Simon Pietro Romano
Whispy: Adapting STT Whisper Models to Real-Time Environments
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Large general-purpose transformer models have recently become the mainstay in the realm of speech analysis. In particular, Whisper achieves state-of-the-art results in relevant tasks such as speech recognition, translation, language identification, and voice activity detection. However, Whisper models are not designed to be used in real-time conditions, and this limitation makes them unsuitable for a vast plethora of practical applications. In this paper, we introduce Whispy, a system intended to bring live capabilities to the Whisper pretrained models. As a result of a number of architectural optimisations, Whispy is able to consume live audio streams and generate high level, coherent voice transcriptions, while still maintaining a low computational cost. We evaluate the performance of our system on a large repository of publicly available speech datasets, investigating how the transcription mechanism introduced by Whispy impacts on the Whisper output. Experimental results show how Whispy excels in robustness, promptness, and accuracy.
Leveraging AI to optimize website structure discovery during Penetration Testing
Jan 18, 2021

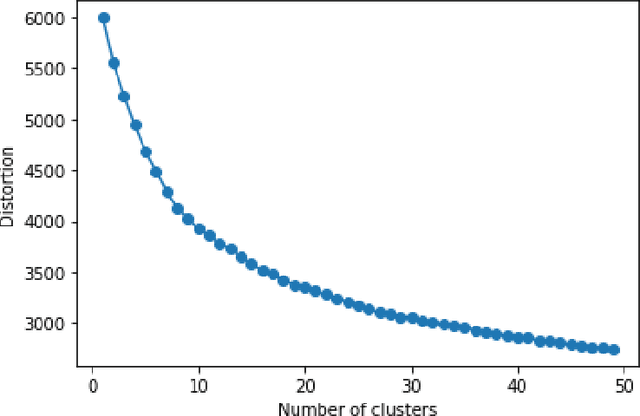

Abstract:Dirbusting is a technique used to brute force directories and file names on web servers while monitoring HTTP responses, in order to enumerate server contents. Such a technique uses lists of common words to discover the hidden structure of the target website. Dirbusting typically relies on response codes as discovery conditions to find new pages. It is widely used in web application penetration testing, an activity that allows companies to detect websites vulnerabilities. Dirbusting techniques are both time and resource consuming and innovative approaches have never been explored in this field. We hence propose an advanced technique to optimize the dirbusting process by leveraging Artificial Intelligence. More specifically, we use semantic clustering techniques in order to organize wordlist items in different groups according to their semantic meaning. The created clusters are used in an ad-hoc implemented next-word intelligent strategy. This paper demonstrates that the usage of clustering techniques outperforms the commonly used brute force methods. Performance is evaluated by testing eight different web applications. Results show a performance increase that is up to 50% for each of the conducted experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge