Plínio Batista dos Santos Filho
Avaliação da doença de Alzheimer pela análise multiespectral de imagens DW-MR por redes RBF como alternativa aos mapas ADC
Dec 03, 2017Abstract:Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia, yet difficult to accurately diagnose without the use of invasive techniques, particularly at the beginning of the disease. This work addresses the classification and analysis of multispectral synthetic images composed by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance brain volumes for evaluation of the area of cerebrospinal fluid and its correlation with the progression of Alzheimer's disease. A 1.5 T MR imaging system was used to acquire all the images presented. The classification methods are based on multilayer perceptrons and classifiers of radial basis function networks. It is assumed that the classes of interest can be separated by hyperquadrics. A polynomial network of degree 2 is used to classify the original volumes, generating a ground-truth volume. The classification results are used to improve the usual analysis by the map of apparent diffusion coefficients.
* in Portuguese
Dialectical Multispectral Classification of Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Images as an Alternative to Apparent Diffusion Coefficients Maps to Perform Anatomical Analysis
Dec 03, 2017
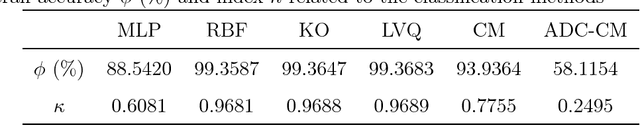


Abstract:Multispectral image analysis is a relatively promising field of research with applications in several areas, such as medical imaging and satellite monitoring. A considerable number of current methods of analysis are based on parametric statistics. Alternatively, some methods in Computational Intelligence are inspired by biology and other sciences. Here we claim that Philosophy can be also considered as a source of inspiration. This work proposes the Objective Dialectical Method (ODM): a method for classification based on the Philosophy of Praxis. ODM is instrumental in assembling evolvable mathematical tools to analyze multispectral images. In the case study described in this paper, multispectral images are composed of diffusion-weighted (DW) magnetic resonance (MR) images. The results are compared to ground-truth images produced by polynomial networks using a morphological similarity index. The classification results are used to improve the usual analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient map. Such results proved that gray and white matter can be distinguished in DW-MR multispectral analysis and, consequently, DW-MR images can also be used to furnish anatomical information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge