Philipp Peterseil
Trustworthiness for an Ultra-Wideband Localization Service
Aug 10, 2024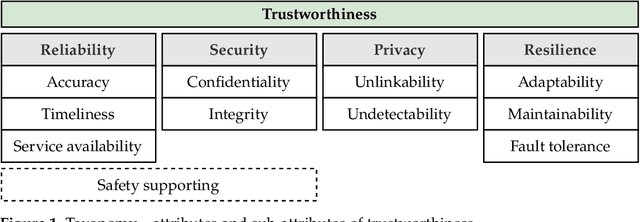

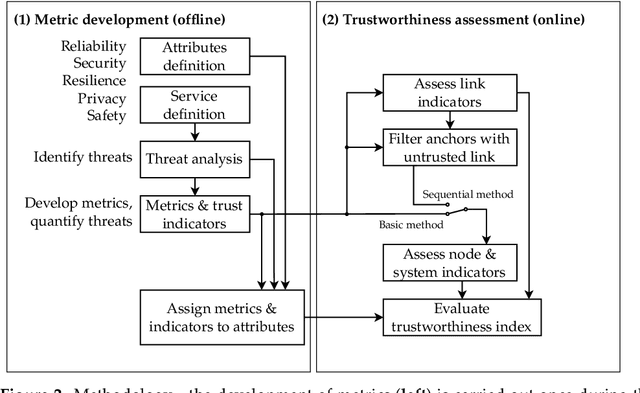

Abstract:Trustworthiness assessment is an essential step to assure that interdependent systems perform critical functions as anticipated, even under adverse conditions. In this paper, a holistic trustworthiness assessment framework for ultra-wideband self-localization is proposed, including attributes of reliability, security, privacy, and resilience. Our goal is to provide guidance for evaluating a system's trustworthiness based on objective evidence, so-called trustworthiness indicators. These indicators are carefully selected through the threat analysis of the particular system. Our approach guarantees that the resulting trustworthiness indicators correspond to chosen real-world threats. Moreover, experimental evaluations are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. While the framework is tailored for this specific use case, the process itself serves as a versatile template, which can be used in other applications in the domains of the Internet of Things or cyber-physical systems.
WIP: Distance Estimation for Contact Tracing -- A Measurement Study of BLE and UWB Traces
Jan 22, 2021
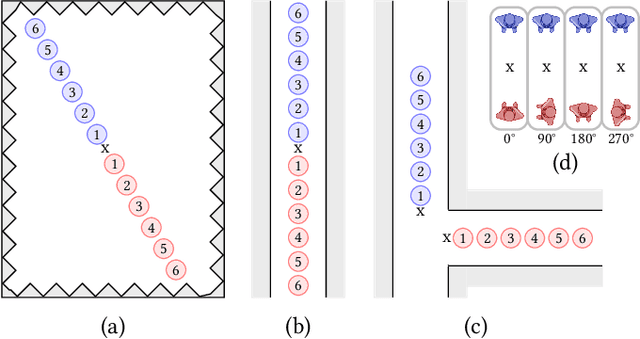
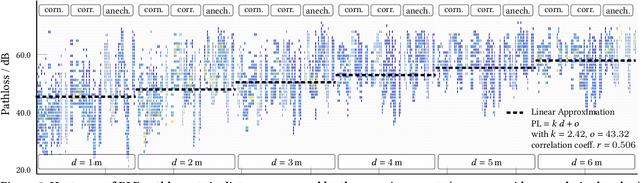
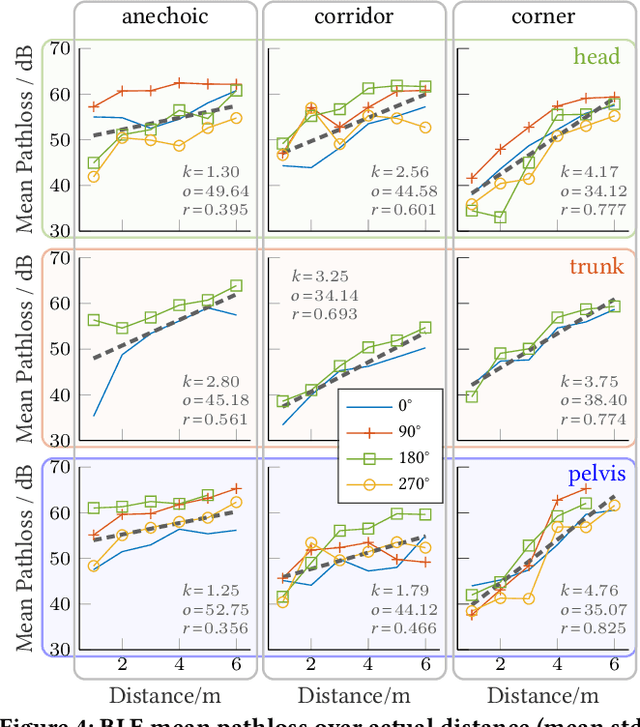
Abstract:Mobile contact tracing apps are -- in principle -- a perfect aid to condemn the human-to-human spread of an infectious disease such as COVID-19 due to the wide use of smartphones worldwide. Yet, the unknown accuracy of contact estimation by wireless technologies hinders the broad use. We address this challenge by conducting a measurement study with a custom testbed to show the benefits and limitations of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) in comparison to distance estimation by ultra-wideband (UWB). Our results confirm that BLE-based distance estimation is not sufficient in real scenarios where smartphones are shielded heavily by the users' bodies. Yet, multi-path signal propagation reduces the effect of body shielding. Finally, we demonstrate that UWB is more robust to the environment than BLE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge