Javier Torón-Artiles
Classifying Soccer Ball-on-Goal Position Through Kicker Shooting Action
Dec 23, 2023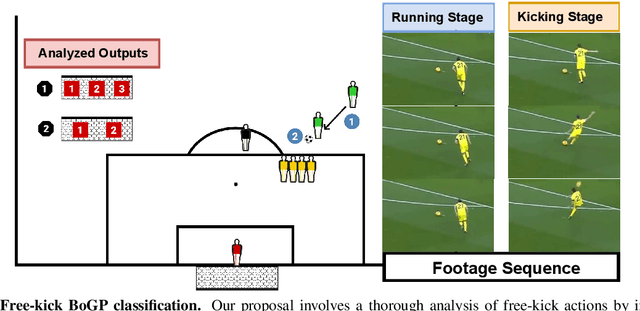
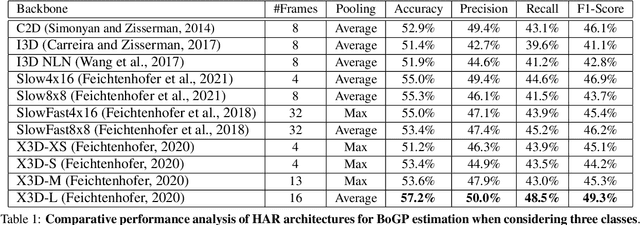

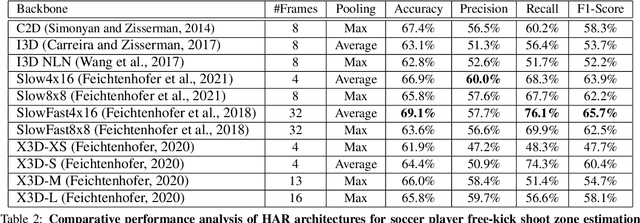
Abstract:This research addresses whether the ball's direction after a soccer free-kick can be accurately predicted solely by observing the shooter's kicking technique. To investigate this, we meticulously curated a dataset of soccer players executing free kicks and conducted manual temporal segmentation to identify the moment of the kick precisely. Our approach involves utilizing neural networks to develop a model that integrates Human Action Recognition (HAR) embeddings with contextual information, predicting the ball-on-goal position (BoGP) based on two temporal states: the kicker's run-up and the instant of the kick. The study encompasses a performance evaluation for eleven distinct HAR backbones, shedding light on their effectiveness in BoGP estimation during free-kick situations. An extra tabular metadata input is introduced, leading to an interesting model enhancement without introducing bias. The promising results reveal 69.1% accuracy when considering two primary BoGP classes: right and left. This underscores the model's proficiency in predicting the ball's destination towards the goal with high accuracy, offering promising implications for understanding free-kick dynamics in soccer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge