Qiumo Yu
Near-Field Wideband Beamforming for RIS Based on Fresnel Zone
Nov 28, 2024



Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) has emerged as a promising solution to overcome the challenges of high path loss and easy signal blockage in millimeter-wave (mmWave) and terahertz (THz) communication systems. With the increase of RIS aperture and system bandwidth, the near-field beam split effect emerges, which causes beams at different frequencies to focus on distinct physical locations, leading to a significant gain loss of beamforming. To address this problem, we leverage the property of Fresnel zone that the beam split disappears for RIS elements along a single Fresnel zone and propose beamforming design on the two dimensions of along and across the Fresnel zones. The phase shift of RIS elements along the same Fresnel zone are designed aligned, so that the signal reflected by these element can add up in-phase at the receiver regardless of the frequency. Then the expression of equivalent channel is simplified to the Fourier transform of reflective intensity across Fresnel zones modulated by the designed phase. Based on this relationship, we prove that the uniformly distributed in-band gain with aligned phase along the Fresnel zone leads to the upper bound of achievable rate. Finally, we design phase shifts of RIS to approach this upper bound by adopting the stationary phase method as well as the Gerchberg-Saxton (GS) algorithm. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of our proposed Fresnel zone-based method in mitigating the near-field beam split effect.
Coded Beam Training
Jan 03, 2024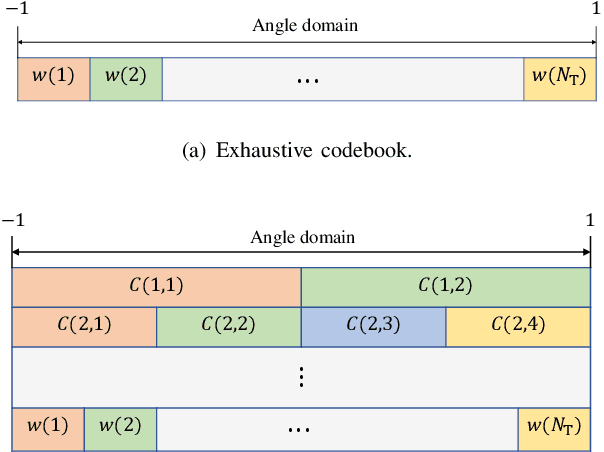
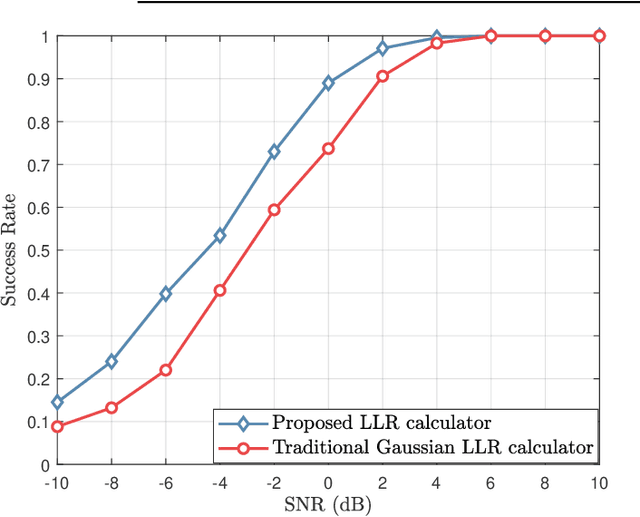
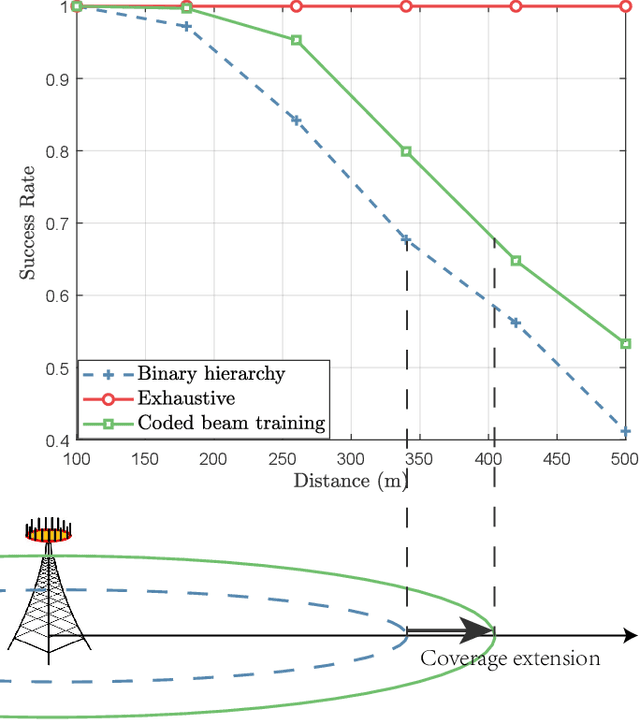
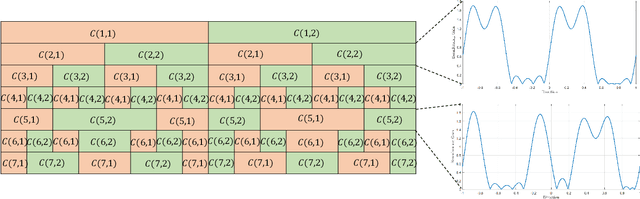
Abstract:In extremely large-scale multiple input multiple output (XL-MIMO) systems for future sixth-generation (6G) communications, codebook-based beam training stands out as a promising technology to acquire channel state information (CSI). Despite their effectiveness, when the pilot overhead is limited, existing beam training methods suffer from significant achievable rate degradation for remote users with low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). To tackle this challenge, leverging the error-correcting capability of channel codes, we introduce channel coding theory into hierarchical beam training to extend the coverage area. Specifically, we establish the duality between hierarchical beam training and channel coding, and the proposed coded beam training scheme serves as a general framework. Then, we present two specific implementations exemplified by coded beam training methods based on Hamming codes and convolutional codes, during which the beam encoding and decoding processes are refined respectively to better accommodate to the beam training problem. Simulation results have demonstrated that, the proposed coded beam training method can enable reliable beam training performance for remote users with low SNR, while keeping training overhead low.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge