Nelly Elsayed
Can Large Language Models Act as Symbolic Reasoners?
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:The performance of Large language models (LLMs) across a broad range of domains has been impressive but have been critiqued as not being able to reason about their process and conclusions derived. This is to explain the conclusions draw, and also for determining a plan or strategy for their approach. This paper explores the current research in investigating symbolic reasoning and LLMs, and whether an LLM can inherently provide some form of reasoning or whether supporting components are necessary, and, if there is evidence for a reasoning capability, is this evident in a specific domain or is this a general capability? In addition, this paper aims to identify the current research gaps and future trends of LLM explainability, presenting a review of the literature, identifying current research into this topic and suggests areas for future work.
TemporalAugmenter: An Ensemble Recurrent Based Deep Learning Approach for Signal Classification
Jan 13, 2024Abstract:Ensemble modeling has been widely used to solve complex problems as it helps to improve overall performance and generalization. In this paper, we propose a novel TemporalAugmenter approach based on ensemble modeling for augmenting the temporal information capturing for long-term and short-term dependencies in data integration of two variations of recurrent neural networks in two learning streams to obtain the maximum possible temporal extraction. Thus, the proposed model augments the extraction of temporal dependencies. In addition, the proposed approach reduces the preprocessing and prior stages of feature extraction, which reduces the required energy to process the models built upon the proposed TemporalAugmenter approach, contributing towards green AI. Moreover, the proposed model can be simply integrated into various domains including industrial, medical, and human-computer interaction applications. Our proposed approach empirically evaluated the speech emotion recognition, electrocardiogram signal, and signal quality examination tasks as three different signals with varying complexity and different temporal dependency features.
Big Data and Deep Learning in Smart Cities: A Comprehensive Dataset for AI-Driven Traffic Accident Detection and Computer Vision Systems
Jan 07, 2024Abstract:In the dynamic urban landscape, where the interplay of vehicles and pedestrians defines the rhythm of life, integrating advanced technology for safety and efficiency is increasingly crucial. This study delves into the application of cutting-edge technological methods in smart cities, focusing on enhancing public safety through improved traffic accident detection. Action recognition plays a pivotal role in interpreting visual data and tracking object motion such as human pose estimation in video sequences. The challenges of action recognition include variability in rapid actions, limited dataset, and environmental factors such as (Weather, Illumination, and Occlusions). In this paper, we present a novel comprehensive dataset for traffic accident detection. This datasets is specifically designed to bolster computer vision and action recognition systems in predicting and detecting road traffic accidents. We integrated datasets from wide variety of data sources, road networks, weather conditions, and regions across the globe. This approach is underpinned by empirical studies, aiming to contribute to the discourse on how technology can enhance the quality of life in densely populated areas. This research aims to bridge existing research gaps by introducing benchmark datasets that leverage state-of-the-art algorithms tailored for traffic accident detection in smart cities. These dataset is expected to advance academic research and also enhance real-time accident detection applications, contributing significantly to the evolution of smart urban environments. Our study marks a pivotal step towards safer, more efficient smart cities, harnessing the power of AI and machine learning to transform urban living.
CautionSuicide: A Deep Learning Based Approach for Detecting Suicidal Ideation in Real Time Chatbot Conversation
Jan 02, 2024
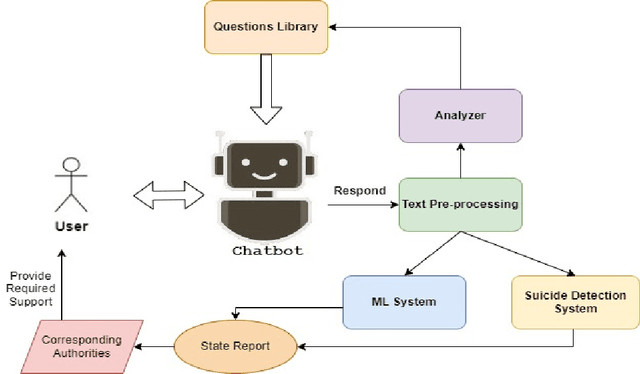
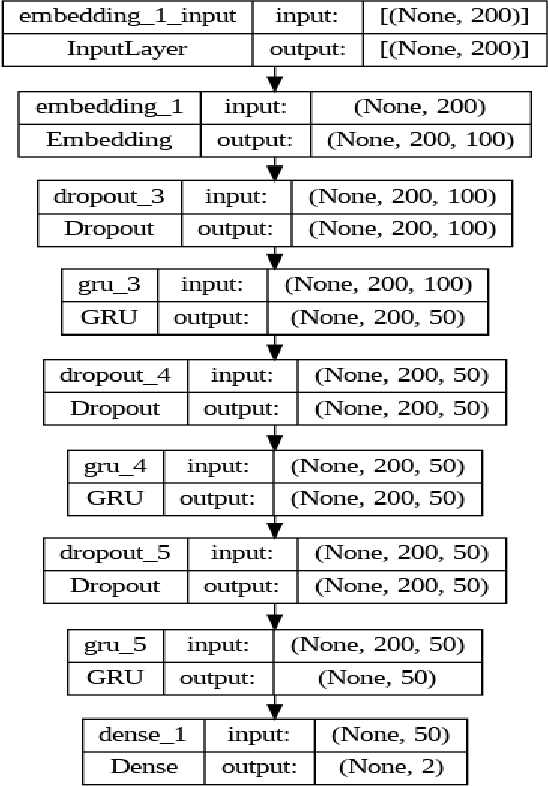
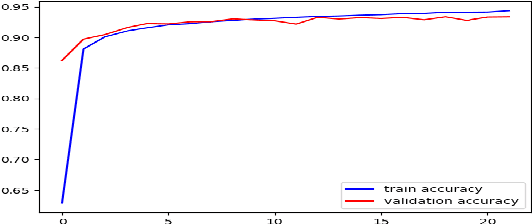
Abstract:Suicide is recognized as one of the most serious concerns in the modern society. Suicide causes tragedy that affects countries, communities, and families. There are many factors that lead to suicidal ideations. Early detection of suicidal ideations can help to prevent suicide occurrence by providing the victim with the required professional support, especially when the victim does not recognize the danger of having suicidal ideations. As technology usage has increased, people share and express their ideations digitally via social media, chatbots, and other digital platforms. In this paper, we proposed a novel, simple deep learning-based model to detect suicidal ideations in digital content, mainly focusing on chatbots as the primary data source. In addition, we provide a framework that employs the proposed suicide detection integration with a chatbot-based support system.
Smart City Transportation: Deep Learning Ensemble Approach for Traffic Accident Detection
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:The dynamic and unpredictable nature of road traffic necessitates effective accident detection methods for enhancing safety and streamlining traffic management in smart cities. This paper offers a comprehensive exploration study of prevailing accident detection techniques, shedding light on the nuances of other state-of-the-art methodologies while providing a detailed overview of distinct traffic accident types like rear-end collisions, T-bone collisions, and frontal impact accidents. Our novel approach introduces the I3D-CONVLSTM2D model architecture, a lightweight solution tailored explicitly for accident detection in smart city traffic surveillance systems by integrating RGB frames with optical flow information. Our experimental study's empirical analysis underscores our approach's efficacy, with the I3D-CONVLSTM2D RGB + Optical-Flow (Trainable) model outperforming its counterparts, achieving an impressive 87\% Mean Average Precision (MAP). Our findings further elaborate on the challenges posed by data imbalances, particularly when working with a limited number of datasets, road structures, and traffic scenarios. Ultimately, our research illuminates the path towards a sophisticated vision-based accident detection system primed for real-time integration into edge IoT devices within smart urban infrastructures.
AI on the Road: A Comprehensive Analysis of Traffic Accidents and Accident Detection System in Smart Cities
Jul 22, 2023Abstract:Accident detection and traffic analysis is a critical component of smart city and autonomous transportation systems that can reduce accident frequency, severity and improve overall traffic management. This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of traffic accidents in different regions across the United States using data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Crash Report Sampling System (CRSS). To address the challenges of accident detection and traffic analysis, this paper proposes a framework that uses traffic surveillance cameras and action recognition systems to detect and respond to traffic accidents spontaneously. Integrating the proposed framework with emergency services will harness the power of traffic cameras and machine learning algorithms to create an efficient solution for responding to traffic accidents and reducing human errors. Advanced intelligence technologies, such as the proposed accident detection systems in smart cities, will improve traffic management and traffic accident severity. Overall, this study provides valuable insights into traffic accidents in the US and presents a practical solution to enhance the safety and efficiency of transportation systems.
Epilepsy Seizure Detection: Anatomy and Analysis
May 30, 2023



Abstract:A seizure tracking system is crucial for monitoring and evaluating epilepsy treatments. Caretaker seizure diaries are used in epilepsy care today, but clinical seizure monitoring may miss seizures. Monitoring devices that can be worn may be better tolerated and more suitable for long-term ambulatory use. Many techniques and methods are proposed for seizure detection; However, simplicity and affordability are key concepts for daily use while preserving the accuracy of the detection. In this study, we propose a versal, affordable noninvasive based on a simple real-time k-Nearest-Neighbors (kNN) machine learning that can be customized and adapted to individual users in less than four (4) seconds of training time; the system was verified and validated using 500 subjects, with seizure detection data sampled at 178 Hz, the operated with a mean accuracy of (94.5%).
A Convolutional-based Model for Early Prediction of Alzheimer's based on the Dementia Stage in the MRI Brain Images
Feb 15, 2023Abstract:Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative brain disease. Being the primary cause of Dementia in adults and progressively destroys brain memory. Though Alzheimer's disease does not have a cure currently, diagnosing it at an earlier stage will help reduce the severity of the disease. Thus, early diagnosis of Alzheimer's could help to reduce or stop the disease from progressing. In this paper, we proposed a deep convolutional neural network-based model for learning model using to determine the stage of Dementia in adults based on the Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images to detect the early onset of Alzheimer's.
Deep Learning Approach for Early Stage Lung Cancer Detection
Feb 15, 2023Abstract:Lung cancer is the leading cause of death among different types of cancers. Every year, the lives lost due to lung cancer exceed those lost to pancreatic, breast, and prostate cancer combined. The survival rate for lung cancer patients is very low compared to other cancer patients due to late diagnostics. Thus, early lung cancer diagnostics is crucial for patients to receive early treatments, increasing the survival rate or even becoming cancer-free. This paper proposed a deep-learning model for early lung cancer prediction and diagnosis from Computed Tomography (CT) scans. The proposed mode achieves high accuracy. In addition, it can be a beneficial tool to support radiologists' decisions in predicting and detecting lung cancer and its stage.
IoT Botnet Detection Using an Economic Deep Learning Model
Feb 03, 2023



Abstract:The rapid progress in technology innovation usage and distribution has increased in the last decade. The rapid growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) systems worldwide has increased network security challenges created by malicious third parties. Thus, reliable intrusion detection and network forensics systems that consider security concerns and IoT systems limitations are essential to protect such systems. IoT botnet attacks are one of the significant threats to enterprises and individuals. Thus, this paper proposed an economic deep learning-based model for detecting IoT botnet attacks along with different types of attacks. The proposed model achieved higher accuracy than the state-of-the-art detection models using a smaller implementation budget and accelerating the training and detecting processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge