Lily Akrapongpisak
Transferable Models for Bioacoustics with Human Language Supervision
Aug 09, 2023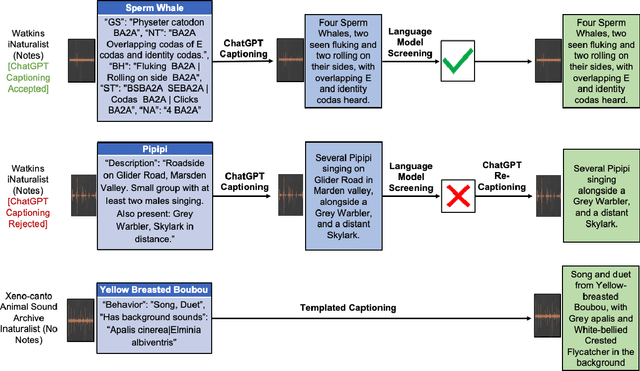
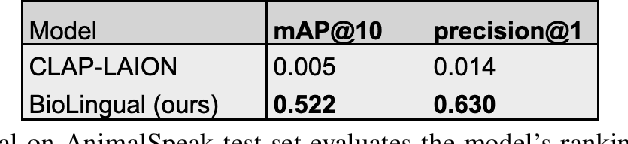
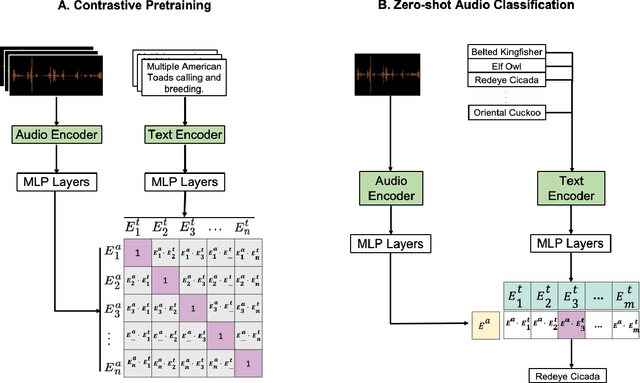
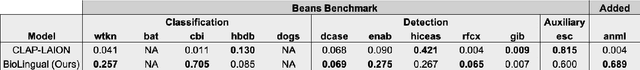
Abstract:Passive acoustic monitoring offers a scalable, non-invasive method for tracking global biodiversity and anthropogenic impacts on species. Although deep learning has become a vital tool for processing this data, current models are inflexible, typically cover only a handful of species, and are limited by data scarcity. In this work, we propose BioLingual, a new model for bioacoustics based on contrastive language-audio pretraining. We first aggregate bioacoustic archives into a language-audio dataset, called AnimalSpeak, with over a million audio-caption pairs holding information on species, vocalization context, and animal behavior. After training on this dataset to connect language and audio representations, our model can identify over a thousand species' calls across taxa, complete bioacoustic tasks zero-shot, and retrieve animal vocalization recordings from natural text queries. When fine-tuned, BioLingual sets a new state-of-the-art on nine tasks in the Benchmark of Animal Sounds. Given its broad taxa coverage and ability to be flexibly queried in human language, we believe this model opens new paradigms in ecological monitoring and research, including free-text search on the world's acoustic monitoring archives. We open-source our models, dataset, and code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge