Sandi Besen
Lightweight Safety Classification Using Pruned Language Models
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel technique for content safety and prompt injection classification for Large Language Models. Our technique, Layer Enhanced Classification (LEC), trains a Penalized Logistic Regression (PLR) classifier on the hidden state of an LLM's optimal intermediate transformer layer. By combining the computational efficiency of a streamlined PLR classifier with the sophisticated language understanding of an LLM, our approach delivers superior performance surpassing GPT-4o and special-purpose models fine-tuned for each task. We find that small general-purpose models (Qwen 2.5 sizes 0.5B, 1.5B, and 3B) and other transformer-based architectures like DeBERTa v3 are robust feature extractors allowing simple classifiers to be effectively trained on fewer than 100 high-quality examples. Importantly, the intermediate transformer layers of these models typically outperform the final layer across both classification tasks. Our results indicate that a single general-purpose LLM can be used to classify content safety, detect prompt injections, and simultaneously generate output tokens. Alternatively, these relatively small LLMs can be pruned to the optimal intermediate layer and used exclusively as robust feature extractors. Since our results are consistent on different transformer architectures, we infer that robust feature extraction is an inherent capability of most, if not all, LLMs.
The Landscape of Emerging AI Agent Architectures for Reasoning, Planning, and Tool Calling: A Survey
Apr 17, 2024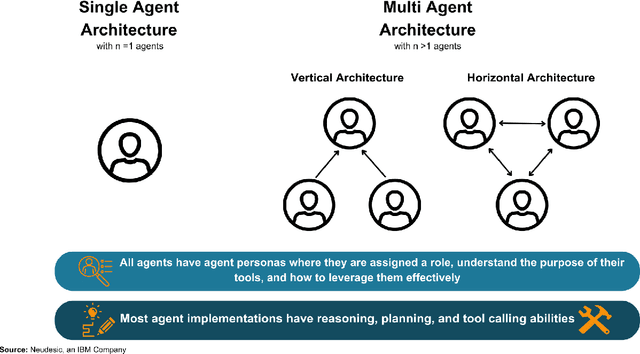
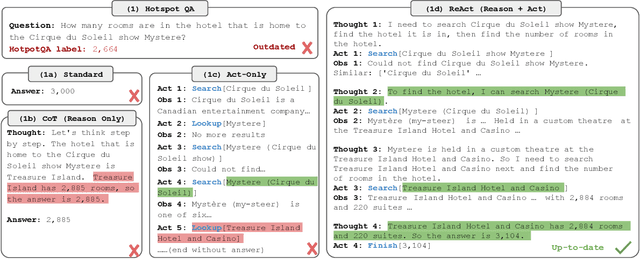
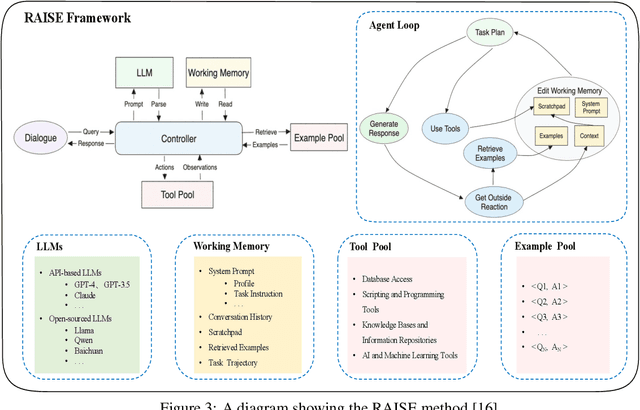
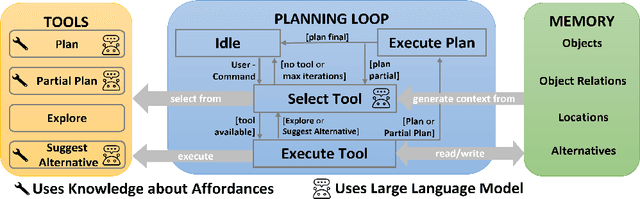
Abstract:This survey paper examines the recent advancements in AI agent implementations, with a focus on their ability to achieve complex goals that require enhanced reasoning, planning, and tool execution capabilities. The primary objectives of this work are to a) communicate the current capabilities and limitations of existing AI agent implementations, b) share insights gained from our observations of these systems in action, and c) suggest important considerations for future developments in AI agent design. We achieve this by providing overviews of single-agent and multi-agent architectures, identifying key patterns and divergences in design choices, and evaluating their overall impact on accomplishing a provided goal. Our contribution outlines key themes when selecting an agentic architecture, the impact of leadership on agent systems, agent communication styles, and key phases for planning, execution, and reflection that enable robust AI agent systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge