Sid Narang
Automated Real-World Sustainability Data Generation from Images of Buildings
May 28, 2024
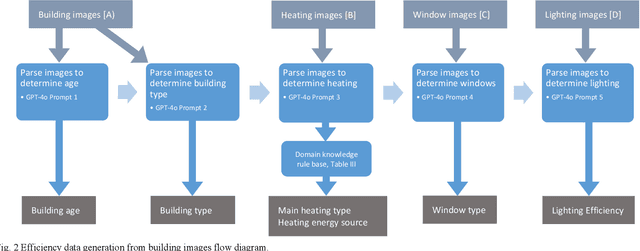


Abstract:When data on building features is unavailable, the task of determining how to improve that building in terms of carbon emissions becomes infeasible. We show that from only a set of images, a Large Language Model with appropriate prompt engineering and domain knowledge can successfully estimate a range of building features relevant for sustainability calculations. We compare our novel image-to-data method with a ground truth comprising real building data for 47 apartments and achieve accuracy better than a human performing the same task. We also demonstrate that the method can generate tailored recommendations to the owner on how best to improve their properties and discuss methods to scale the approach.
Address-Specific Sustainable Accommodation Choice Through Real-World Data Integration
May 21, 2024
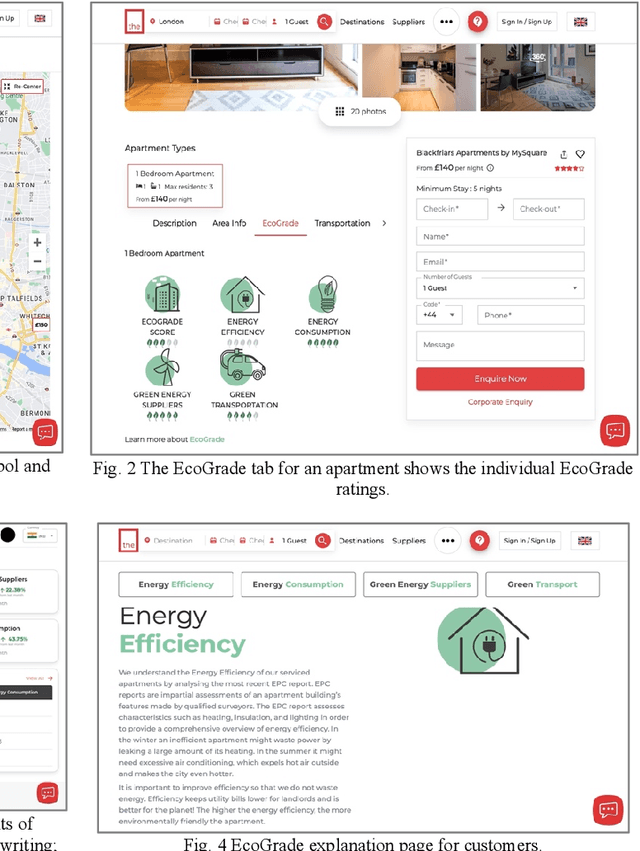


Abstract:Consumers wish to choose sustainable accommodation for their travels, and in the case of corporations, may be required to do so. Yet accommodation marketplaces provide no meaningful capability for sustainable choice: typically CO2 estimates are provided that are identical for all accommodation of the same type across an entire country. We propose a decision support system that enables real choice of sustainable accommodation. We develop a data-driven address-specific metric called EcoGrade, which integrates government approved datasets and uses interpolation where data is sparse. We validate the metric on 10,000 UK addresses in 10 cities, showing the match of our interpolations to reality is statistically significant. We show how the metric has been embedded into a decision support system for a global accommodation marketplace and tested by real users over several months with positive user feedback. In the EU, forty percent of final energy consumption is from buildings. We need to encourage all building owners to make their accommodation more efficient. The rental sector is one area where change can occur rapidly, as rented accommodation is renovated frequently. We anticipate our decision support system using EcoGrade will encourage this positive change.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge