Karthik Narayanaswami
A Model-Based Approach to Predicting Predator-Prey & Friend-Foe Relationships in Ant Colonies
Dec 14, 2009
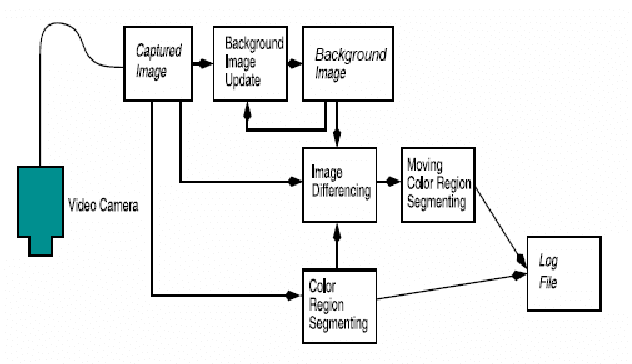
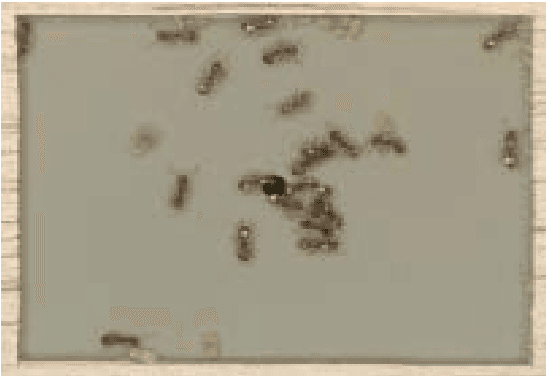
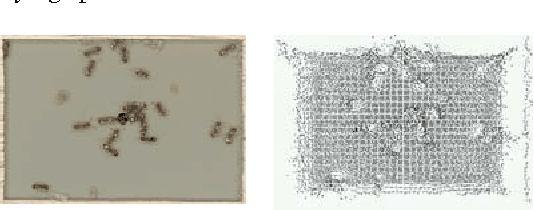
Abstract:Understanding predator-prey relationships among insects is a challenging task in the domain of insect-colony research. This is due to several factors involved, such as determining whether a particular behavior is the result of a predator-prey interaction, a friend-foe interaction or another kind of interaction. In this paper, we analyze a series of predator-prey and friend-foe interactions in two colonies of carpenter ants to better understand and predict such behavior. Using the data gathered, we have also come up with a preliminary model for predicting such behavior under the specific conditions the experiment was conducted in. In this paper, we present the results of our data analysis as well as an overview of the processes involved.
ScheduleNanny: Using GPS to Learn the User's Significant Locations, Travel Times and Schedule
Sep 02, 2004



Abstract:As computing technology becomes more pervasive, personal devices such as the PDA, cell-phone, and notebook should use context to determine how to act. Location is one form of context that can be used in many ways. We present a multiple-device system that collects and clusters GPS data into significant locations. These locations are then used to determine travel times and a probabilistic model of the user's schedule, which is used to intelligently alert the user. We evaluate our system and suggest how it should be integrated with a variety of applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge