Matthias Kaschube
Linking in Style: Understanding learned features in deep learning models
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) learn abstract features to perform object classification, but understanding these features remains challenging due to difficult-to-interpret results or high computational costs. We propose an automatic method to visualize and systematically analyze learned features in CNNs. Specifically, we introduce a linking network that maps the penultimate layer of a pre-trained classifier to the latent space of a generative model (StyleGAN-XL), thereby enabling an interpretable, human-friendly visualization of the classifier's representations. Our findings indicate a congruent semantic order in both spaces, enabling a direct linear mapping between them. Training the linking network is computationally inexpensive and decoupled from training both the GAN and the classifier. We introduce an automatic pipeline that utilizes such GAN-based visualizations to quantify learned representations by analyzing activation changes in the classifier in the image domain. This quantification allows us to systematically study the learned representations in several thousand units simultaneously and to extract and visualize units selective for specific semantic concepts. Further, we illustrate how our method can be used to quantify and interpret the classifier's decision boundary using counterfactual examples. Overall, our method offers systematic and objective perspectives on learned abstract representations in CNNs. https://github.com/kaschube-lab/LinkingInStyle.git
Denoising diffusion models for high-resolution microscopy image restoration
Sep 18, 2024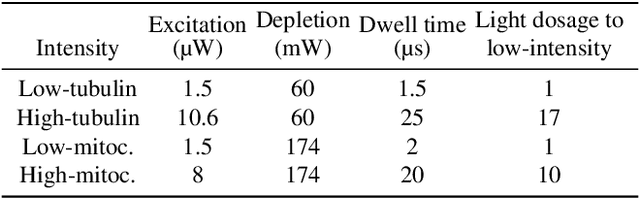


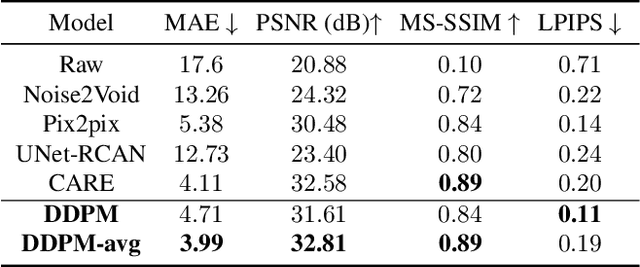
Abstract:Advances in microscopy imaging enable researchers to visualize structures at the nanoscale level thereby unraveling intricate details of biological organization. However, challenges such as image noise, photobleaching of fluorophores, and low tolerability of biological samples to high light doses remain, restricting temporal resolutions and experiment durations. Reduced laser doses enable longer measurements at the cost of lower resolution and increased noise, which hinders accurate downstream analyses. Here we train a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) to predict high-resolution images by conditioning the model on low-resolution information. Additionally, the probabilistic aspect of the DDPM allows for repeated generation of images that tend to further increase the signal-to-noise ratio. We show that our model achieves a performance that is better or similar to the previously best-performing methods, across four highly diverse datasets. Importantly, while any of the previous methods show competitive performance for some, but not all datasets, our method consistently achieves high performance across all four data sets, suggesting high generalizability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge