Jan Deeken
Machine Learning Methods for the Design and Operation of Liquid Rocket Engines -- Research Activities at the DLR Institute of Space Propulsion
Feb 14, 2021
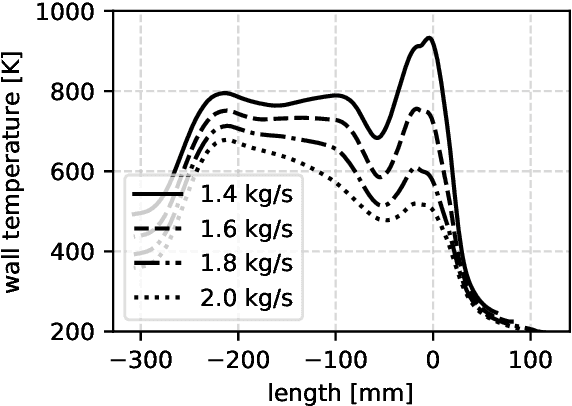
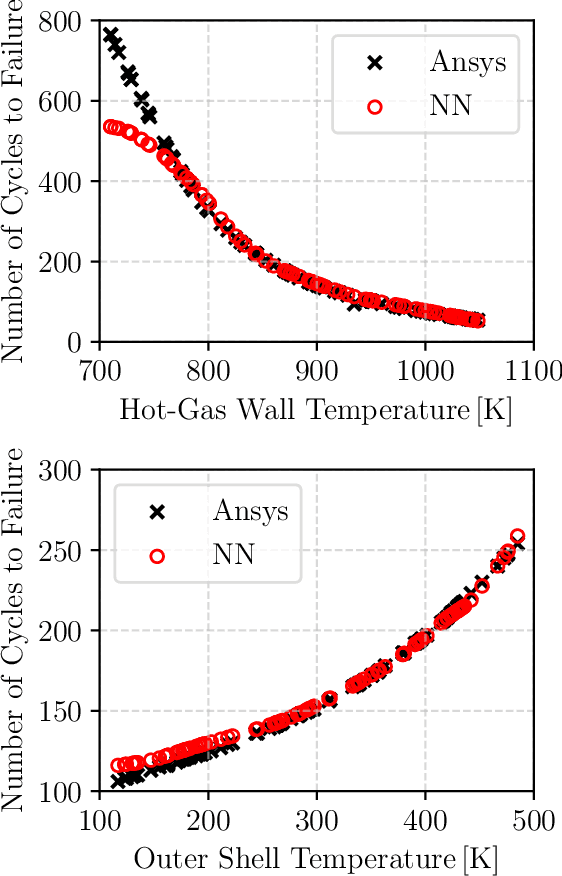
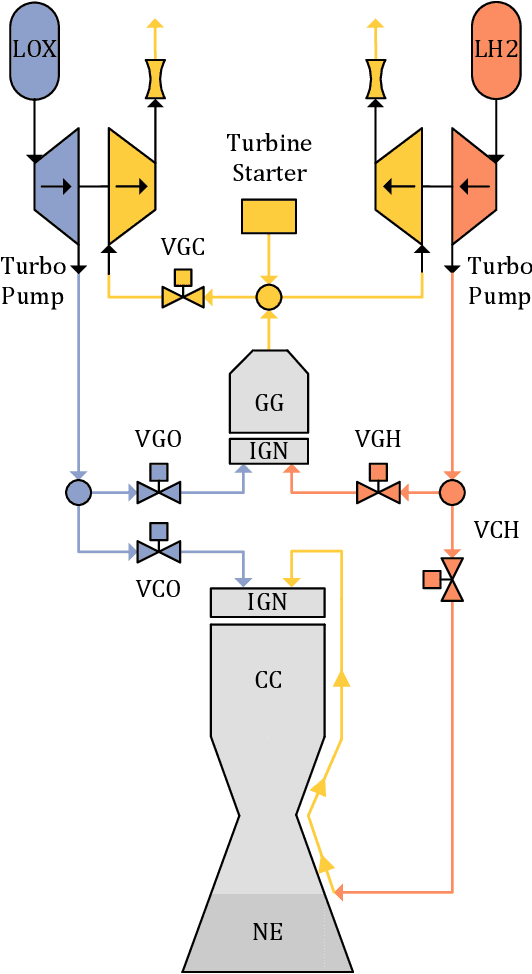
Abstract:The last years have witnessed an enormous interest in the use of artificial intelligence methods, especially machine learning algorithms. This also has a major impact on aerospace engineering in general, and the design and operation of liquid rocket engines in particular, and research in this area is growing rapidly. The paper describes current machine learning applications at the DLR Institute of Space Propulsion. Not only applications in the field of modeling are presented, but also convincing results that prove the capabilities of machine learning methods for control and condition monitoring are described in detail. Furthermore, the advantages and disadvantages of the presented methods as well as current and future research directions are discussed.
Multidisciplinary Design Optimization of Reusable Launch Vehicles for Different Propellants and Objectives
Sep 03, 2020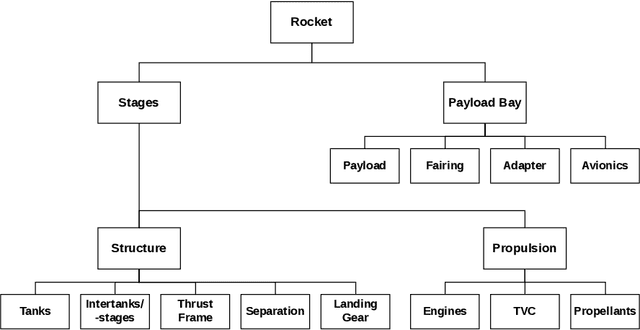
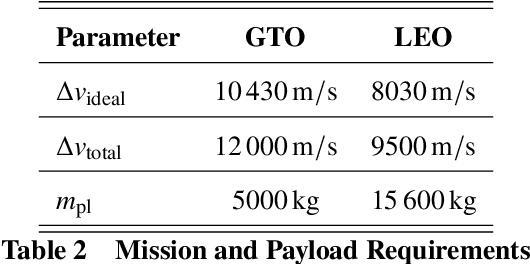
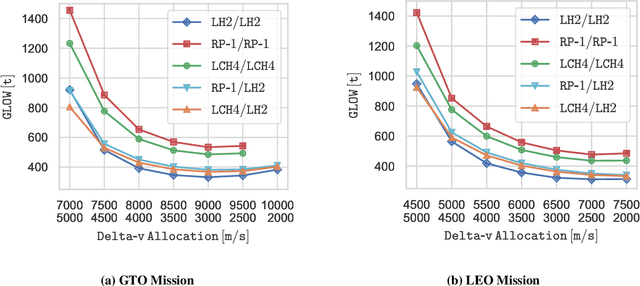
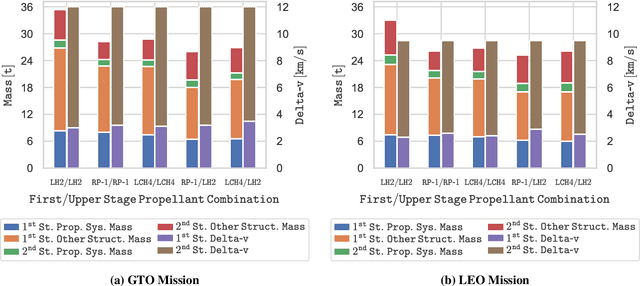
Abstract:Identifying the optimal design of a new launch vehicle is most important since design decisions made in the early development phase limit the vehicles' later performance and determines the associated costs. Reusing the first stage via retro-propulsive landing increases the complexity even more. Therefore, we develop an optimization framework for partially reusable launch vehicles, which enables multidisciplinary design studies. The framework contains suitable mass estimates of all essential subsystems and a routine to calculate the needed propellant for the ascent and landing maneuvers. For design optimization, the framework can be coupled with a genetic algorithm. The overall goal is to reveal the implications of different propellant combinations and objective functions on the launcher's optimal design for various mission scenarios. The results show that the optimization objective influences the most suitable propellant choice and the overall launcher design, concerning staging, weight, size, and rocket engine parameters. In terms of gross lift-off weight, liquid hydrogen seems to be favorable. When optimizing for a minimum structural mass or an expandable structural mass, hydrocarbon-based solutions show better results. Finally, launch vehicles using a hydrocarbon fuel in the first stage and liquid hydrogen in the upper stage are an appealing alternative, combining both fuels' benefits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge