Manfred Stede
FAW Ulm and University of Toronto
Assessing Open-Source Large Language Models on Argumentation Mining Subtasks
Nov 08, 2024Abstract:We explore the capability of four open-sourcelarge language models (LLMs) in argumentation mining (AM). We conduct experiments on three different corpora; persuasive essays(PE), argumentative microtexts (AMT) Part 1 and Part 2, based on two argumentation mining sub-tasks: (i) argumentative discourse units classifications (ADUC), and (ii) argumentative relation classification (ARC). This work aims to assess the argumentation capability of open-source LLMs, including Mistral 7B, Mixtral8x7B, LlamA2 7B and LlamA3 8B in both, zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. Our analysis contributes to further assessing computational argumentation with open-source LLMs in future research efforts.
Generating Sentiment Lexicons for German Twitter
Oct 31, 2016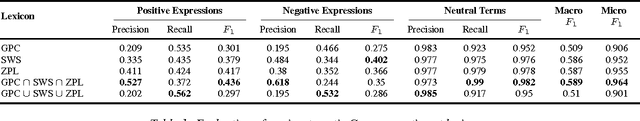
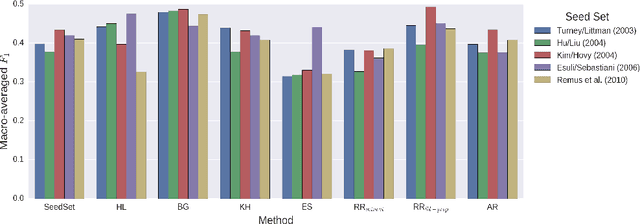


Abstract:Despite a substantial progress made in developing new sentiment lexicon generation (SLG) methods for English, the task of transferring these approaches to other languages and domains in a sound way still remains open. In this paper, we contribute to the solution of this problem by systematically comparing semi-automatic translations of common English polarity lists with the results of the original automatic SLG algorithms, which were applied directly to German data. We evaluate these lexicons on a corpus of 7,992 manually annotated tweets. In addition to that, we also collate the results of dictionary- and corpus-based SLG methods in order to find out which of these paradigms is better suited for the inherently noisy domain of social media. Our experiments show that semi-automatic translations notably outperform automatic systems (reaching a macro-averaged F1-score of 0.589), and that dictionary-based techniques produce much better polarity lists as compared to corpus-based approaches (whose best F1-scores run up to 0.479 and 0.419 respectively) even for the non-standard Twitter genre.
Ma(r)king concessions in English and German
Jun 01, 1995

Abstract:In order to generate cohesive discourse, many of the relations holding between text segments need to be signalled to the reader by means of cue words, or {\em discourse markers}. Programs usually do this in a simplistic way, e.g., by using one marker per relation. In reality, however, language offers a very wide range of markers from which informed choices should be made. In order to account for the variety and to identify the parameters governing the choices, detailled linguistic analyses are necessary. We worked with one area of discourse relations, the Concession family, identified its underlying pragmatics and semantics, and undertook extensive corpus studies to examine the range of markers used in both English and German. On the basis of an initial classification of these markers, we propose a generation model for producing bilingual text that can incorporate marker choice into its overall decision framework.
* 23 pages, uuencoded compressed postscript
Generating Multilingual Documents from a Knowledge Base: The TECHDOC Project
Jul 22, 1994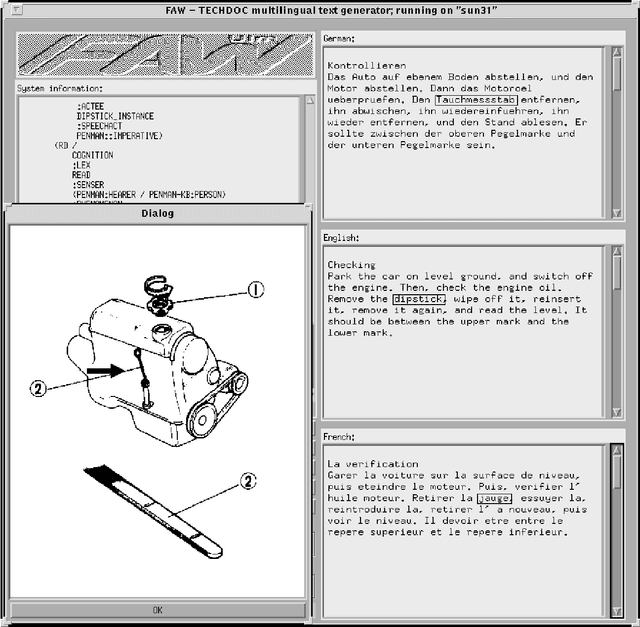
Abstract:TECHDOC is an implemented system demonstrating the feasibility of generating multilingual technical documents on the basis of a language-independent knowledge base. Its application domain is user and maintenance instructions, which are produced from underlying plan structures representing the activities, the participating objects with their properties, relations, and so on. This paper gives a brief outline of the system architecture and discusses some recent developments in the project: the addition of actual event simulation in the KB, steps towards a document authoring tool, and a multimodal user interface. (slightly corrected version of a paper to appear in: COLING 94, Proceedings)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge