Simon Caton
A Case For Noisy Shallow Gate-Based Circuits In Quantum Machine Learning
Dec 13, 2021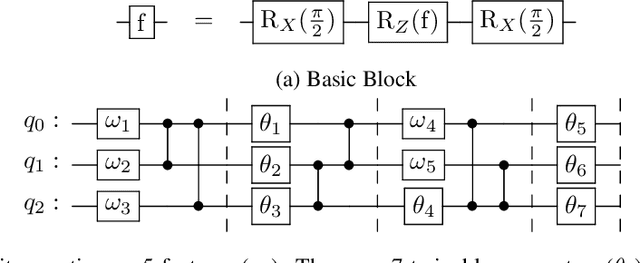
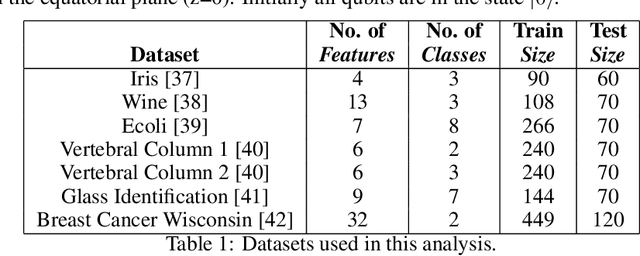
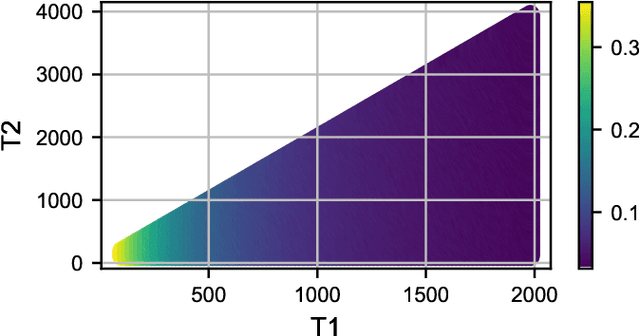
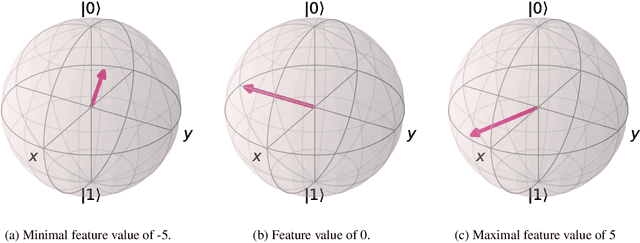
Abstract:There is increasing interest in the development of gate-based quantum circuits for the training of machine learning models. Yet, little is understood concerning the parameters of circuit design, and the effects of noise and other measurement errors on the performance of quantum machine learning models. In this paper, we explore the practical implications of key circuit design parameters (number of qubits, depth etc.) using several standard machine learning datasets and IBM's Qiskit simulator. In total we evaluate over 6500 unique circuits with $n \approx 120700$ individual runs. We find that in general shallow (low depth) wide (more qubits) circuit topologies tend to outperform deeper ones in settings without noise. We also explore the implications and effects of different notions of noise and discuss circuit topologies that are more / less robust to noise for classification machine learning tasks. Based on the findings we define guidelines for circuit topologies that show near-term promise for the realisation of quantum machine learning algorithms using gate-based NISQ quantum computer.
Fairness in Machine Learning: A Survey
Oct 04, 2020



Abstract:As Machine Learning technologies become increasingly used in contexts that affect citizens, companies as well as researchers need to be confident that their application of these methods will not have unexpected social implications, such as bias towards gender, ethnicity, and/or people with disabilities. There is significant literature on approaches to mitigate bias and promote fairness, yet the area is complex and hard to penetrate for newcomers to the domain. This article seeks to provide an overview of the different schools of thought and approaches to mitigating (social) biases and increase fairness in the Machine Learning literature. It organises approaches into the widely accepted framework of pre-processing, in-processing, and post-processing methods, subcategorizing into a further 11 method areas. Although much of the literature emphasizes binary classification, a discussion of fairness in regression, recommender systems, unsupervised learning, and natural language processing is also provided along with a selection of currently available open source libraries. The article concludes by summarising open challenges articulated as four dilemmas for fairness research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge