Mitt Shah
A Review On Software Defects Prediction Methods
Oct 30, 2020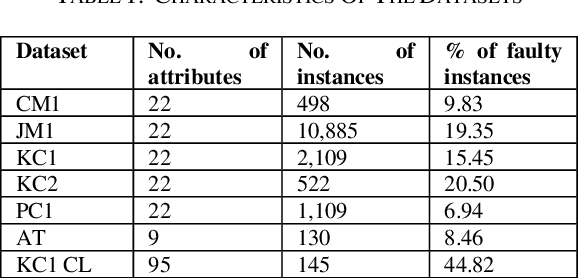
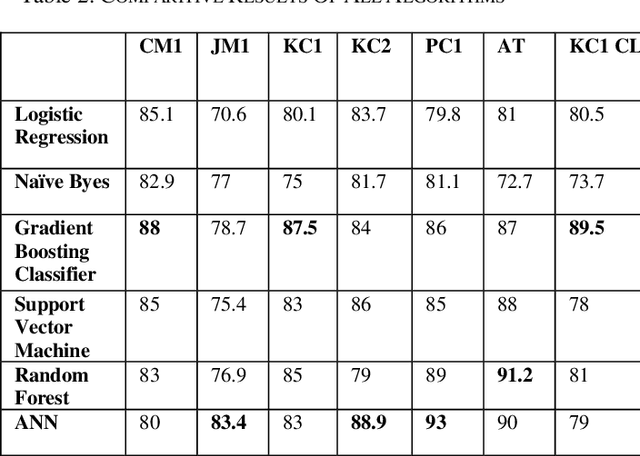
Abstract:Software quality is one of the essential aspects of a software. With increasing demand, software designs are becoming more complex, increasing the probability of software defects. Testers improve the quality of software by fixing defects. Hence the analysis of defects significantly improves software quality. The complexity of software also results in a higher number of defects, and thus manual detection can become a very time-consuming process. This gave researchers incentives to develop techniques for automatic software defects detection. In this paper, we try to analyze the state of the art machine learning algorithms' performance for software defect classification. We used seven datasets from the NASA promise dataset repository for this research work. The performance of Neural Networks and Gradient Boosting classifier dominated other algorithms.
Dermatologist vs Neural Network
Jun 15, 2020



Abstract:Cancer, in general, is very deadly. Timely treatment of any cancer is the key to saving a life. Skin cancer is no exception. There have been thousands of Skin Cancer cases registered per year all over the world. There have been 123,000 deadly melanoma cases detected in a single year. This huge number is proven to be a cause of a high amount of UV rays present in the sunlight due to the degradation of the Ozone layer. If not detected at an early stage, skin cancer can lead to the death of the patient. Unavailability of proper resources such as expert dermatologists, state of the art testing facilities, and quick biopsy results have led researchers to develop a technology that can solve the above problem. Deep Learning is one such method that has offered extraordinary results. The Convolutional Neural Network proposed in this study out performs every pretrained models. We trained our model on the HAM10000 dataset which offers 10015 images belonging to 7 classes of skin disease. The model we proposed gave an accuracy of 89%. This model can predict deadly melanoma skin cancer with a great accuracy. Hopefully, this study can help save people's life where there is the unavailability of proper dermatological resources by bridging the gap using our proposed study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge