Mehdi Saeedi
Combining Reinforcement Learning and Behavior Trees for NPCs in Video Games with AMD Schola
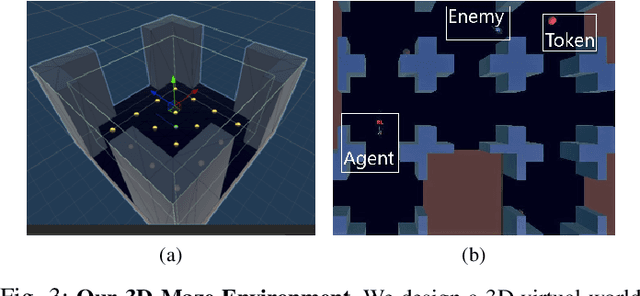
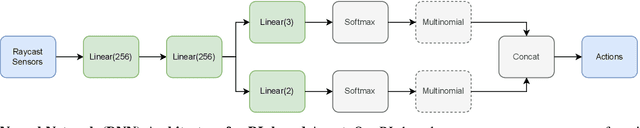
Oct 15, 2025Abstract:While the rapid advancements in the reinforcement learning (RL) research community have been remarkable, the adoption in commercial video games remains slow. In this paper, we outline common challenges the Game AI community faces when using RL-driven NPCs in practice, and highlight the intersection of RL with traditional behavior trees (BTs) as a crucial juncture to be explored further. Although the BT+RL intersection has been suggested in several research papers, its adoption is rare. We demonstrate the viability of this approach using AMD Schola -- a plugin for training RL agents in Unreal Engine -- by creating multi-task NPCs in a complex 3D environment inspired by the commercial video game ``The Last of Us". We provide detailed methodologies for jointly training RL models with BTs while showcasing various skills.
Human-Like Navigation Behavior: A Statistical Evaluation Framework
Mar 10, 2022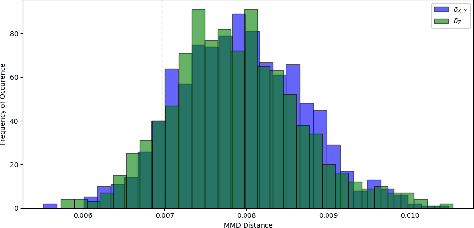
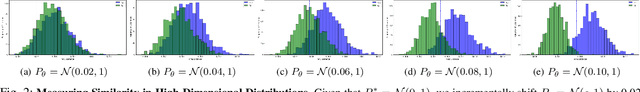
Abstract:Recent advancements in deep reinforcement learning have brought forth an impressive display of highly skilled artificial agents capable of complex intelligent behavior. In video games, these artificial agents are increasingly deployed as non-playable characters (NPCs) designed to enhance the experience of human players. However, while it has been shown that the convincing human-like behavior of NPCs leads to increased engagement in video games, the believability of an artificial agent's behavior is most often measured solely by its proficiency at a given task. Recent work has hinted that proficiency alone is not sufficient to discern human-like behavior. Motivated by this, we build a non-parametric two-sample hypothesis test designed to compare the behaviors of artificial agents to those of human players. We show that the resulting $p$-value not only aligns with anonymous human judgment of human-like behavior, but also that it can be used as a measure of similarity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge