency domains purpose. The DWT can give a good decomposition of the signals in different frequency bands and feature extraction. We use the tri-dimensionality reduction algorithm.; Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Independent Component Analysis (ICA) and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA). Finally, features are selected by using a fusion rule and at the last step three different classifiers Support Vector Machine (SVM), Naive Bayes (NB) and K-Nearest-Neighbor (KNN) has been used for the classification. The proposed framework is tested on the Bonn dataset and the simulation results provide the maximum accuracy for the combination of LDA and NB for 10-fold cross validation technique. It shows the maximum average sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, Precision and Recall of 100%, 100%, 100%, 100% and 100%. The results prove the effectiveness of this model.
An Efficient Epileptic Seizure Detection Technique using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Machine Learning Classifiers
Sep 26, 2021


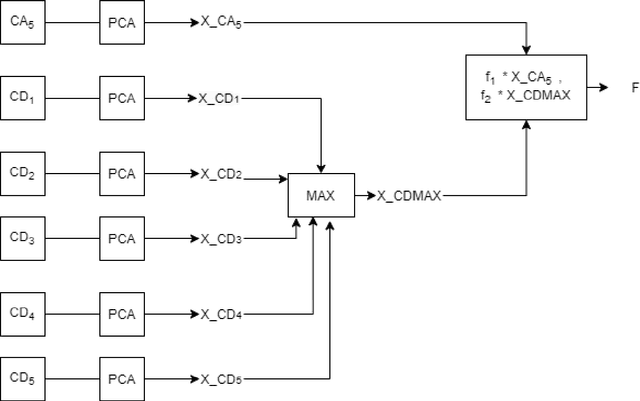
Abstract:This paper presents an epilepsy detection method based on discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and Machine learning classifiers. Here DWT has been used for feature extraction as it provides a better decomposition of the signals in different frequency bands. At first, DWT has been applied to the EEG signal to extract the detail and approximate coefficients or different sub-bands. After the extraction of the coefficients, principal component analysis (PCA) has been applied on different sub-bands and then a feature level fusion technique is used to extract the important features in low dimensional feature space. Three classifiers namely: Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier, K-Nearest-Neighbor (KNN) classifier, and Naive Bayes (NB) Classifiers have been used in the proposed work for classifying the EEG signals. The proposed method is tested on Bonn databases and provides a maximum of 100% recognition accuracy for KNN, SVM, NB classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge