Manuel-Vicente Garnacho-Castaño
Reliability and Validity of the Polar V800 Sports Watch for Estimating Vertical Jump Height
Mar 28, 2022
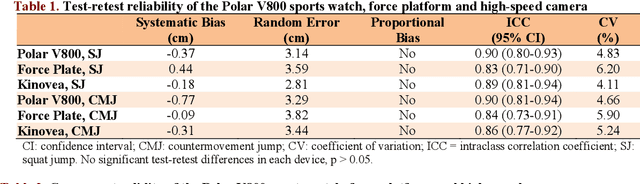
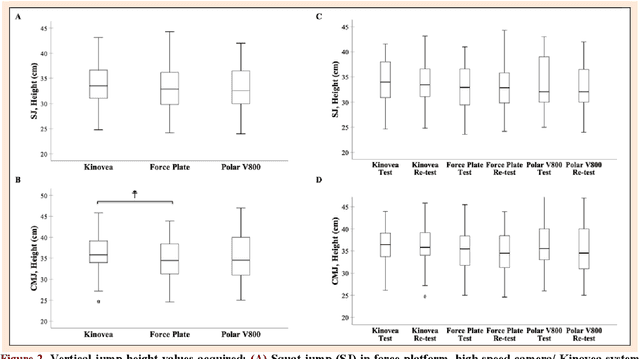
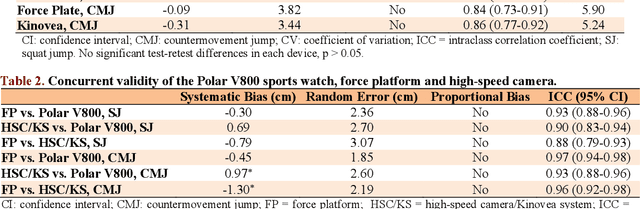
Abstract:This study aimed to assess the reliability and validity of the Polar V800 to measure vertical jump height. Twenty-two physically active healthy men (age: 22.89 +- 4.23 years; body mass: 70.74 +- 8.04 kg; height: 1.74 +- 0.76 m) were recruited for the study. The reliability was evaluated by comparing measurements acquired by the Polar V800 in two identical testing sessions one week apart. Validity was assessed by comparing measurements simultaneously obtained using a force platform (gold standard), high-speed camera and the Polar V800 during squat jump (SJ) and countermovement jump (CMJ) tests. In the test-retest reliability, high intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were observed (mean: 0.90, SJ and CMJ) in the Polar V800. There was no significant systematic bias +- random errors (p > 0.05) between test-retest. Low coefficients of variation (<5%) were detected in both jumps in the Polar V800. In the validity assessment, similar jump height was detected among devices (p > 0.05). There was almost perfect agreement between the Polar V800 compared to a force platform for the SJ and CMJ tests (Mean ICCs = 0.95; no systematic bias +- random errors in SJ mean: -0.38 +- 2.10 cm, p > 0.05). Mean ICC between the Polar V800 versus high-speed camera was 0.91 for the SJ and CMJ tests, however, a significant systematic bias +- random error (0.97 +- 2.60 cm; p = 0.01) was detected in CMJ test. The Polar V800 offers valid, compared to force platform, and reliable information about vertical jump height performance in physically active healthy young men.
* 9 pages, published in Journal of sports science and medicine, 20, 149 157
On the Handwriting Tasks' Analysis to Detect Fatigue
Mar 28, 2022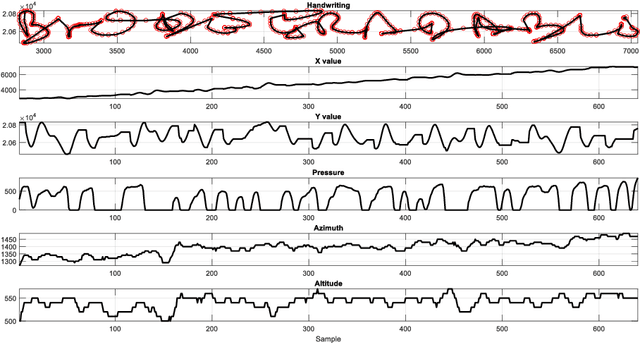
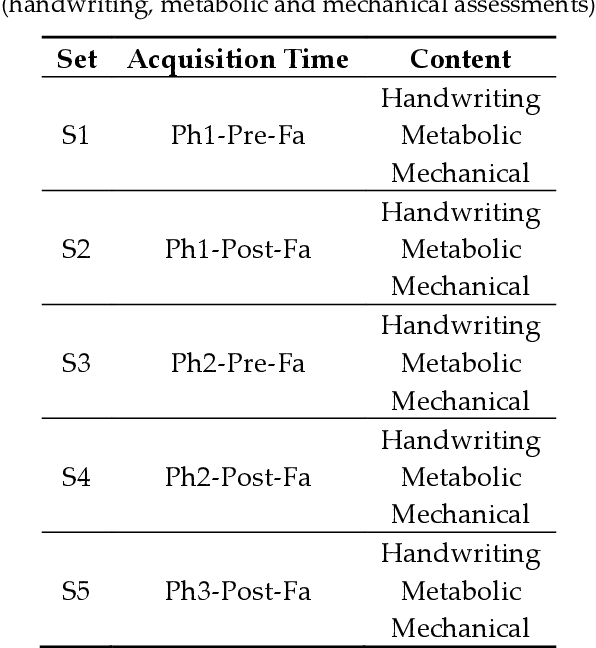
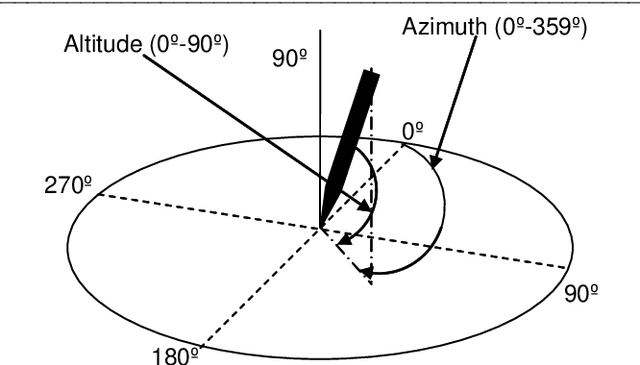
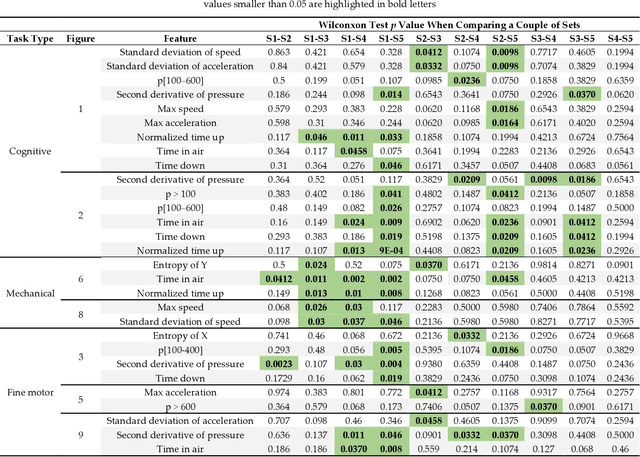
Abstract:Practical determination of physical recovery after intense exercise is a challenging topic that must include mechanical aspects as well as cognitive ones because most of physical sport activities, as well as professional activities (including brain computer interface-operated systems), require good shape in both of them. This paper presents a new online handwritten database of 20 healthy subjects. The main goal was to study the influence of several physical exercise stimuli in different handwritten tasks and to evaluate the recovery after strenuous exercise. To this aim, they performed different handwritten tasks before and after physical exercise as well as other measurements such as metabolic and mechanical fatigue assessment. Experimental results showed that although a fast mechanical recovery happens and can be measured by lactate concentrations and mechanical fatigue, this is not the case when cognitive effort is required. Handwriting analysis revealed that statistical differences exist on handwriting performance even after lactate concentration and mechanical assessment recovery. Conclusions: This points out a necessity of more recovering time in sport and professional activities than those measured in classic ways.
* 16 pages, published in Applied Sciences 10, no. 21: 7630, 2020
The effect of fatigue on the performance of online writer recognition
Feb 24, 2022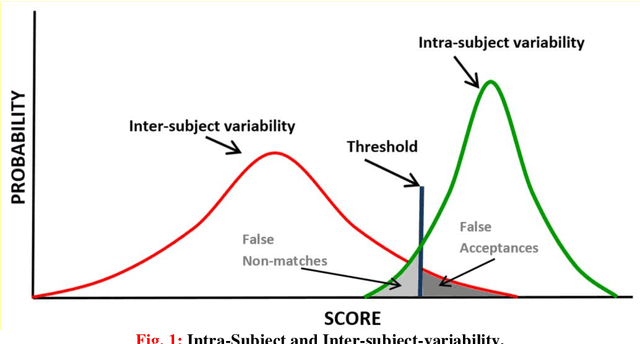


Abstract:Background: The performance of biometric modalities based on things done by the subject, like signature and text-based recognition, may be affected by the subject state. Fatigue is one of the conditions that can significantly affect the outcome of handwriting tasks. Recent research has already shown that physical fatigue produces measurable differences in some features extracted from common writing and drawing tasks. It is important to establish to which extent physical fatigue contributes to the intra-person variability observed in these biometric modalities and also to know whether the performance of recognition methods is affected by fatigue. Goal: In this paper we assess the impact of fatigue on intra-user variability and on the performance of signature-based and text-based writer recognition approaches encompassing both identification and verification. Methods: Several signature and text recognition methods are considered and applied to samples gathered after different levels of induced fatigue, measured by metabolic and mechanical assessment and, also by subjective perception. The recognition methods are Dynamic Time Warping and Multi Section Vector Quantization, for signatures, and Allographic Text-Dependent Recognition for text in capital letters. For each fatigue level, the identification and verification performance of these methods is measured. Results: Signature shows no statistically significant intra-user impact, but text does. On the other hand, performance of signature-based recognition approaches is negatively impacted by fatigue whereas the impact is not noticeable in text-based recognition, provided long enough sequences are considered.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge