Jozsef Molnar
Surface Segmentation Using Implicit Divergence Constraint Between Adjacent Minimal Paths
Nov 25, 2021
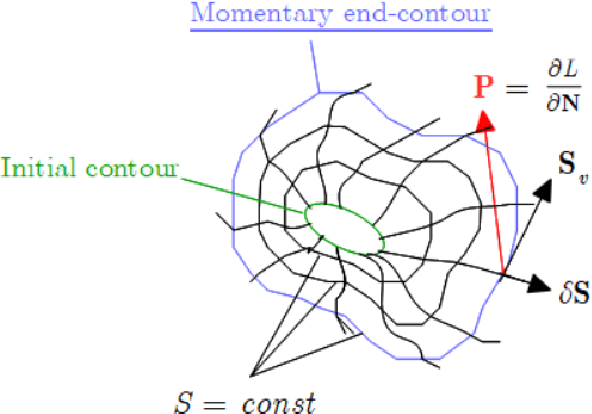
Abstract:We introduce a novel approach for object segmentation from 3D images using modified minimal path Eikonal equation. The proposed method utilizes an implicit constraint - a second order correction to the inhomogeneous minimal path Eikonal - preventing the adjacent minimal path trajectories to diverge uncontrollably. The proposed modification greatly reduces the surface area uncovered by minimal paths allowing the use of the calculated minimal path set as parameter lines of an approximate surface. It also has a loose connection with the true minimal surface Eikonal equations that are also deduced.
An Elastic Energy Minimization Framework for Mean Surface Calculation
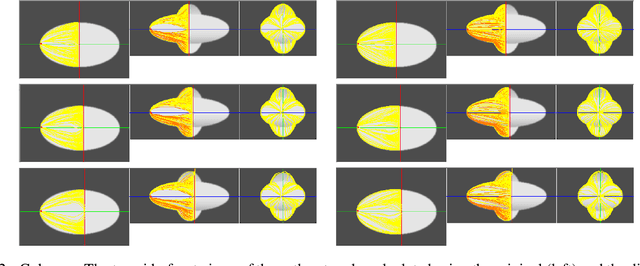
Jul 31, 2019Abstract:As the continuation of the contour mean calculation - designed for averaging the manual delineations of 3D layer stack images - in this paper, the most important equations: a) the reparameterization equations to determine the minimizing diffeomorphism and b) the proper centroid calculation for the surface mean calculation are presented. The chosen representation space: escaled Position by Square root Normal (RPSN) is a real valued vector space, invariant under the action of the reparameterization group and the imposed L2 metric (used to define the distance function) has well defined meaning: the sum of the central second moments of the coordinate functions. For comparision purpose, the reparameterization equations for elastic surface matching, using the Square Root Normal Function (SRNF) are also provided. The reparameterization equations for these cases have formal similarity, albeit the targeted applications differ: SRNF representation suitable for shape analysis purpose whereas RPSN is more fit for the cases where all contextual information - including the relative translation between the constituent surfaces - are to be retained (but the sake of theoretical completeness, the possibility of the consistent relative displacement removal in the RPSN case is also addressed).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge