Johannes Wollbold
Constructing a Knowledge Base for Gene Regulatory Dynamics by Formal Concept Analysis Methods
Jul 21, 2008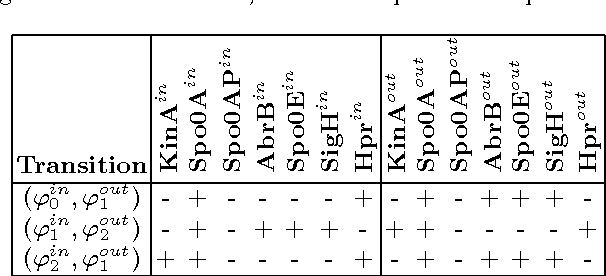
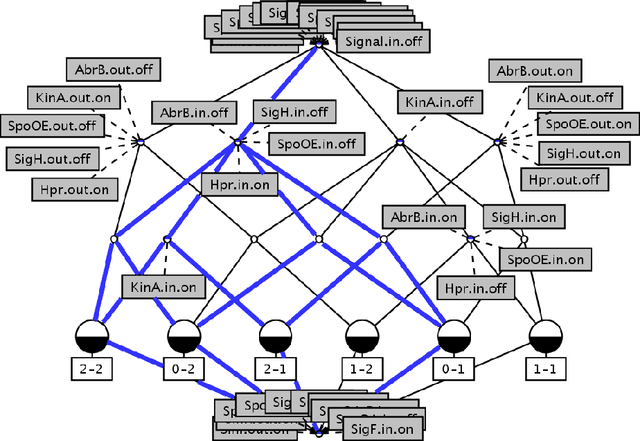
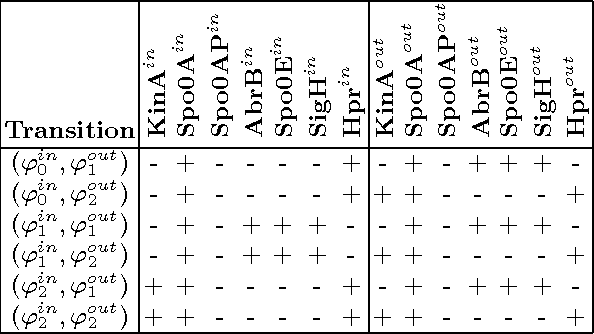
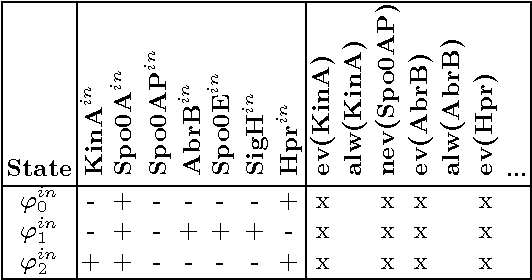
Abstract:Our aim is to build a set of rules, such that reasoning over temporal dependencies within gene regulatory networks is possible. The underlying transitions may be obtained by discretizing observed time series, or they are generated based on existing knowledge, e.g. by Boolean networks or their nondeterministic generalization. We use the mathematical discipline of formal concept analysis (FCA), which has been applied successfully in domains as knowledge representation, data mining or software engineering. By the attribute exploration algorithm, an expert or a supporting computer program is enabled to decide about the validity of a minimal set of implications and thus to construct a sound and complete knowledge base. From this all valid implications are derivable that relate to the selected properties of a set of genes. We present results of our method for the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. However the formal structures are exhibited in a most general manner. Therefore the approach may be adapted to signal transduction or metabolic networks, as well as to discrete temporal transitions in many biological and nonbiological areas.
* 15 pages, 1 figure, LaTeX style llncsdoc.sty
Attribute Exploration of Discrete Temporal Transitions
Sep 18, 2007



Abstract:Discrete temporal transitions occur in a variety of domains, but this work is mainly motivated by applications in molecular biology: explaining and analyzing observed transcriptome and proteome time series by literature and database knowledge. The starting point of a formal concept analysis model is presented. The objects of a formal context are states of the interesting entities, and the attributes are the variable properties defining the current state (e.g. observed presence or absence of proteins). Temporal transitions assign a relation to the objects, defined by deterministic or non-deterministic transition rules between sets of pre- and postconditions. This relation can be generalized to its transitive closure, i.e. states are related if one results from the other by a transition sequence of arbitrary length. The focus of the work is the adaptation of the attribute exploration algorithm to such a relational context, so that questions concerning temporal dependencies can be asked during the exploration process and be answered from the computed stem base. Results are given for the abstract example of a game and a small gene regulatory network relevant to a biomedical question.
* Only the email address and reference have been replaced
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge