Sebastião Pais
A Cluster-Based Opposition Differential Evolution Algorithm Boosted by a Local Search for ECG Signal Classification
May 04, 2023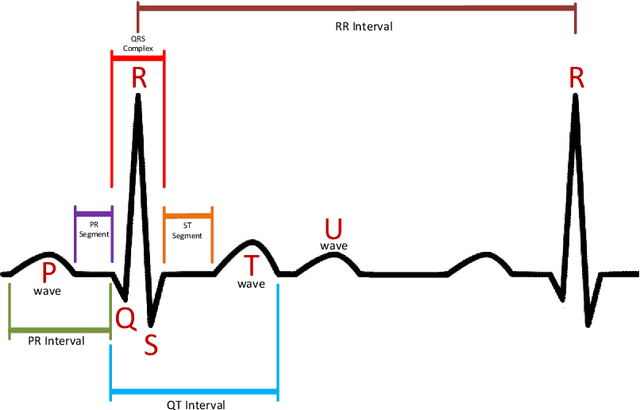
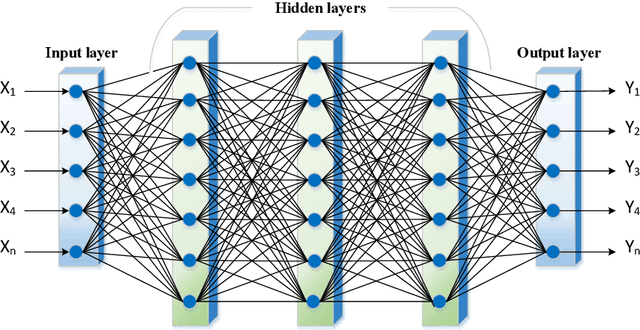
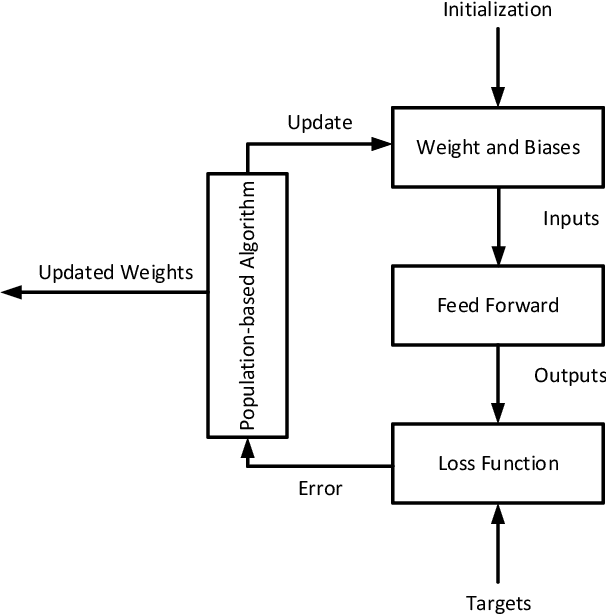
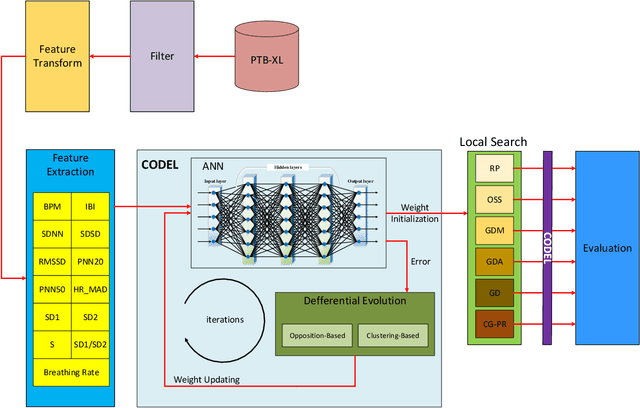
Abstract:Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals are recordings of the heart's electrical activity and are widely used in the medical field to diagnose various cardiac conditions and monitor heart function. The accurate classification of ECG signals is crucial for the early detection and treatment of heart-related diseases. This paper proposes a novel approach based on an improved differential evolution (DE) algorithm for ECG signal classification. To this end, after the preprocessing step, we extracted several features such as BPM, IBI, and SDNN. Then, the features are fed into a multi-layer perceptron (MLP). While MLPs are still widely used for ECG signal classification, using gradient-based training methods, the most widely used algorithm for the training process, has significant disadvantages, such as the possibility of being stuck in local optimums. Population-based metaheuristic techniques have been effectively used to address this. This paper employs an enhanced differential evolution (DE) algorithm for the training process as one of the most effective population-based algorithms. To this end, we improved DE based on a clustering-based strategy, opposition-based learning, and a local search. Clustering-based strategies can act as crossover operators, while the goal of the opposition operator is to improve the exploration of the DE algorithm. The weights and biases found by the improved DE algorithm are then fed into six gradient-based local search algorithms. In other words, the weights found by the DE are employed as an initialization point. Therefore, we introduced six different algorithms for the training process (in terms of different local search algorithms). In an extensive set of experiments, we showed that our proposed training algorithm could provide better results than the conventional training algorithms.
Detection of Dangerous Events on Social Media: A Perspective Review
Apr 04, 2022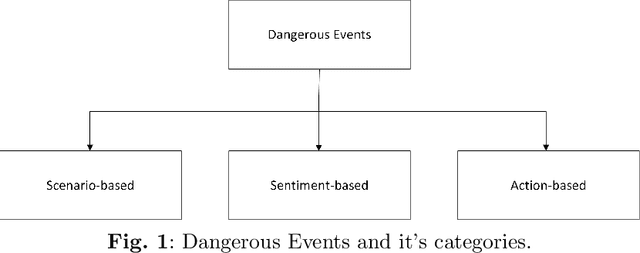

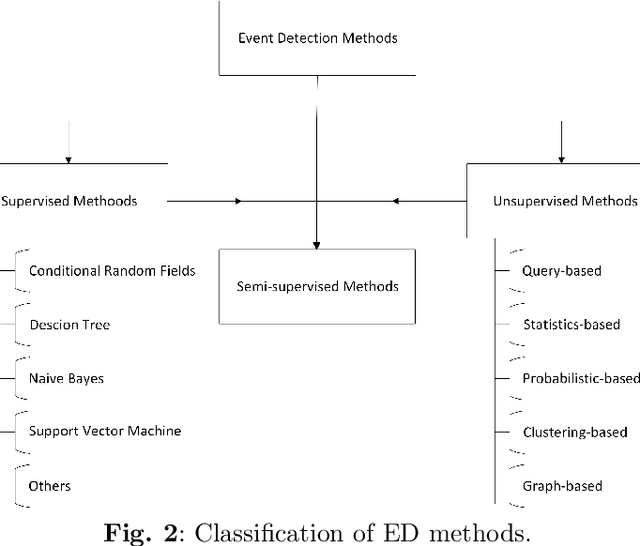
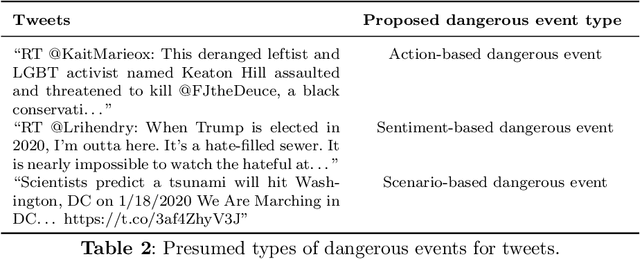
Abstract:Social media is an essential gateway of information and communication for people worldwide. The amount of time spent and reliance of people on social media makes it a vital resource for detecting events happening in real life. Thousands of significant events are posted by users every hour in the form of multimedia. Some individuals and groups target the audience to promote their agenda among these users. Their cause can threaten other groups and individuals who do not share the same views or have specific differences. Any group with a definitive cause cannot survive without the support which acts as a catalyst for their agenda. A phenomenon occurs where people are fed information that motivates them to act on their behalf and carry out their agenda. One is benefit results in the loss of the others by putting their lives, assets, physical and emotional health in danger. This paper introduces a concept of dangerous events to approach this problem and their three main types based on their characteristics: action, scenarios, and sentiment-based dangerous events.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge