M. Rosati
AI-assisted Optimization of the ECCE Tracking System at the Electron Ion Collider
May 20, 2022Abstract:The Electron-Ion Collider (EIC) is a cutting-edge accelerator facility that will study the nature of the "glue" that binds the building blocks of the visible matter in the universe. The proposed experiment will be realized at Brookhaven National Laboratory in approximately 10 years from now, with detector design and R&D currently ongoing. Notably, EIC is one of the first large-scale facilities to leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) already starting from the design and R&D phases. The EIC Comprehensive Chromodynamics Experiment (ECCE) is a consortium that proposed a detector design based on a 1.5T solenoid. The EIC detector proposal review concluded that the ECCE design will serve as the reference design for an EIC detector. Herein we describe a comprehensive optimization of the ECCE tracker using AI. The work required a complex parametrization of the simulated detector system. Our approach dealt with an optimization problem in a multidimensional design space driven by multiple objectives that encode the detector performance, while satisfying several mechanical constraints. We describe our strategy and show results obtained for the ECCE tracking system. The AI-assisted design is agnostic to the simulation framework and can be extended to other sub-detectors or to a system of sub-detectors to further optimize the performance of the EIC detector.
Real-time calibration of coherent-state receivers: learning by trial and error
Jan 28, 2020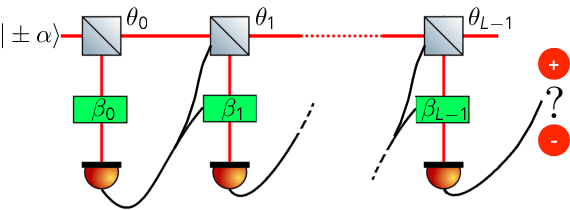

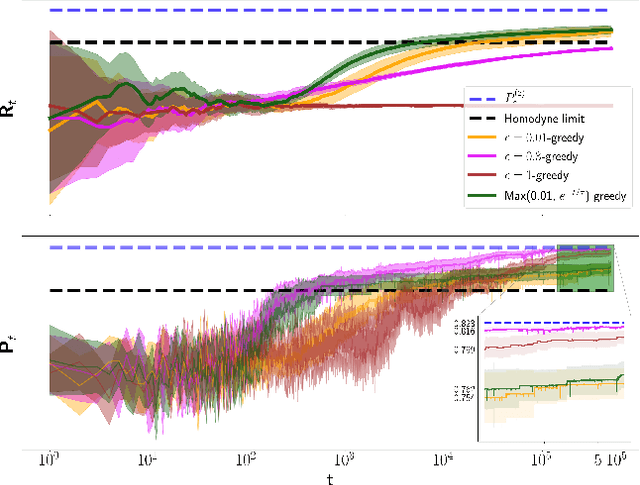

Abstract:The optimal discrimination of coherent states of light with current technology is a key problem in classical and quantum communication, whose solution would enable the realization of efficient receivers for long-distance communications in free-space and optical fiber channels. In this article, we show that reinforcement learning (RL) protocols allow an agent to learn near-optimal coherent-state receivers made of passive linear optics, photodetectors and classical adaptive control. Each agent is trained and tested in real time over several runs of independent discrimination experiments and has no knowledge about the energy of the states nor the receiver setup nor the quantum-mechanical laws governing the experiments. Based exclusively on the observed photodetector outcomes, the agent adaptively chooses among a set of ~3 10^3 possible receiver setups, and obtains a reward at the end of each experiment if its guess is correct. At variance with previous applications of RL in quantum physics, the information gathered in each run is intrinsically stochastic and thus insufficient to evaluate exactly the performance of the chosen receiver. Nevertheless, we present families of agents that: (i) discover a receiver beating the best Gaussian receiver after ~3 10^2 experiments; (ii) surpass the cumulative reward of the best Gaussian receiver after ~10^3 experiments; (iii) simultaneously discover a near-optimal receiver and attain its cumulative reward after ~10^5 experiments. Our results show that RL techniques are suitable for on-line control of quantum receivers and can be employed for long-distance communications over potentially unknown channels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge