Sanjit Mitra
Towards a robust and reliable deep learning approach for detection of compact binary mergers in gravitational wave data
Jun 20, 2023Abstract:The ability of deep learning (DL) approaches to learn generalised signal and noise models, coupled with their fast inference on GPUs, holds great promise for enhancing gravitational-wave (GW) searches in terms of speed, parameter space coverage, and search sensitivity. However, the opaque nature of DL models severely harms their reliability. In this work, we meticulously develop a DL model stage-wise and work towards improving its robustness and reliability. First, we address the problems in maintaining the purity of training data by deriving a new metric that better reflects the visual strength of the "chirp" signal features in the data. Using a reduced, smooth representation obtained through a variational auto-encoder (VAE), we build a classifier to search for compact binary coalescence (CBC) signals. Our tests on real LIGO data show an impressive performance of the model. However, upon probing the robustness of the model through adversarial attacks, its simple failure modes were identified, underlining how such models can still be highly fragile. As a first step towards bringing robustness, we retrain the model in a novel framework involving a generative adversarial network (GAN). Over the course of training, the model learns to eliminate the primary modes of failure identified by the adversaries. Although absolute robustness is practically impossible to achieve, we demonstrate some fundamental improvements earned through such training, like sparseness and reduced degeneracy in the extracted features at different layers inside the model. Through comparative inference on real LIGO data, we show that the prescribed robustness is achieved at practically zero cost in terms of performance. Through a direct search on ~8.8 days of LIGO data, we recover two significant CBC events from GWTC-2.1, GW190519_153544 and GW190521_074359, and report the search sensitivity.
Improving significance of binary black hole mergers in Advanced LIGO data using deep learning : Confirmation of GW151216
Oct 22, 2020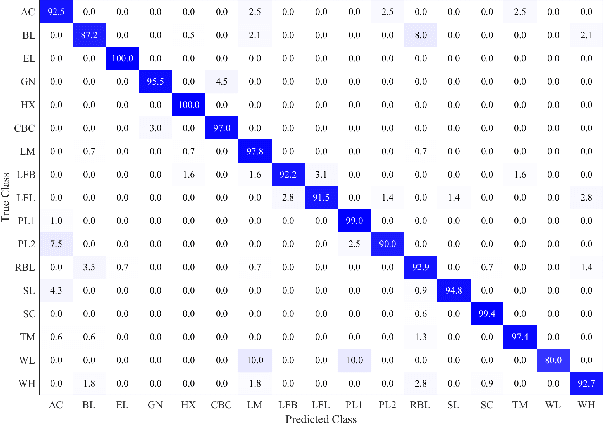
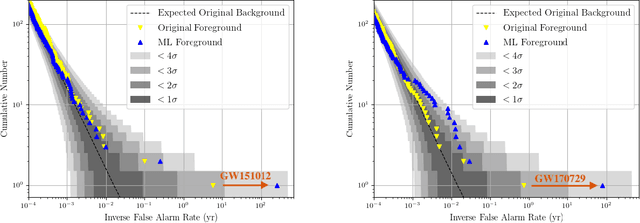
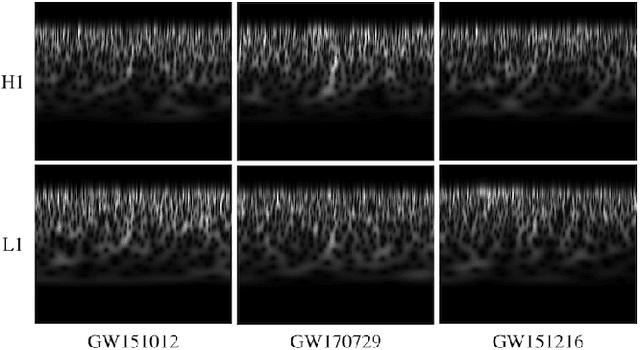
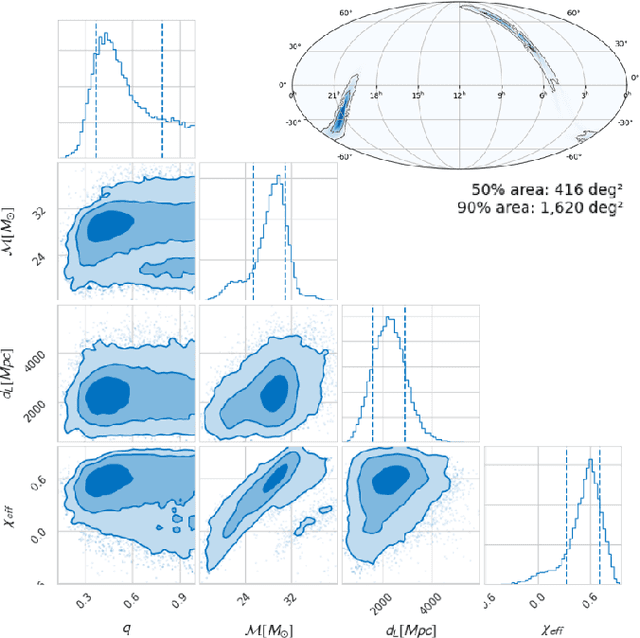
Abstract:We present a novel Machine Learning (ML) based strategy to search for compact binary coalescences (CBCs) in data from ground-based gravitational wave (GW) observatories. This is the first ML-based search that not only recovers all the binary black hole mergers in the first GW transients calalog (GWTC-1), but also makes a clean detection of GW151216, which was not significant enough to be included in the catalogue. Moreover, we achieve this by only adding a new coincident ranking statistic (MLStat) to a standard analysis that was used for GWTC-1. In CBC searches, reducing contamination by terrestrial and instrumental transients, which create a loud noise background by triggering numerous false alarms, is crucial to improving the sensitivity for detecting true events. The sheer volume of data and and large number of expected detections also prompts the use of ML techniques. We perform transfer learning to train "InceptionV3", a pre-trained deep neural network, along with curriculum learning to distinguish GW signals from noisy events by analysing their continuous wavelet transform (CWT) maps. MLStat incorporates information from this ML classifier into the standard coincident search likelihood used by the conventional search. This leads to at least an order of magnitude improvement in the inverse false-alarm-rate (IFAR) for the previously "low significance" events GW151012, GW170729 and GW151216. The confidence in detection of GW151216 is further strengthened by performing its parameter estimation using SEOBNRv4HM_ROM. Considering the impressive ability of the statistic to distinguish signals from glitches, the list of marginal events from MLStat could be quite reliable for astrophysical population studies and further follow-up. This work demonstrates the immense potential and readiness of MLStat for finding new sources in current data and possibility of its adaptation in similar searches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge