Jose Ignacio Hernandez
An economically-consistent discrete choice model with flexible utility specification based on artificial neural networks
Apr 19, 2024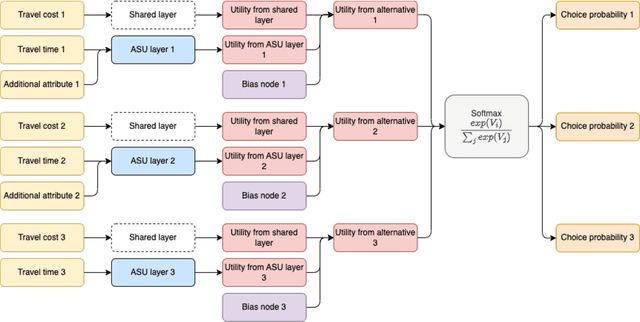

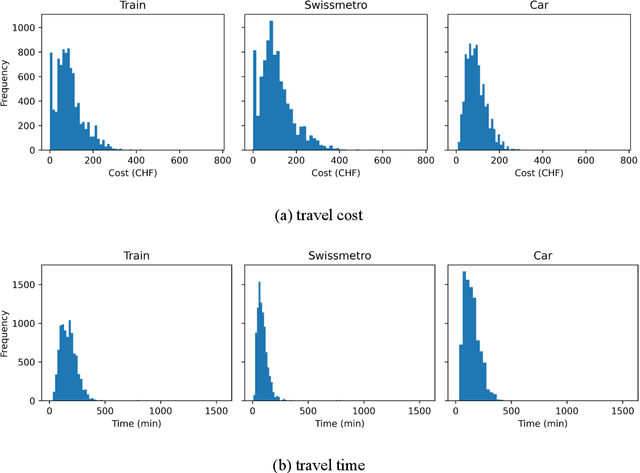
Abstract:Random utility maximisation (RUM) models are one of the cornerstones of discrete choice modelling. However, specifying the utility function of RUM models is not straightforward and has a considerable impact on the resulting interpretable outcomes and welfare measures. In this paper, we propose a new discrete choice model based on artificial neural networks (ANNs) named "Alternative-Specific and Shared weights Neural Network (ASS-NN)", which provides a further balance between flexible utility approximation from the data and consistency with two assumptions: RUM theory and fungibility of money (i.e., "one euro is one euro"). Therefore, the ASS-NN can derive economically-consistent outcomes, such as marginal utilities or willingness to pay, without explicitly specifying the utility functional form. Using a Monte Carlo experiment and empirical data from the Swissmetro dataset, we show that ASS-NN outperforms (in terms of goodness of fit) conventional multinomial logit (MNL) models under different utility specifications. Furthermore, we show how the ASS-NN is used to derive marginal utilities and willingness to pay measures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge