Paul Kirk
Leveraging LLMs for Legacy Code Modernization: Challenges and Opportunities for LLM-Generated Documentation
Nov 22, 2024

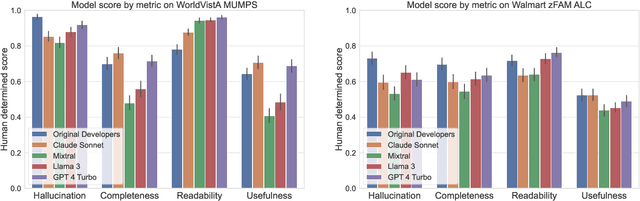

Abstract:Legacy software systems, written in outdated languages like MUMPS and mainframe assembly, pose challenges in efficiency, maintenance, staffing, and security. While LLMs offer promise for modernizing these systems, their ability to understand legacy languages is largely unknown. This paper investigates the utilization of LLMs to generate documentation for legacy code using two datasets: an electronic health records (EHR) system in MUMPS and open-source applications in IBM mainframe Assembly Language Code (ALC). We propose a prompting strategy for generating line-wise code comments and a rubric to evaluate their completeness, readability, usefulness, and hallucination. Our study assesses the correlation between human evaluations and automated metrics, such as code complexity and reference-based metrics. We find that LLM-generated comments for MUMPS and ALC are generally hallucination-free, complete, readable, and useful compared to ground-truth comments, though ALC poses challenges. However, no automated metrics strongly correlate with comment quality to predict or measure LLM performance. Our findings highlight the limitations of current automated measures and the need for better evaluation metrics for LLM-generated documentation in legacy systems.
Identifying cancer subtypes in glioblastoma by combining genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic data
Apr 15, 2013



Abstract:We present a nonparametric Bayesian method for disease subtype discovery in multi-dimensional cancer data. Our method can simultaneously analyse a wide range of data types, allowing for both agreement and disagreement between their underlying clustering structure. It includes feature selection and infers the most likely number of disease subtypes, given the data. We apply the method to 277 glioblastoma samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas, for which there are gene expression, copy number variation, methylation and microRNA data. We identify 8 distinct consensus subtypes and study their prognostic value for death, new tumour events, progression and recurrence. The consensus subtypes are prognostic of tumour recurrence (log-rank p-value of $3.6 \times 10^{-4}$ after correction for multiple hypothesis tests). This is driven principally by the methylation data (log-rank p-value of $2.0 \times 10^{-3}$) but the effect is strengthened by the other 3 data types, demonstrating the value of integrating multiple data types. Of particular note is a subtype of 47 patients characterised by very low levels of methylation. This subtype has very low rates of tumour recurrence and no new events in 10 years of follow up. We also identify a small gene expression subtype of 6 patients that shows particularly poor survival outcomes. Additionally, we note a consensus subtype that showly a highly distinctive data signature and suggest that it is therefore a biologically distinct subtype of glioblastoma. The code is available from https://sites.google.com/site/multipledatafusion/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge