Lejla Batina
Emerging Threats and Countermeasures in Neuromorphic Systems: A Survey
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Neuromorphic computing mimics brain-inspired mechanisms through spiking neurons and energy-efficient processing, offering a pathway to efficient in-memory computing (IMC). However, these advancements raise critical security and privacy concerns. As the adoption of bio-inspired architectures and memristive devices increases, so does the urgency to assess the vulnerability of these emerging technologies to hardware and software attacks. Emerging architectures introduce new attack surfaces, particularly due to asynchronous, event-driven processing and stochastic device behavior. The integration of memristors into neuromorphic hardware and software implementations in spiking neural networks offers diverse possibilities for advanced computing architectures, including their role in security-aware applications. This survey systematically analyzes the security landscape of neuromorphic systems, covering attack methodologies, side-channel vulnerabilities, and countermeasures. We focus on both hardware and software concerns relevant to spiking neural networks (SNNs) and hardware primitives, such as Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs) and True Random Number Generators (TRNGs) for cryptographic and secure computation applications. We approach this analysis from diverse perspectives, from attack methodologies to countermeasure strategies that integrate efficiency and protection in brain-inspired hardware. This review not only maps the current landscape of security threats but provides a foundation for developing secure and trustworthy neuromorphic architectures.
CNN architecture extraction on edge GPU
Jan 24, 2024Abstract:Neural networks have become popular due to their versatility and state-of-the-art results in many applications, such as image classification, natural language processing, speech recognition, forecasting, etc. These applications are also used in resource-constrained environments such as embedded devices. In this work, the susceptibility of neural network implementations to reverse engineering is explored on the NVIDIA Jetson Nano microcomputer via side-channel analysis. To this end, an architecture extraction attack is presented. In the attack, 15 popular convolutional neural network architectures (EfficientNets, MobileNets, NasNet, etc.) are implemented on the GPU of Jetson Nano and the electromagnetic radiation of the GPU is analyzed during the inference operation of the neural networks. The results of the analysis show that neural network architectures are easily distinguishable using deep learning-based side-channel analysis.
Playing with blocks: Toward re-usable deep learning models for side-channel profiled attacks
Mar 17, 2022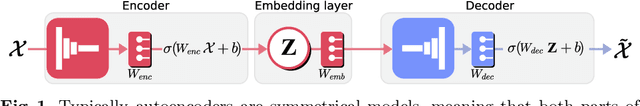
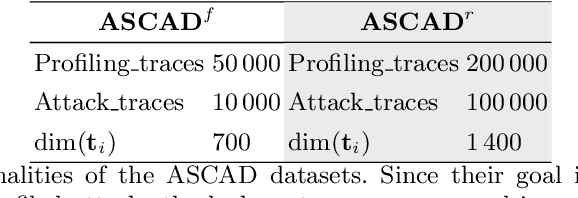
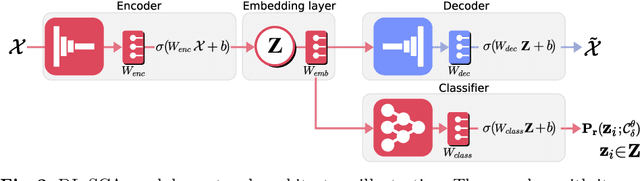
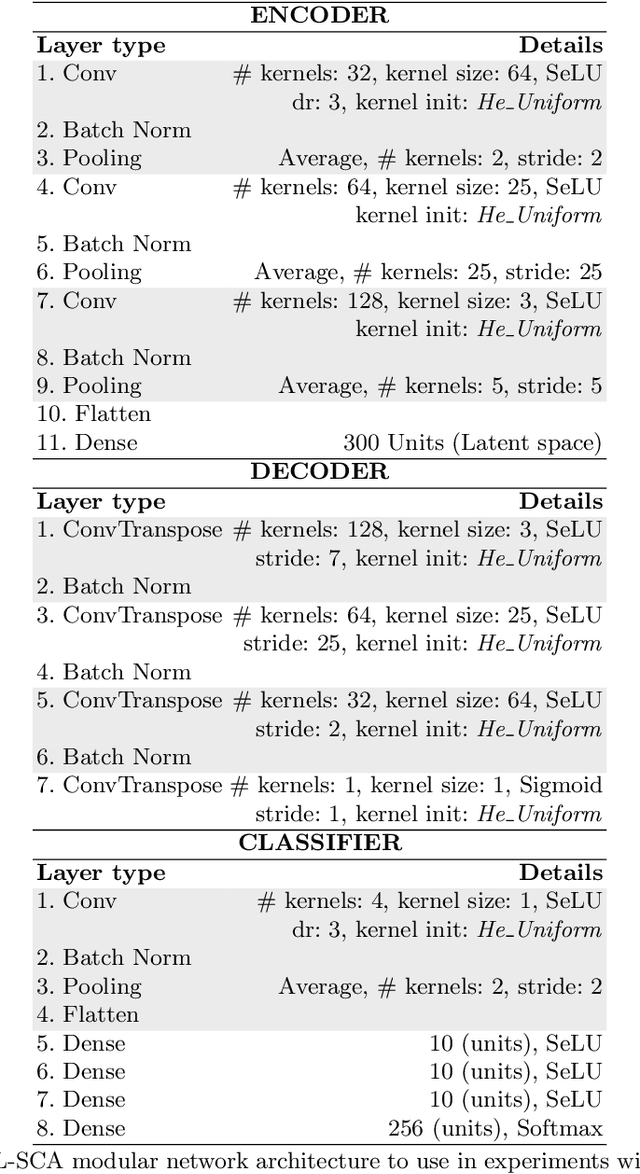
Abstract:This paper introduces a deep learning modular network for side-channel analysis. Our deep learning approach features the capability to exchange part of it (modules) with others networks. We aim to introduce reusable trained modules into side-channel analysis instead of building architectures for each evaluation, reducing the body of work when conducting those. Our experiments demonstrate that our architecture feasibly assesses a side-channel evaluation suggesting that learning transferability is possible with the network we propose in this paper.
Being Patient and Persistent: Optimizing An Early Stopping Strategy for Deep Learning in Profiled Attacks
Nov 29, 2021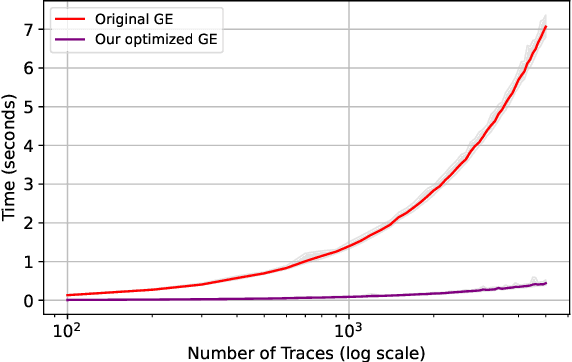


Abstract:The absence of an algorithm that effectively monitors deep learning models used in side-channel attacks increases the difficulty of evaluation. If the attack is unsuccessful, the question is if we are dealing with a resistant implementation or a faulty model. We propose an early stopping algorithm that reliably recognizes the model's optimal state during training. The novelty of our solution is an efficient implementation of guessing entropy estimation. Additionally, we formalize two conditions, persistence and patience, for a deep learning model to be optimal. As a result, the model converges with fewer traces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge