Jens Kley-Holsteg
tsrobprep -- an R package for robust preprocessing of time series data
Apr 26, 2021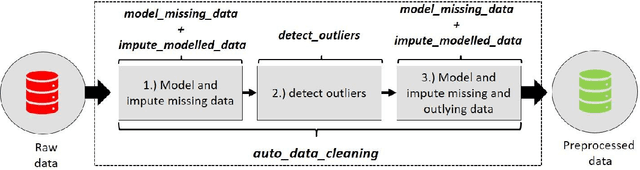
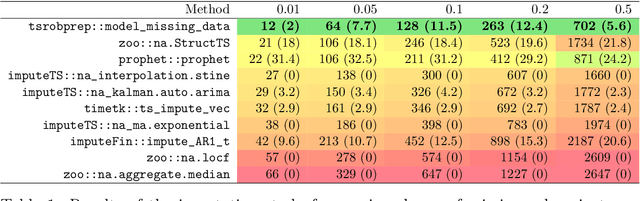
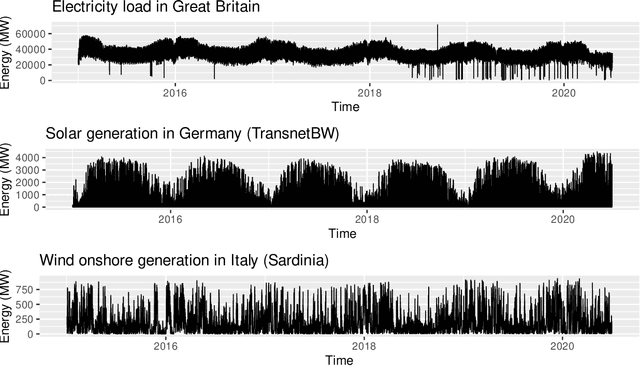
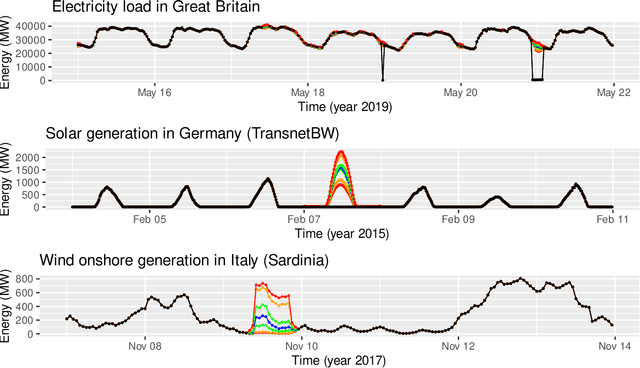
Abstract:Data cleaning is a crucial part of every data analysis exercise. Yet, the currently available R packages do not provide fast and robust methods for cleaning and preparation of time series data. The open source package tsrobprep introduces efficient methods for handling missing values and outliers using model based approaches. For data imputation a probabilistic replacement model is proposed, which may consist of autoregressive components and external inputs. For outlier detection a clustering algorithm based on finite mixture modelling is introduced, which considers typical time series related properties as features. By assigning to each observation a probability of being an outlying data point, the degree of outlyingness can be determined. The methods work robust and are fully tunable. Moreover, by providing the auto_data_cleaning function the data preprocessing can be carried out in one cast, without manual tuning and providing suitable results. The primary motivation of the package is the preprocessing of energy system data, however, the package is also suited for other moderate and large sized time series data set. We present application for electricity load, wind and solar power data.
Probabilistic Multi-Step-Ahead Short-Term Water Demand Forecasting with Lasso
May 09, 2020



Abstract:Water demand is a highly important variable for operational control and decision making. Hence, the development of accurate forecasts is a valuable field of research to further improve the efficiency of water utilities. Focusing on probabilistic multi-step-ahead forecasting, a time series model is introduced, to capture typical autoregressive, calendar and seasonal effects, to account for time-varying variance, and to quantify the uncertainty and path-dependency of the water demand process. To deal with the high complexity of the water demand process a high-dimensional feature space is applied, which is efficiently tuned by an automatic shrinkage and selection operator (lasso). It allows to obtain an accurate, simple interpretable and fast computable forecasting model, which is well suited for real-time applications. The complete probabilistic forecasting framework allows not only for simulating the mean and the marginal properties, but also the correlation structure between hours within the forecasting horizon. For practitioners, complete probabilistic multi-step-ahead forecasts are of considerable relevance as they provide additional information about the expected aggregated or cumulative water demand, so that a statement can be made about the probability with which a water storage capacity can guarantee the supply over a certain period of time. This information allows to better control storage capacities and to better ensure the smooth operation of pumps. To appropriately evaluate the forecasting performance of the considered models, the energy score (ES) as a strictly proper multidimensional evaluation criterion, is introduced. The methodology is applied to the hourly water demand data of a German water supplier.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge