Konstantinos Kalais
Stochastic Deep Networks with Linear Competing Units for Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning
Aug 02, 2022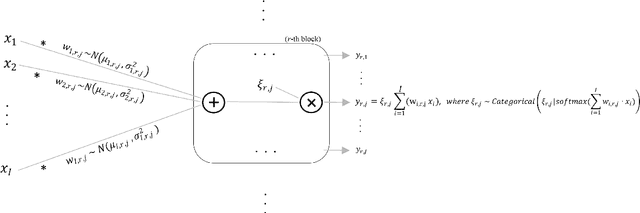



Abstract:This work addresses meta-learning (ML) by considering deep networks with stochastic local winner-takes-all (LWTA) activations. This type of network units results in sparse representations from each model layer, as the units are organized into blocks where only one unit generates a non-zero output. The main operating principle of the introduced units rely on stochastic principles, as the network performs posterior sampling over competing units to select the winner. Therefore, the proposed networks are explicitly designed to extract input data representations of sparse stochastic nature, as opposed to the currently standard deterministic representation paradigm. Our approach produces state-of-the-art predictive accuracy on few-shot image classification and regression experiments, as well as reduced predictive error on an active learning setting; these improvements come with an immensely reduced computational cost.
* Proc. ICML 2022
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge