Joseph Near
Beyond Fixed Psychological Personas: State Beats Trait, but Language Models are State-Blind
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:User interactions with language models vary due to static properties of the user (trait) and the specific context of the interaction (state). However, existing persona datasets (like PersonaChat, PANDORA etc.) capture only trait, and ignore the impact of state. We introduce Chameleon, a dataset of 5,001 contextual psychological profiles from 1,667 Reddit users, each measured across multiple contexts. Using the Chameleon dataset, we present three key findings. First, inspired by Latent State-Trait theory, we decompose variance and find that 74\% is within-person(state) while only 26\% is between-person (trait). Second, we find that LLMs are state-blind: they focus on trait only, and produce similar responses regardless of state. Third, we find that reward models react to user state, but inconsistently: different models favor or penalize the same users in opposite directions. We release Chameleon to support research on affective computing, personalized dialogue, and RLHF alignment.
Efficient Differentially Private Secure Aggregation for Federated Learning via Hardness of Learning with Errors
Dec 13, 2021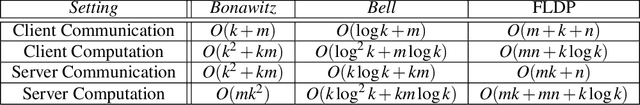
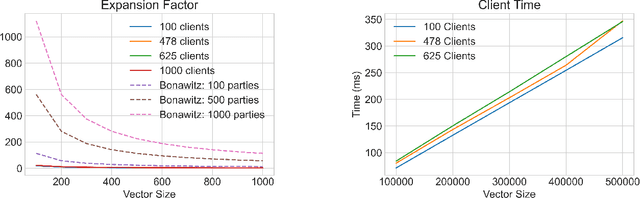
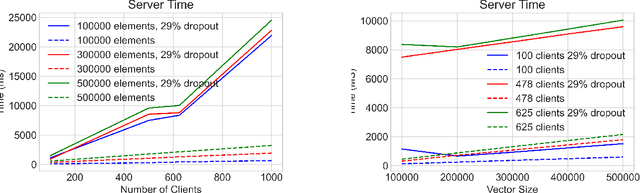
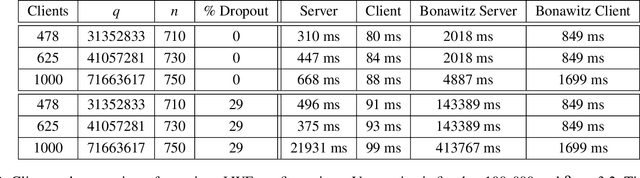
Abstract:Federated machine learning leverages edge computing to develop models from network user data, but privacy in federated learning remains a major challenge. Techniques using differential privacy have been proposed to address this, but bring their own challenges -- many require a trusted third party or else add too much noise to produce useful models. Recent advances in \emph{secure aggregation} using multiparty computation eliminate the need for a third party, but are computationally expensive especially at scale. We present a new federated learning protocol that leverages a novel differentially private, malicious secure aggregation protocol based on techniques from Learning With Errors. Our protocol outperforms current state-of-the art techniques, and empirical results show that it scales to a large number of parties, with optimal accuracy for any differentially private federated learning scheme.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge