Pratchaya Jaisudthi
iOn-Profiler: intelligent Online multi-objective VNF Profiling with Reinforcement Learning
Dec 14, 2023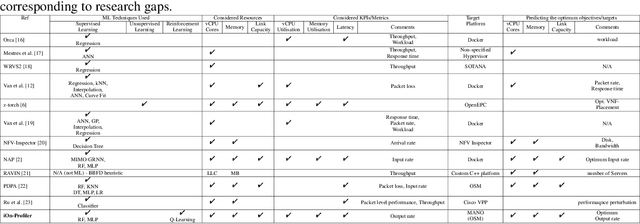
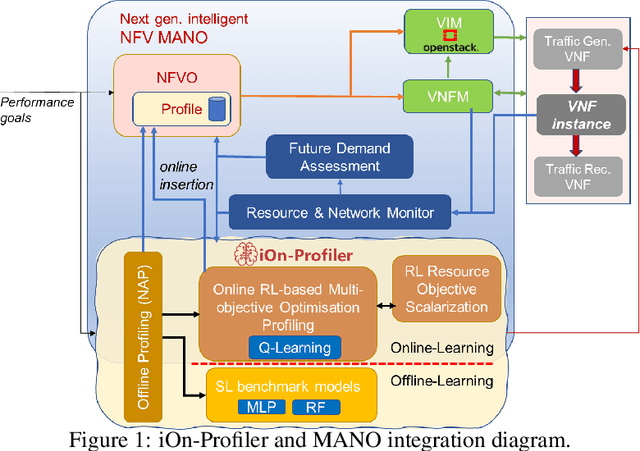
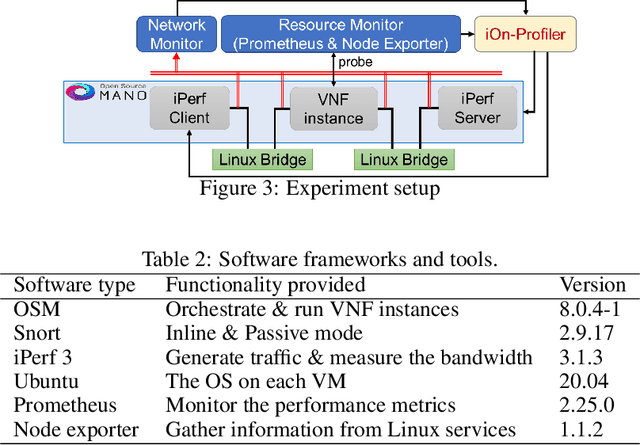
Abstract:Leveraging the potential of Virtualised Network Functions (VNFs) requires a clear understanding of the link between resource consumption and performance. The current state of the art tries to do that by utilising Machine Learning (ML) and specifically Supervised Learning (SL) models for given network environments and VNF types assuming single-objective optimisation targets. Taking a different approach poses a novel VNF profiler optimising multi-resource type allocation and performance objectives using adapted Reinforcement Learning (RL). Our approach can meet Key Performance Indicator (KPI) targets while minimising multi-resource type consumption and optimising the VNF output rate compared to existing single-objective solutions. Our experimental evaluation with three real-world VNF types over a total of 39 study scenarios (13 per VNF), for three resource types (virtual CPU, memory, and network link capacity), verifies the accuracy of resource allocation predictions and corresponding successful profiling decisions via a benchmark comparison between our RL model and SL models. We also conduct a complementary exhaustive search-space study revealing that different resources impact performance in varying ways per VNF type, implying the necessity of multi-objective optimisation, individualised examination per VNF type, and adaptable online profile learning, such as with the autonomous online learning approach of iOn-Profiler.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge