Manjeet Dahiya
Metaheuristic for Hub-Spoke Facility Location Problem: Application to Indian E-commerce Industry
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:Indian e-commerce industry has evolved over the last decade and is expected to grow over the next few years. The focus has now shifted to turnaround time (TAT) due to the emergence of many third-party logistics providers and higher customer expectations. The key consideration for delivery providers is to balance their overall operating costs while meeting the promised TAT to their customers. E-commerce delivery partners operate through a network of facilities whose strategic locations help to run the operations efficiently. In this work, we identify the locations of hubs throughout the country and their corresponding mapping with the distribution centers. The objective is to minimize the total network costs with TAT adherence. We use Genetic Algorithm and leverage business constraints to reduce the solution search space and hence the solution time. The results indicate an improvement of 9.73% in TAT compliance compared with the current scenario.
Multi-task Learning with Metadata for Music Mood Classification
Oct 10, 2021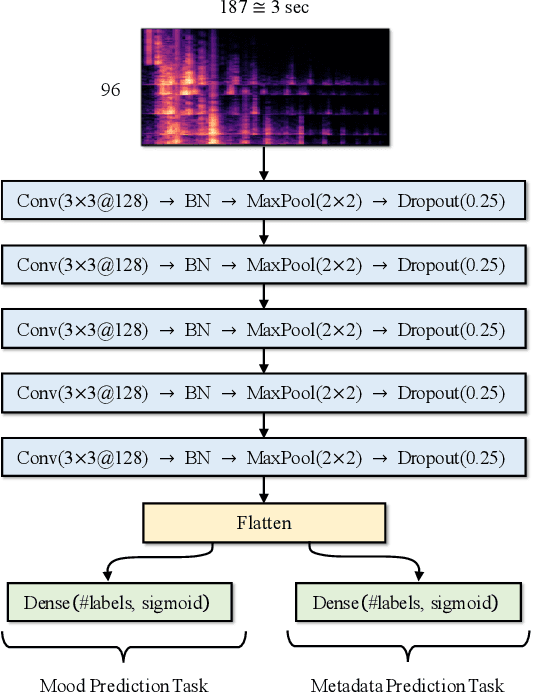
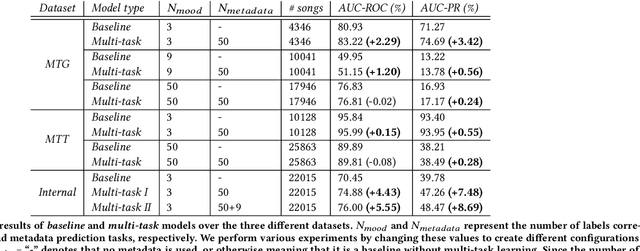
Abstract:Mood recognition is an important problem in music informatics and has key applications in music discovery and recommendation. These applications have become even more relevant with the rise of music streaming. Our work investigates the research question of whether we can leverage audio metadata such as artist and year, which is readily available, to improve the performance of mood classification models. To this end, we propose a multi-task learning approach in which a shared model is simultaneously trained for mood and metadata prediction tasks with the goal to learn richer representations. Experimentally, we demonstrate that applying our technique on the existing state-of-the-art convolutional neural networks for mood classification improves their performances consistently. We conduct experiments on multiple datasets and report that our approach can lead to improvements in the average precision metric by up to 8.7 points.
Automatic Collection Creation and Recommendation
May 03, 2021

Abstract:We present a collection recommender system that can automatically create and recommend collections of items at a user level. Unlike regular recommender systems, which output top-N relevant items, a collection recommender system outputs collections of items such that the items in the collections are relevant to a user, and the items within a collection follow a specific theme. Our system builds on top of the user-item representations learnt by item recommender systems. We employ dimensionality reduction and clustering techniques along with intuitive heuristics to create collections with their ratings and titles. We test these ideas in a real-world setting of music recommendation, within a popular music streaming service. We find that there is a 2.3x increase in recommendation-driven consumption when recommending collections over items. Further, it results in effective utilization of real estate and leads to recommending a more and diverse set of items. To our knowledge, these are first of its kind experiments at such a large scale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge