Nguyen Van Minh
A Neutrosophic Recommender System for Medical Diagnosis Based on Algebraic Neutrosophic Measures
Feb 25, 2016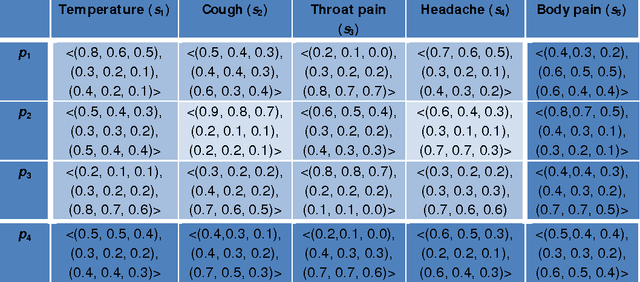
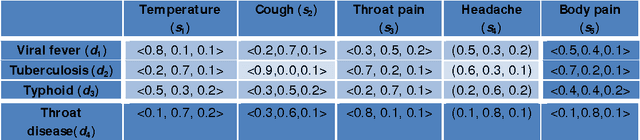
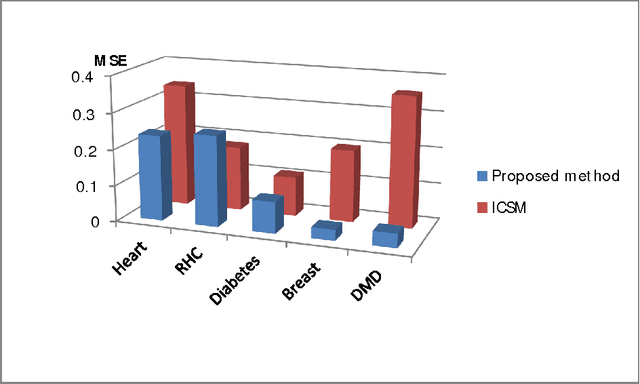
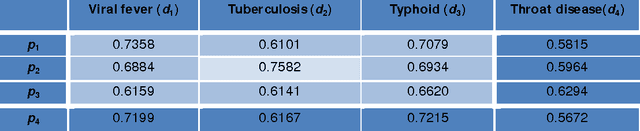
Abstract:Neutrosophic set has the ability to handle uncertain, incomplete, inconsistent, indeterminate information in a more accurate way. In this paper, we proposed a neutrosophic recommender system to predict the diseases based on neutrosophic set which includes single-criterion neutrosophic recommender system (SC-NRS) and multi-criterion neutrosophic recommender system (MC-NRS). Further, we investigated some algebraic operations of neutrosophic recommender system such as union, complement, intersection, probabilistic sum, bold sum, bold intersection, bounded difference, symmetric difference, convex linear sum of min and max operators, Cartesian product, associativity, commutativity and distributive. Based on these operations, we studied the algebraic structures such as lattices, Kleen algebra, de Morgan algebra, Brouwerian algebra, BCK algebra, Stone algebra and MV algebra. In addition, we introduced several types of similarity measures based on these algebraic operations and studied some of their theoretic properties. Moreover, we accomplished a prediction formula using the proposed algebraic similarity measure. We also proposed a new algorithm for medical diagnosis based on neutrosophic recommender system. Finally to check the validity of the proposed methodology, we made experiments on the datasets Heart, RHC, Breast cancer, Diabetes and DMD. At the end, we presented the MSE and computational time by comparing the proposed algorithm with the relevant ones such as ICSM, DSM, CARE, CFMD, as well as other variants namely Variant 67, Variant 69, and Varian 71 both in tabular and graphical form to analyze the efficiency and accuracy. Finally we analyzed the strength of all 8 algorithms by ANOVA statistical tool.
Fuzzy approaches to context variable in fuzzy geographically weighted clustering
Apr 13, 2015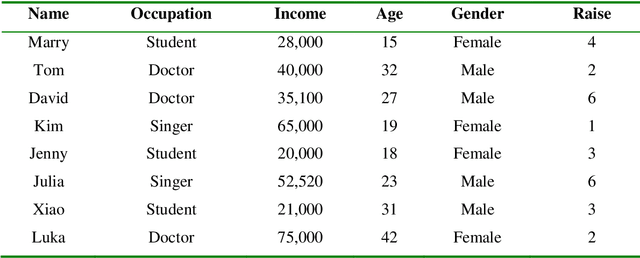
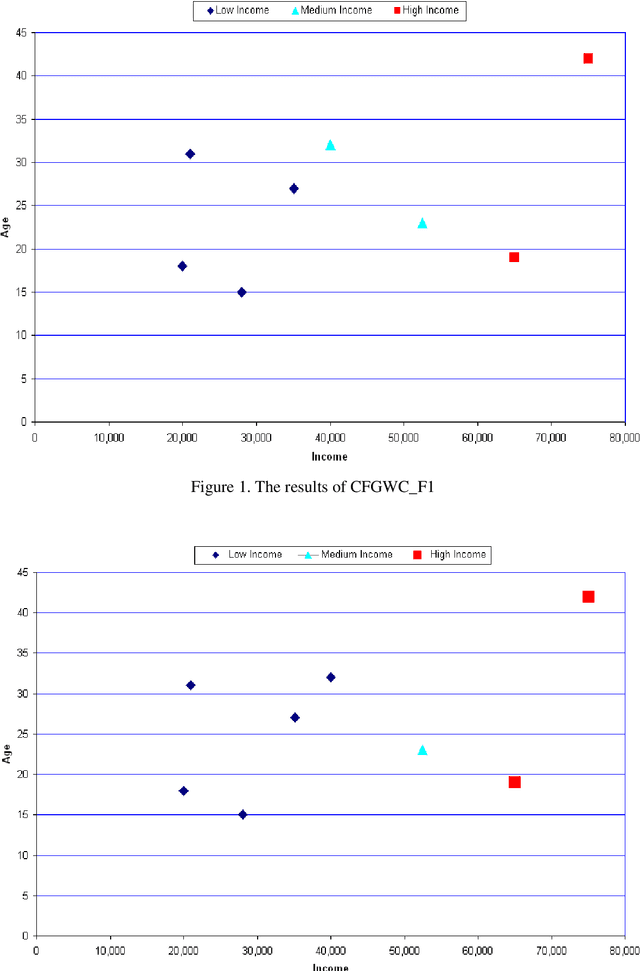
Abstract:Fuzzy Geographically Weighted Clustering (FGWC) is considered as a suitable tool for the analysis of geo-demographic data that assists the provision and planning of products and services to local people. Context variables were attached to FGWC in order to accelerate the computing speed of the algorithm and to focus the results on the domain of interests. Nonetheless, the determination of exact, crisp values of the context variable is a hard task. In this paper, we propose two novel methods using fuzzy approaches for that determination. A numerical example is given to illustrate the uses of the proposed methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge