Stéphane Mottelet
La production de nitrites lors de la dénitrification des eaux usées par biofiltration - Stratégie de contrôle et de réduction des concentrations résiduelles
Nov 28, 2017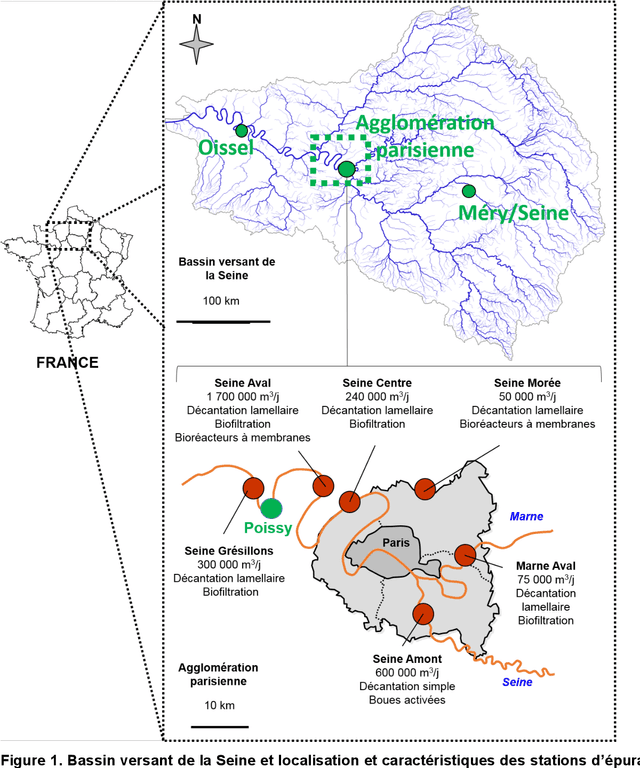
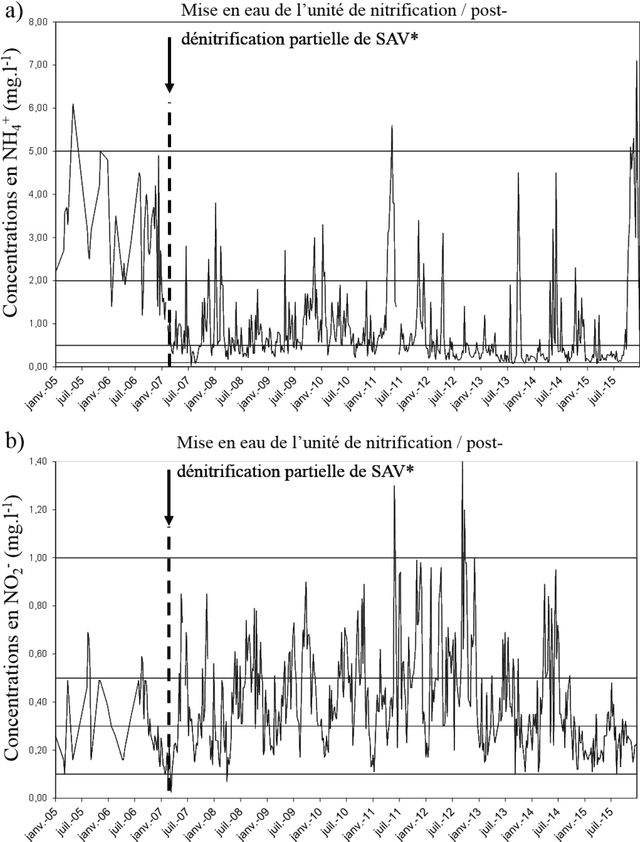
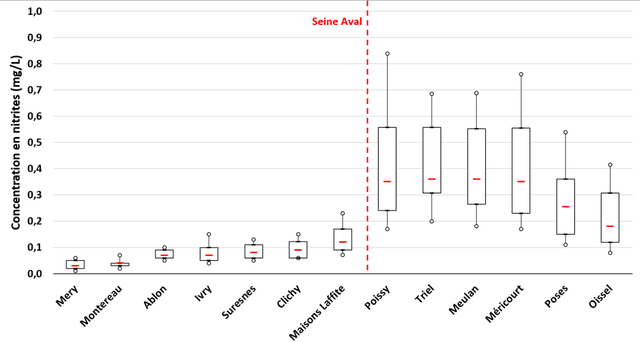
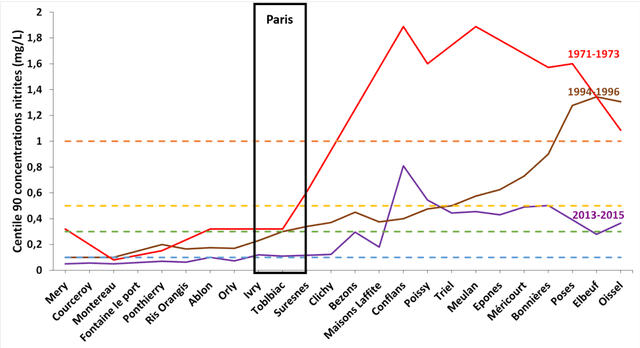
Abstract:The recent popularity of post-denitrification processes in the greater Paris area wastewater treatment plants has caused a resurgence of the presence of nitrite in the Seine river. Controlling the production of nitrite during the post-denitrification has thus become a major technical issue. Research studies have been led in the MOCOPEE program (www.mocopee.com) to better understand the underlying mechanisms behind the production of nitrite during wastewater denitrification and to develop technical tools (measurement and control solutions) to assist on-site reductions of nitrite productions. Prior studies have shown that typical methanol dosage strategies produce a varying carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in the reactor, which in turn leads to unstable nitrite concentrations in the effluent. The possibility of adding a model-free control to the actual classical dosage strategy has thus been tested on the SimBio model, which simulates the behavior of wastewater biofilters. The corresponding "intelligent" feedback loop, which is using effluent nitrite concentrations, compensates the classical strategy only when needed. Simulation results show a clear improvement in average nitrite concentration level and level stability in the effluent, without a notable overcost in methanol.
* in french, Journal of Water Science, to appear
Smart depth of field optimization applied to a robotised view camera
Apr 18, 2011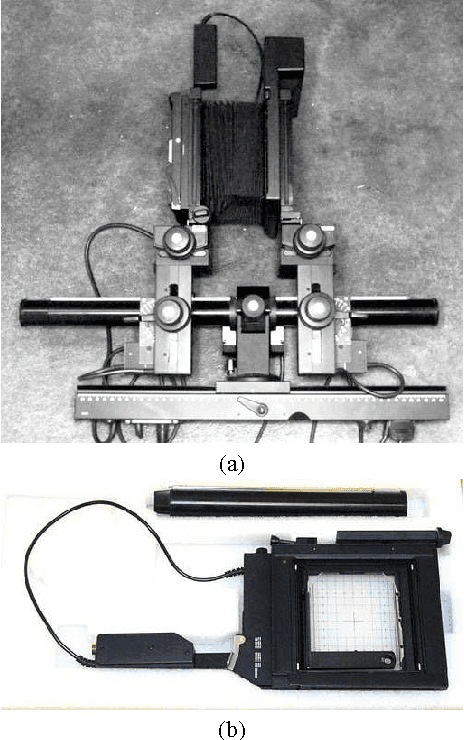
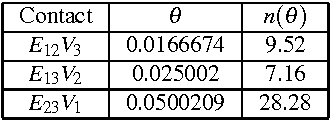
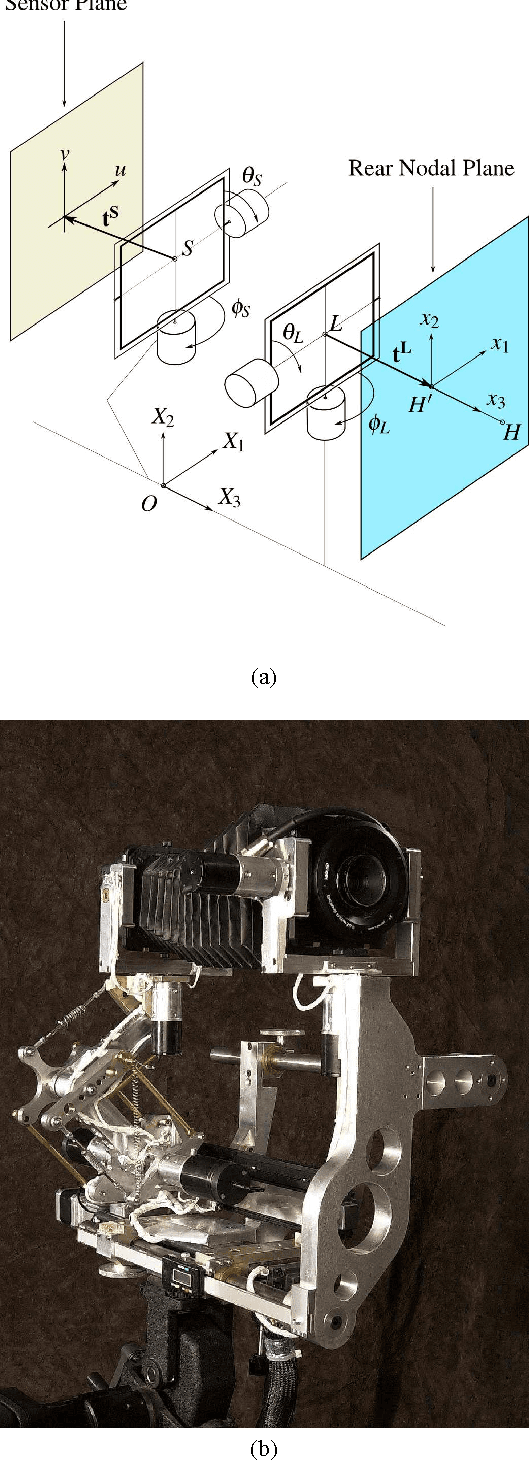
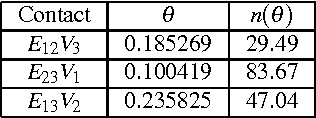
Abstract:The great flexibility of a view camera allows to take high quality photographs that would not be possible any other way. But making a given object into focus is a long and tedious task, although the underlying laws are well known. This paper presents the result of a project which has lead to the design of a computer controlled view camera and to its companion software. Thanks to the high precision machining of its components, and to the known optical parameters of lenses and sensor, we have been able to consider a reliable mathematical model of the view camera, allowing the acquisition of 3D coordinates to build a geometrical model of the object. Then many problems can be solved, e.g. minimizing the f-number while maintaining the object within the depth of field, which takes the form of a constrained optimization problem. All optimization algorithms have been validated on a virtual view camera before implementation on the prototype
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge