Kelly B. Wagman
Generative AI Uses and Risks for Knowledge Workers in a Science Organization
Jan 27, 2025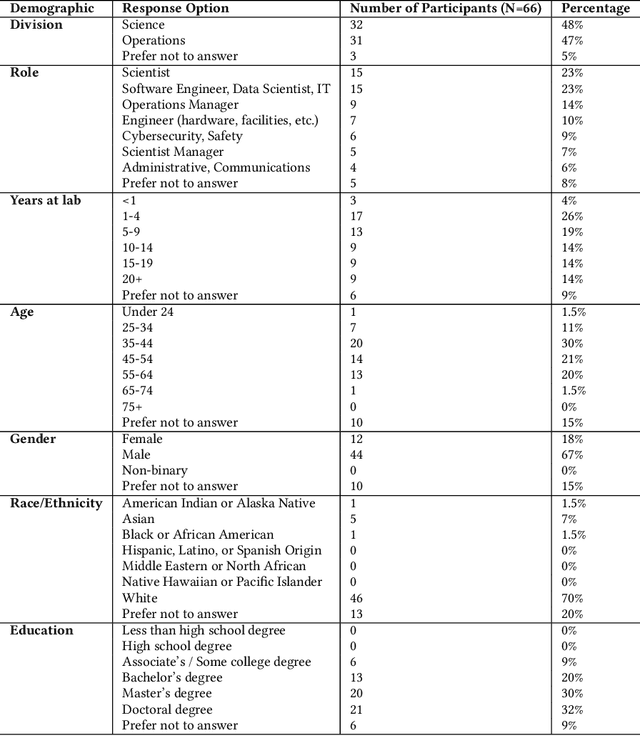

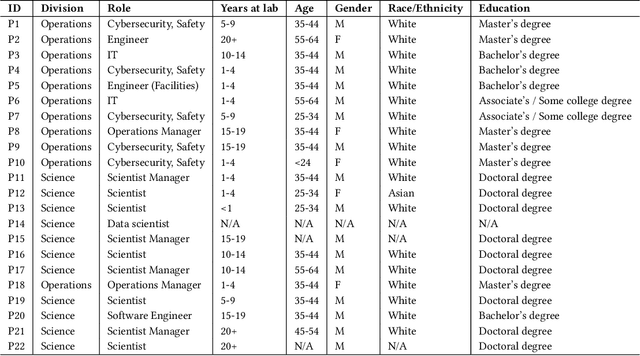

Abstract:Generative AI could enhance scientific discovery by supporting knowledge workers in science organizations. However, the real-world applications and perceived concerns of generative AI use in these organizations are uncertain. In this paper, we report on a collaborative study with a US national laboratory with employees spanning Science and Operations about their use of generative AI tools. We surveyed 66 employees, interviewed a subset (N=22), and measured early adoption of an internal generative AI interface called Argo lab-wide. We have four findings: (1) Argo usage data shows small but increasing use by Science and Operations employees; Common current and envisioned use cases for generative AI in this context conceptually fall into either a (2) copilot or (3) workflow agent modality; and (4) Concerns include sensitive data security, academic publishing, and job impacts. Based on our findings, we make recommendations for generative AI use in science and other organizations.
Beyond the Command: Feminist STS Research and Critical Issues for the Design of Social Machines
Jan 31, 2021Abstract:Machines, from artificially intelligent digital assistants to embodied robots, are becoming more pervasive in everyday life. Drawing on feminist science and technology studies (STS) perspectives, we demonstrate how machine designers are not just crafting neutral objects, but relationships between machines and humans that are entangled in human social issues such as gender and power dynamics. Thus, in order to create a more ethical and just future, the dominant assumptions currently underpinning the design of these human-machine relations must be challenged and reoriented toward relations of justice and inclusivity. This paper contributes the "social machine" as a model for technology designers who seek to recognize the importance, diversity and complexity of the social in their work, and to engage with the agential power of machines. In our model, the social machine is imagined as a potentially equitable relationship partner that has agency and as an "other" that is distinct from, yet related to, humans, objects, and animals. We critically examine and contrast our model with tendencies in robotics that consider robots as tools, human companions, animals or creatures, and/or slaves. In doing so, we demonstrate ingrained dominant assumptions about human-machine relations and reveal the challenges of radical thinking in the social machine design space. Finally, we present two design challenges based on non-anthropomorphic figuration and mutuality, and call for experimentation, unlearning dominant tendencies, and reimagining of sociotechnical futures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge