Lionel Lacassagne
ALSOC
A new meteor detection application robust to camera movements
Sep 12, 2023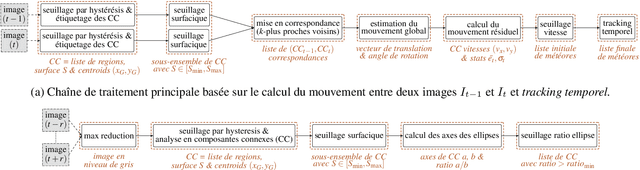



Abstract:This article presents a new tool for the automatic detection of meteors. Fast Meteor Detection Toolbox (FMDT) is able to detect meteor sightings by analyzing videos acquired by cameras onboard weather balloons or within airplane with stabilization. The challenge consists in designing a processing chain composed of simple algorithms, that are robust to the high fluctuation of the videos and that satisfy the constraints on power consumption (10 W) and real-time processing (25 frames per second).
Parallelization of a new embedded application for automatic meteor detection
Jul 20, 2023Abstract:This article presents the methods used to parallelize a new computer vision application. The system is able to automatically detect meteor from non-stabilized cameras and noisy video sequences. The application is designed to be embedded in weather balloons or for airborne observation campaigns. Thus, the final target is a low power system-on-chip (< 10 Watts) while the software needs to compute a stream of frames in real-time (> 25 frames per second). For this, first the application is split in a tasks graph, then different parallelization techniques are applied. Experiment results demonstrate the efficiency of the parallelization methods. For instance, on the Raspberry Pi 4 and on a HD video sequence, the processing chain reaches 42 frames per second while it only consumes 6 Watts.
A New Run-based Connected Component Labeling for Efficiently Analyzing and Processing Holes
Jun 16, 2020



Abstract:This article introduces a new connected component labeling and analysis algorithm for foreground and background labeling that computes the adjacency tree. The computation of features (bounding boxes, first statistical moments, Euler number) is done on-the-fly. The transitive closure enables an efficient hole processing that can be filled while their features are merged with the surrounding connected component without the need to rescan the image. A comparison with existing algorithms shows that this new algorithm can do all these computations faster than algorithms processing black and white components.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge