Meena Abdelmaseeh
Affine and Regional Dynamic Time Warpng
May 25, 2015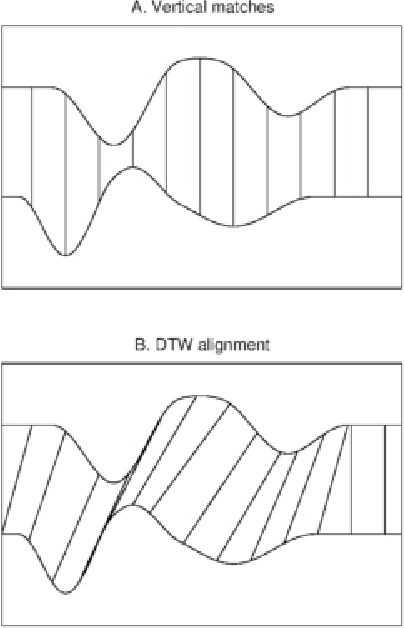
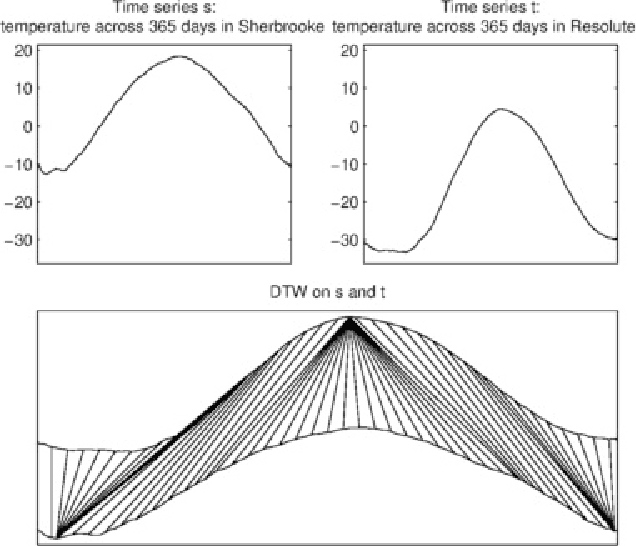
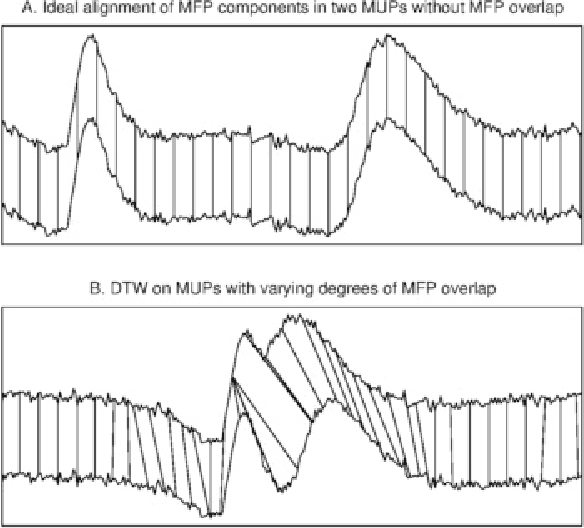
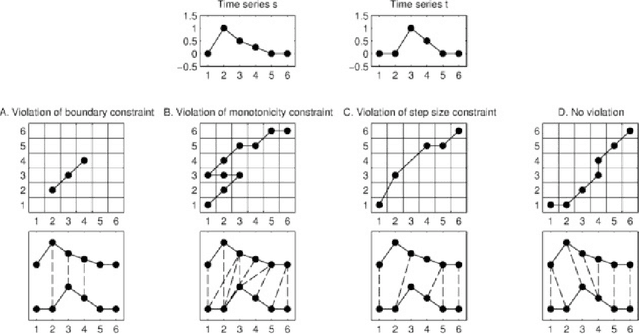
Abstract:Pointwise matches between two time series are of great importance in time series analysis, and dynamic time warping (DTW) is known to provide generally reasonable matches. There are situations where time series alignment should be invariant to scaling and offset in amplitude or where local regions of the considered time series should be strongly reflected in pointwise matches. Two different variants of DTW, affine DTW (ADTW) and regional DTW (RDTW), are proposed to handle scaling and offset in amplitude and provide regional emphasis respectively. Furthermore, ADTW and RDTW can be combined in two different ways to generate alignments that incorporate advantages from both methods, where the affine model can be applied either globally to the entire time series or locally to each region. The proposed alignment methods outperform DTW on specific simulated datasets, and one-nearest-neighbor classifiers using their associated difference measures are competitive with the difference measures associated with state-of-the-art alignment methods on real datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge