Mogens Plessen
From 2D to 3D terrain-following area coverage path planning
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:An algorithm for 3D terrain-following area coverage path planning is presented. Multiple adjacent paths are generated that are (i) locally apart from each other by a distance equal to the working width of a machinery, while (ii) simultaneously floating at a projection distance equal to a specific working height above the terrain. The complexities of the algorithm in comparison to its 2D equivalent are highlighted. These include uniformly spaced elevation data generation using an Inverse Distance Weighting-approach and a local search. Area coverage path planning results for real-world 3D data within an agricultural context are presented to validate the algorithm.
Predictive Spray Switching for an Efficient Path Planning Pattern for Area Coverage
Apr 01, 2025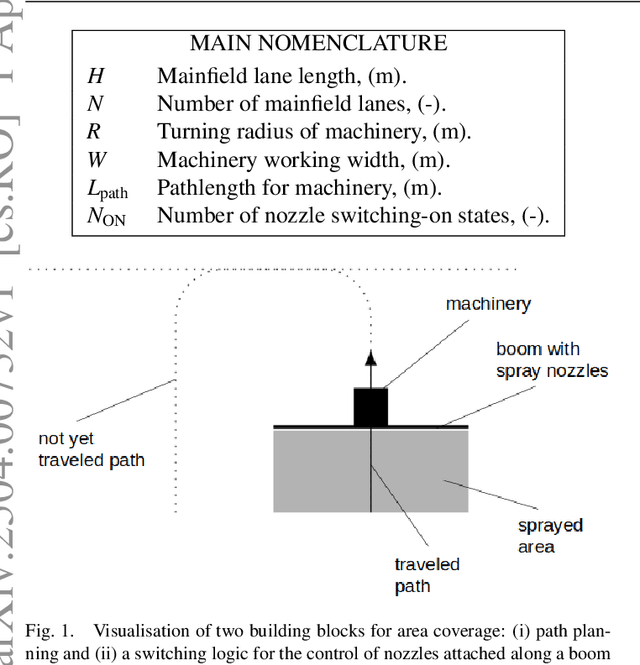
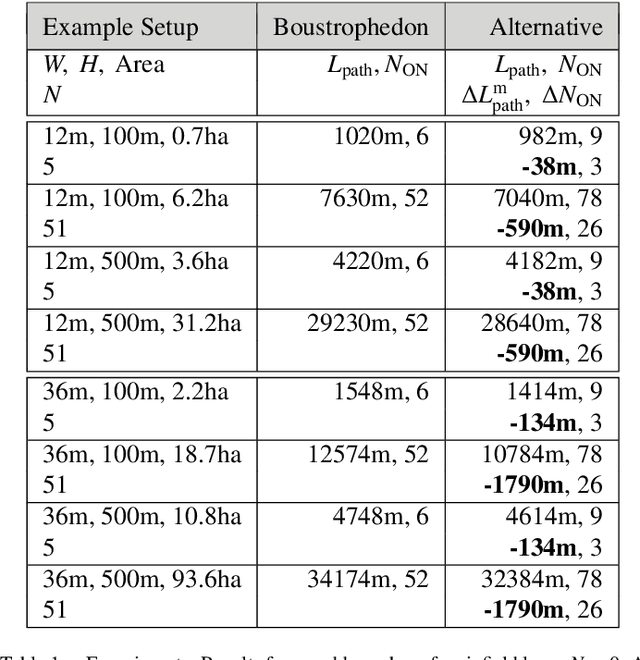
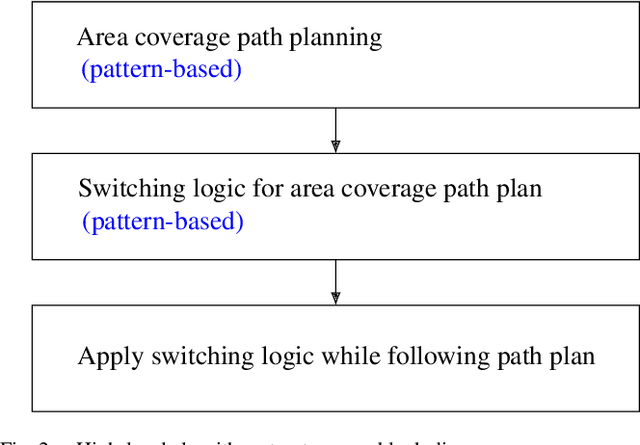
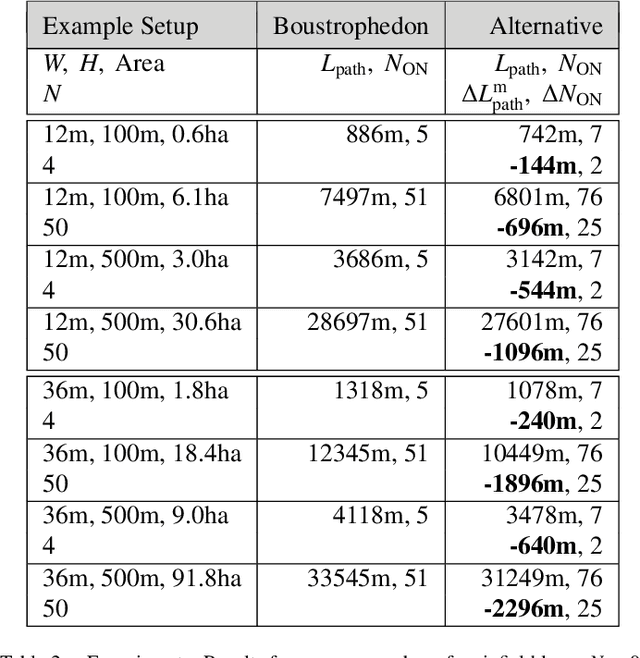
Abstract:This paper presents within an arable farming context a predictive logic for the on- and off-switching of a set of nozzles attached to a boom aligned along a working width and carried by a machinery with the purpose of applying spray along the working width while the machinery is traveling along a specific path planning pattern. Concatenation of multiple of those path patterns and corresponding concatenation of proposed switching logics enables nominal lossless spray application for area coverage tasks. Proposed predictive switching logic is compared to the common and state-of-the-art reactive switching logic for Boustrophedon-based path planning for area coverage. The trade-off between reduction in pathlength and increase in the number of required on- and off-switchings for proposed method is discussed.
Accelerated Sub-Image Search For Variable-Size Patches Identification Based On Virtual Time Series Transformation And Segmentation
Oct 20, 2024Abstract:This paper addresses two tasks: (i) fixed-size objects such as hay bales are to be identified in an aerial image for a given reference image of the object, and (ii) variable-size patches such as areas on fields requiring spot spraying or other handling are to be identified in an image for a given small-scale reference image. Both tasks are related. The second differs in that identified sub-images similar to the reference image are further clustered before patches contours are determined by solving a traveling salesman problem. Both tasks are complex in that the exact number of similar sub-images is not known a priori. The main discussion of this paper is presentation of an acceleration mechanism for sub-image search that is based on a transformation of an image to multivariate time series along the RGB-channels and subsequent segmentation to reduce the 2D search space in the image. Two variations of the acceleration mechanism are compared to exhaustive search on diverse synthetic and real-world images. Quantitatively, proposed method results in solve time reductions of up to 2 orders of magnitude, while qualitatively delivering comparative visual results. Proposed method is neural network-free and does not use any image pre-processing.
Path Planning for Spot Spraying with UAVs Combining TSP and Area Coverages
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:This paper addresses the following task: given a set of patches or areas of varying sizes that are meant to be serviced within a bounding contour calculate a minimal length path plan for an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) such that the path additionally avoids given obstacles areas and does never leave the bounding contour. The application in mind is agricultural spot spraying, where the bounding contour represents the field contour and multiple patches represent multiple weed areas meant to be sprayed. Obstacle areas are ponds or tree islands. The proposed method combines a heuristic solution to a traveling salesman problem (TSP) with optimised area coverage path planning. Two TSP-initialisation and 4 TSP-refinement heuristics as well as two area coverage path planning methods are evaluated on three real-world experiments with three obstacle areas and 15, 19 and 197 patches, respectively. The unsuitability of a Baustrophedon-path for area coverage gap avoidance is discussed and inclusion of a headland path for area coverage is motivated. Two main findings are (i) the particular suitability of one TSP-refinement heuristic, and (ii) the unexpected high contribution of patches areas coverage pathlengths on total pathlength, highlighting the importance of optimised area coverage path planning for spot spraying.
Smoothing of Headland Path Edges and Headland-to-Mainfield Lane Transitions Based on a Spatial Domain Transformation and Linear Programming
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:Within the context of in-field path planning and under the assumption of nonholonomic vehicle models this paper addresses two tasks: smoothing of headland path edges and smoothing of headland-to-mainfield lane transitions. Both tasks are solved by a two-step hierarchical algorithm. The first step differs for the two tasks generating either a piecewise-affine or a Dubins reference path. The second step leverages a transformation of vehicle dynamics from the time domain into the spatial domain and linear programming. Benefits such as a hyperparameter-free objective function and spatial constraints useful for area coverage gaps avoidance and precision path planning are discussed. The method, which is a deterministic optimisation-based method, is evaluated on a real-world field solving 3 instances of the first task and 16 instances of the second task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge