Sarah Sterz
AI Act for the Working Programmer
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:The European AI Act is a new, legally binding instrument that will enforce certain requirements on the development and use of AI technology potentially affecting people in Europe. It can be expected that the stipulations of the Act, in turn, are going to affect the work of many software engineers, software testers, data engineers, and other professionals across the IT sector in Europe and beyond. The 113 articles, 180 recitals, and 13 annexes that make up the Act cover 144 pages. This paper aims at providing an aid for navigating the Act from the perspective of some professional in the software domain, termed "the working programmer", who feels the need to know about the stipulations of the Act.
Software Doping Analysis for Human Oversight
Aug 11, 2023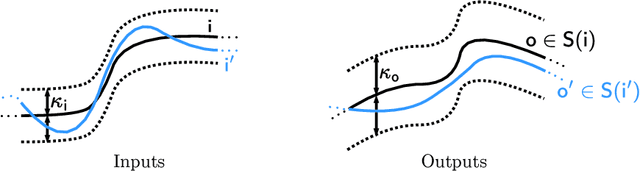
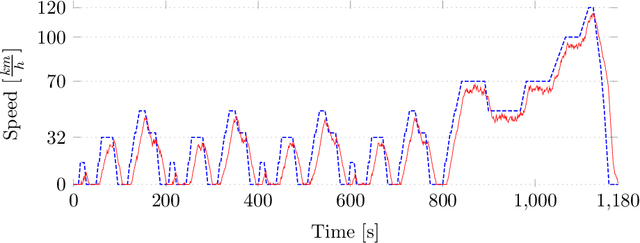
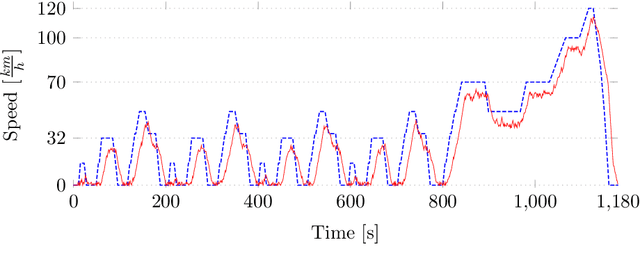
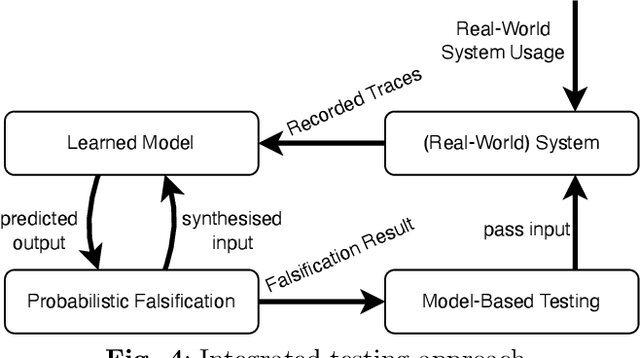
Abstract:This article introduces a framework that is meant to assist in mitigating societal risks that software can pose. Concretely, this encompasses facets of software doping as well as unfairness and discrimination in high-risk decision-making systems. The term software doping refers to software that contains surreptitiously added functionality that is against the interest of the user. A prominent example of software doping are the tampered emission cleaning systems that were found in millions of cars around the world when the diesel emissions scandal surfaced. The first part of this article combines the formal foundations of software doping analysis with established probabilistic falsification techniques to arrive at a black-box analysis technique for identifying undesired effects of software. We apply this technique to emission cleaning systems in diesel cars but also to high-risk systems that evaluate humans in a possibly unfair or discriminating way. We demonstrate how our approach can assist humans-in-the-loop to make better informed and more responsible decisions. This is to promote effective human oversight, which will be a central requirement enforced by the European Union's upcoming AI Act. We complement our technical contribution with a juridically, philosophically, and psychologically informed perspective on the potential problems caused by such systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge