Soo Hyun Ryu
Plausibility Processing in Transformer Language Models: Focusing on the Role of Attention Heads in GPT
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:The goal of this paper is to explore how Transformer language models process semantic knowledge, especially regarding the plausibility of noun-verb relations. First, I demonstrate GPT2 exhibits a higher degree of similarity with humans in plausibility processing compared to other Transformer language models. Next, I delve into how knowledge of plausibility is contained within attention heads of GPT2 and how these heads causally contribute to GPT2's plausibility processing ability. Through several experiments, it was found that: i) GPT2 has a number of attention heads that detect plausible noun-verb relationships; ii) these heads collectively contribute to the Transformer's ability to process plausibility, albeit to varying degrees; and iii) attention heads' individual performance in detecting plausibility does not necessarily correlate with how much they contribute to GPT2's plausibility processing ability.
Accounting for Agreement Phenomena in Sentence Comprehension with Transformer Language Models: Effects of Similarity-based Interference on Surprisal and Attention
Apr 26, 2021
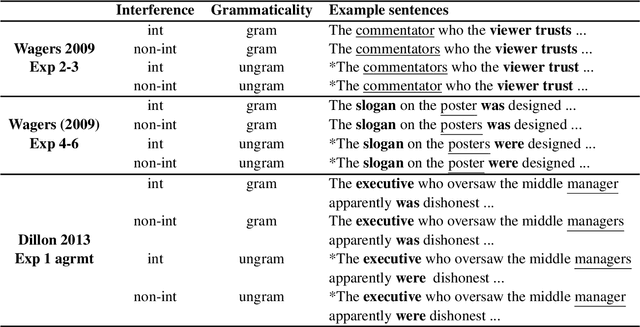
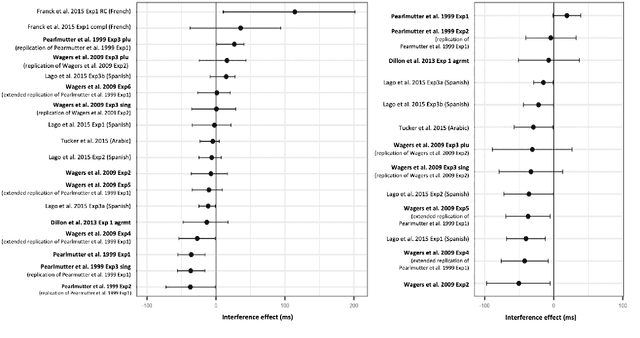
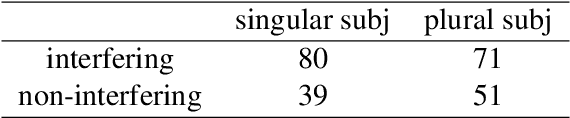
Abstract:We advance a novel explanation of similarity-based interference effects in subject-verb and reflexive pronoun agreement processing, grounded in surprisal values computed from a pretrained large-scale Transformer model, GPT-2. Specifically, we show that surprisal of the verb or reflexive pronoun predicts facilitatory interference effects in ungrammatical sentences, where a distractor noun that matches in number with the verb or pronoun leads to faster reading times, despite the distractor not participating in the agreement relation. We review the human empirical evidence for such effects, including recent meta-analyses and large-scale studies. We also show that attention patterns (indexed by entropy and other measures) in the Transformer show patterns of diffuse attention in the presence of similar distractors, consistent with cue-based retrieval models of parsing. But in contrast to these models, the attentional cues and memory representations are learned entirely from the simple self-supervised task of predicting the next word.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge