Mengfan Yao
Relaxed Clustered Hawkes Process for Procrastination Modeling in MOOCs
Jan 29, 2021
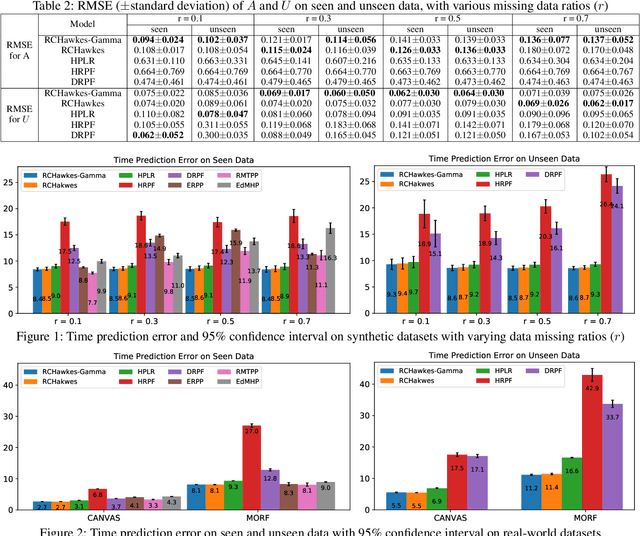

Abstract:Hawkes processes have been shown to be efficient in modeling bursty sequences in a variety of applications, such as finance and social network activity analysis. Traditionally, these models parameterize each process independently and assume that the history of each point process can be fully observed. Such models could however be inefficient or even prohibited in certain real-world applications, such as in the field of education, where such assumptions are violated. Motivated by the problem of detecting and predicting student procrastination in students Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) with missing and partially observed data, in this work, we propose a novel personalized Hawkes process model (RCHawkes-Gamma) that discovers meaningful student behavior clusters by jointly learning all partially observed processes simultaneously, without relying on auxiliary features. Our experiments on both synthetic and real-world education datasets show that RCHawkes-Gamma can effectively recover student clusters and their temporal procrastination dynamics, resulting in better predictive performance of future student activities. Our further analyses of the learned parameters and their association with student delays show that the discovered student clusters unveil meaningful representations of various procrastination behaviors in students.
Stimuli-Sensitive Hawkes Processes for Personalized Student Procrastination Modeling
Jan 29, 2021
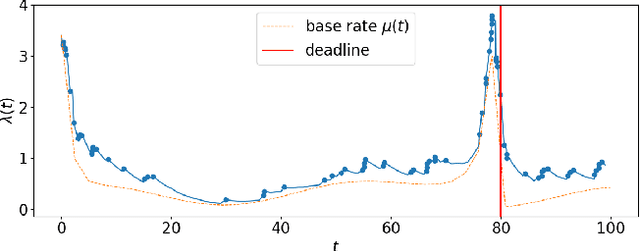
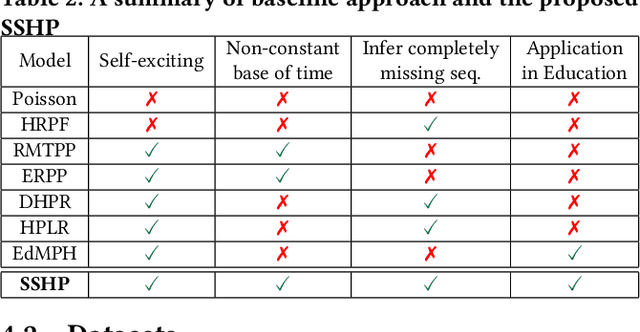
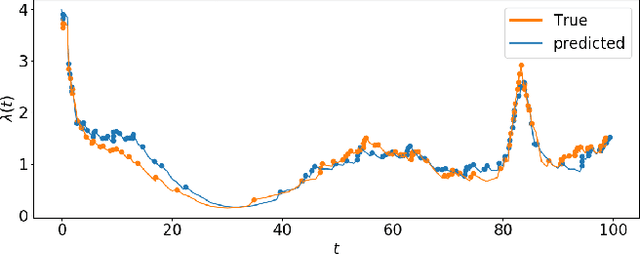
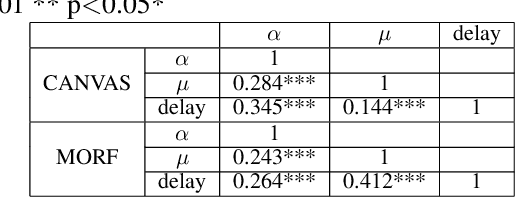
Abstract:Student procrastination and cramming for deadlines are major challenges in online learning environments, with negative educational and well-being side effects. Modeling student activities in continuous time and predicting their next study time are important problems that can help in creating personalized timely interventions to mitigate these challenges. However, previous attempts on dynamic modeling of student procrastination suffer from major issues: they are unable to predict the next activity times, cannot deal with missing activity history, are not personalized, and disregard important course properties, such as assignment deadlines, that are essential in explaining the cramming behavior. To resolve these problems, we introduce a new personalized stimuli-sensitive Hawkes process model (SSHP), by jointly modeling all student-assignment pairs and utilizing their similarities, to predict students' next activity times even when there are no historical observations. Unlike regular point processes that assume a constant external triggering effect from the environment, we model three dynamic types of external stimuli, according to assignment availabilities, assignment deadlines, and each student's time management habits. Our experiments on two synthetic datasets and two real-world datasets show a superior performance of future activity prediction, comparing with state-of-the-art models. Moreover, we show that our model achieves a flexible and accurate parameterization of activity intensities in students.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge