James McLaughlin
Seizure Classification Using Parallel Genetic Naive Bayes Classifiers
Oct 06, 2021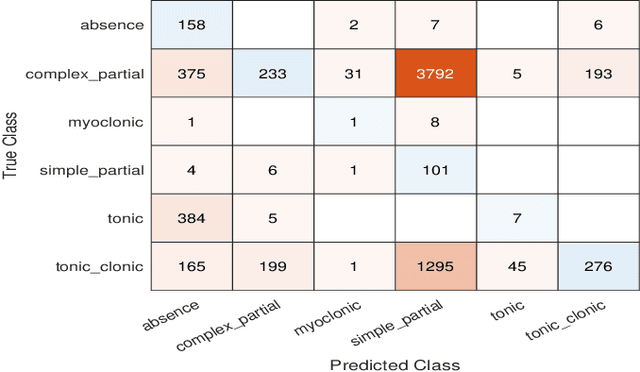

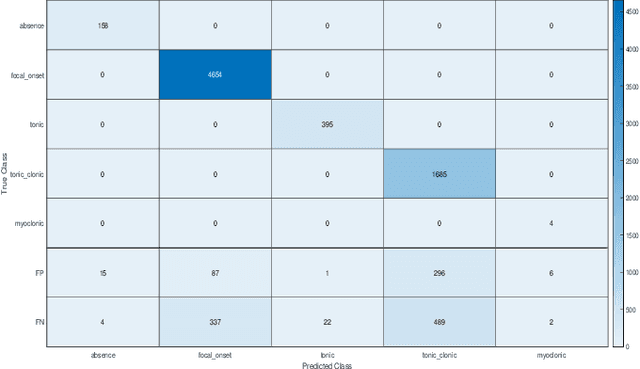
Abstract:Epilepsy affects 50 million people worldwide and is one of the most common serious brain disorders. Seizure detection and classification is a valuable tool for maintaining the condition. An automated detection algorithm will allow for accurate diagnosis. This study proposes a method using unique features with a novel parallel classifier trained using a genetic algorithm. Ictal states from the EEG are segmented into 1.8 s windows, where the epochs are then further decomposed into 13 different features from the first IMF. All of the features are fed into a genetic algorithm (Binary Grey Wolf Optimisation Option 1) with a Naive Bayes classifier. Combining the simple partial and complex partial seizures provides the highest accuracy of all the models tested.
Augmenting expert detection of early coronary artery occlusion from 12 lead electrocardiograms using deep learning
Mar 20, 2019



Abstract:Early diagnosis of acute coronary artery occlusion based on electrocardiogram (ECG) findings is essential for prompt delivery of primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Current ST elevation (STE) criteria are specific but insensitive. Consequently, it is likely that many patients are missing out on potentially life-saving treatment. Experts combining non-specific ECG changes with STE detect ischaemia with higher sensitivity, but at the cost of specificity. We show that a deep learning model can detect ischaemia caused by acute coronary artery occlusion with a better balance of sensitivity and specificity than STE criteria, existing computerised analysers or expert cardiologists.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge