John Musgrave
kNN Classification of Malware Data Dependency Graph Features
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:Feature resolution impacts the ability of classifiers to make explainable inferences when applied to malware classification. We explore classification based on features constructed from data dependency graphs, and present results from k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) classifiers. Our study demonstrates that classification based on a novel feature representation not only yields high accuracy, but also increases explainability in inference, as features of data dependency are directly representative of program behavior. We present classification results using the Microsoft Kaggle 2015 malware dataset which was processed with a novel approach to feature extraction and representation. We show that non-parametric approaches to classification in the metric space are able to obtain classification accuracy of 87.5\% when applied to multi-class classification in the Kaggle malware dataset. Additionally, similarity in the metric space can be calculated directly without prior training. Our results provide evidence that data dependency graphs accurately capture both semantic and structural information.
A Novel Feature Representation for Malware Classification
Oct 18, 2022
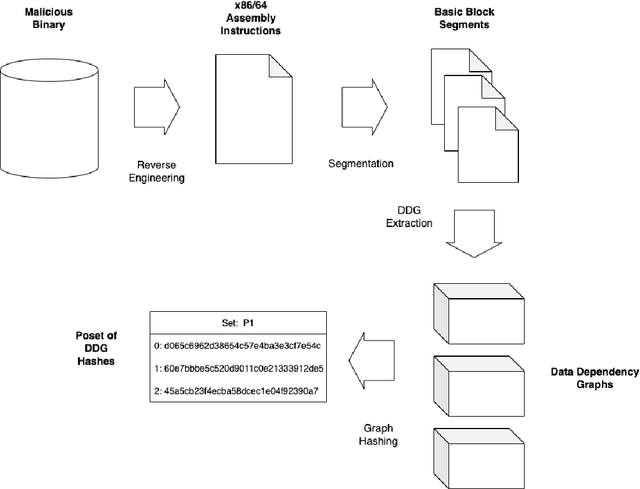
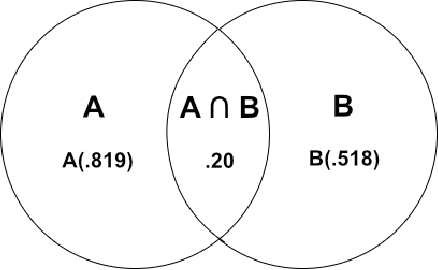
Abstract:In this study we have presented a novel feature representation for malicious programs that can be used for malware classification. We have shown how to construct the features in a bottom-up approach, and analyzed the overlap of malicious and benign programs in terms of their components. We have shown that our method of analysis offers an increase in feature resolution that is descriptive of data movement in comparison to tf-idf features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge