Philippe Poggi
SPE
Bayesian rules and stochastic models for high accuracy prediction of solar radiation
Sep 18, 2013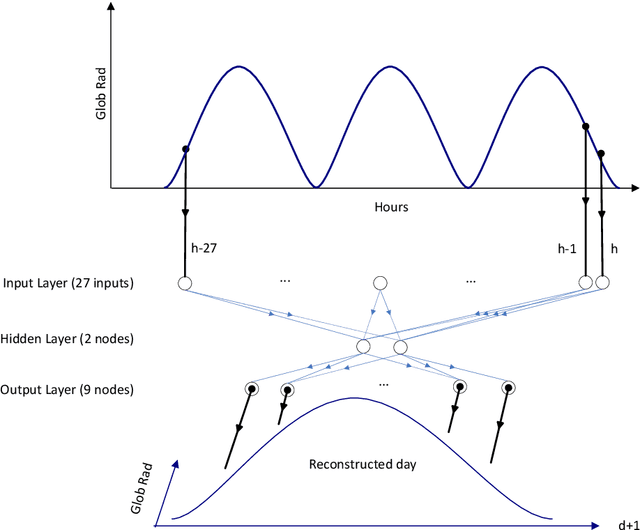
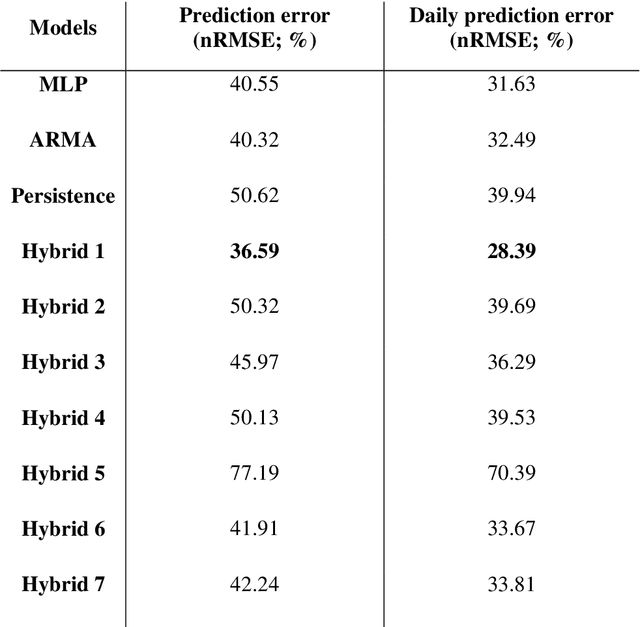
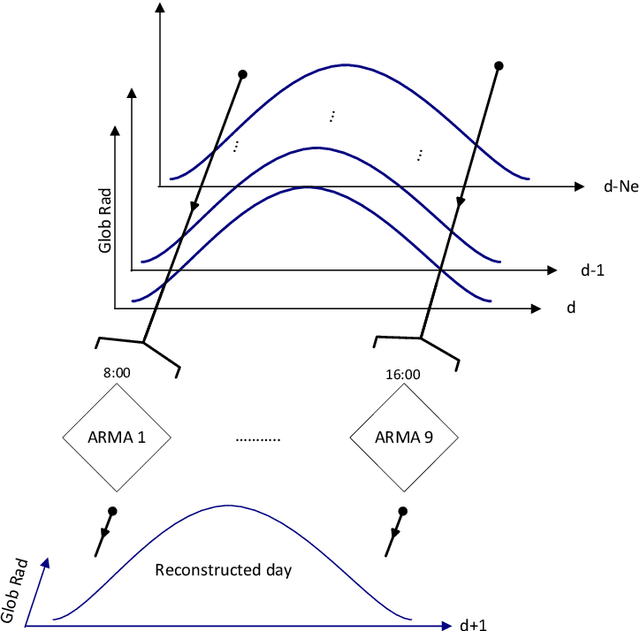
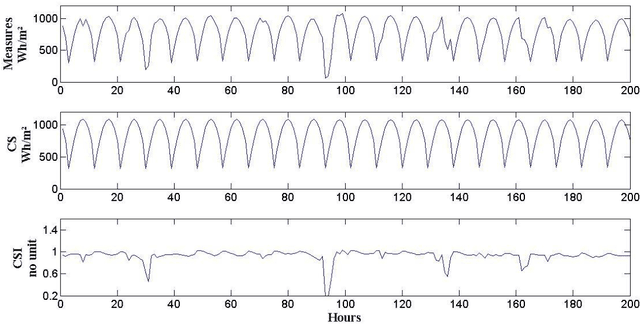
Abstract:It is essential to find solar predictive methods to massively insert renewable energies on the electrical distribution grid. The goal of this study is to find the best methodology allowing predicting with high accuracy the hourly global radiation. The knowledge of this quantity is essential for the grid manager or the private PV producer in order to anticipate fluctuations related to clouds occurrences and to stabilize the injected PV power. In this paper, we test both methodologies: single and hybrid predictors. In the first class, we include the multi-layer perceptron (MLP), auto-regressive and moving average (ARMA), and persistence models. In the second class, we mix these predictors with Bayesian rules to obtain ad-hoc models selections, and Bayesian averages of outputs related to single models. If MLP and ARMA are equivalent (nRMSE close to 40.5% for the both), this hybridization allows a nRMSE gain upper than 14 percentage points compared to the persistence estimation (nRMSE=37% versus 51%).
Predictability of PV power grid performance on insular sites without weather stations: use of artificial neural networks
Jan 13, 2010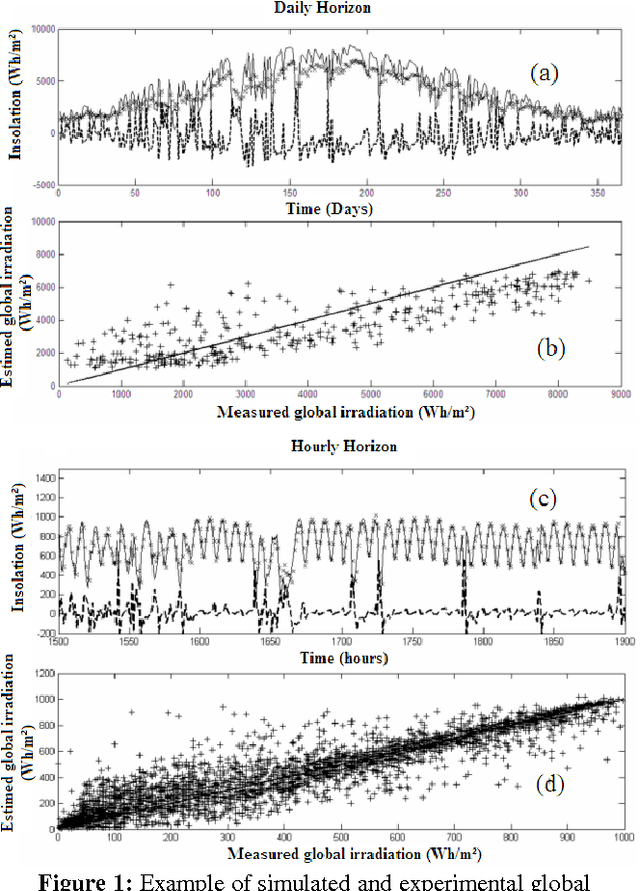
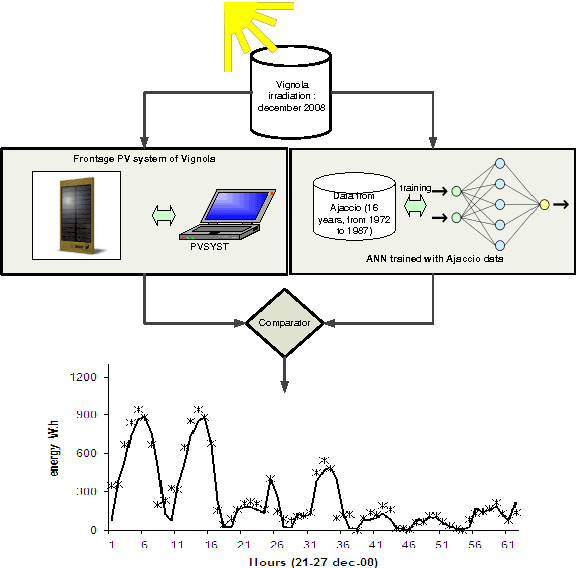


Abstract:The official meteorological network is poor on the island of Corsica: only three sites being about 50 km apart are equipped with pyranometers which enable measurements by hourly and daily step. These sites are Ajaccio (41\degree 55'N and 8\degree 48'E, seaside), Bastia (42\degree 33'N, 9\degree 29'E, seaside) and Corte (42\degree 30'N, 9\degree 15'E average altitude of 486 meters). This lack of weather station makes difficult the predictability of PV power grid performance. This work intends to study a methodology which can predict global solar irradiation using data available from another location for daily and hourly horizon. In order to achieve this prediction, we have used Artificial Neural Network which is a popular artificial intelligence technique in the forecasting domain. A simulator has been obtained using data available for the station of Ajaccio that is the only station for which we have a lot of data: 16 years from 1972 to 1987. Then we have tested the efficiency of this simulator in two places with different geographical features: Corte, a mountainous region and Bastia, a coastal region. On daily horizon, the relocation has implied fewer errors than a "na\"ive" prediction method based on the persistence (RMSE=1468 Vs 1383Wh/m^2 to Bastia and 1325 Vs 1213Wh/m^2 to Corte). On hourly case, the results were still satisfactory, and widely better than persistence (RMSE=138.8 Vs 109.3 Wh/m^2 to Bastia and 135.1 Vs 114.7 Wh/m^2 to Corte). The last experiment was to evaluate the accuracy of our simulator on a PV power grid localized at 10 km from the station of Ajaccio. We got errors very suitable (nRMSE=27.9%, RMSE=99.0 W.h) compared to those obtained with the persistence (nRMSE=42.2%, RMSE=149.7 W.h).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge