Ismail A. Ismail
Design of a Framework to Facilitate Decisions Using Information Fusion
Feb 21, 2015Abstract:Information fusion is an advanced research area which can assist decision makers in enhancing their decisions. This paper aims at designing a new multi-layer framework that can support the process of performing decisions from the obtained beliefs using information fusion. Since it is not an easy task to cross the gap between computed beliefs of certain hypothesis and decisions, the proposed framework consists of the following layers in order to provide a suitable architecture (ordered bottom up): 1. A layer for combination of basic belief assignments using an information fusion approach. Such approach exploits Dezert-Smarandache Theory, DSmT, and proportional conflict redistribution to provide more realistic final beliefs. 2. A layer for computation of pignistic probability of the underlying propositions from the corresponding final beliefs. 3. A layer for performing probabilistic reasoning using a Bayesian network that can obtain the probable reason of a proposition from its pignistic probability. 4. Ranking the system decisions is ultimately used to support decision making. A case study has been accomplished at various operational conditions in order to prove the concept, in addition it pointed out that: 1. The use of DSmT for information fusion yields not only more realistic beliefs but also reliable pignistic probabilities for the underlying propositions. 2. Exploiting the pignistic probability for the integration of the information fusion with the Bayesian network provides probabilistic inference and enable decision making on the basis of both belief based probabilities for the underlying propositions and Bayesian based probabilities for the corresponding reasons. A comparative study of the proposed framework with respect to other information fusion systems confirms its superiority to support decision making.
* 17 pages, 5 figures, Journal of Al Azhar University Engineering Sector, Vol. 8, No. 28, July 2013, 1237-1250. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:cs/0409007 by other authors
Signature Recognition using Multi Scale Fourier Descriptor And Wavelet Transform
Apr 08, 2010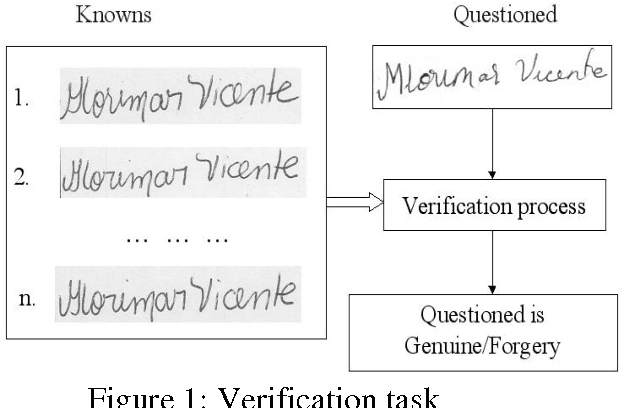



Abstract:This paper present a novel off-line signature recognition method based on multi scale Fourier Descriptor and wavelet transform . The main steps of constructing a signature recognition system are discussed and experiments on real data sets show that the average error rate can reach 1%. Finally we compare 8 distance measures between feature vectors with respect to the recognition performance. Key words: signature recognition; Fourier Descriptor; Wavelet transform; personal verification
* IEEE Publication format, ISSN 1947 5500, http://sites.google.com/site/ijcsis/
Genetic Programming Framework for Fingerprint Matching
Dec 05, 2009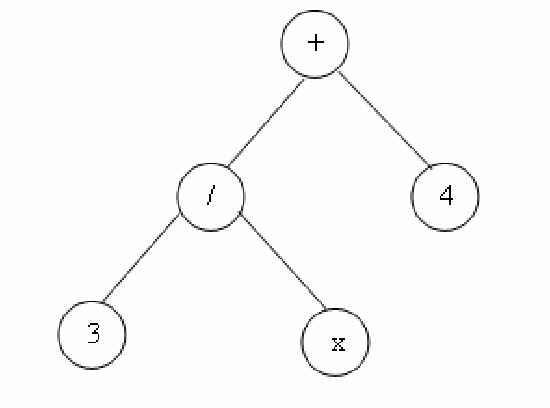
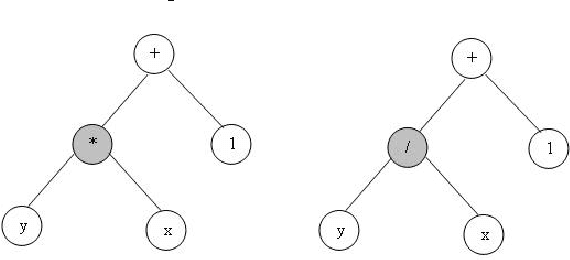
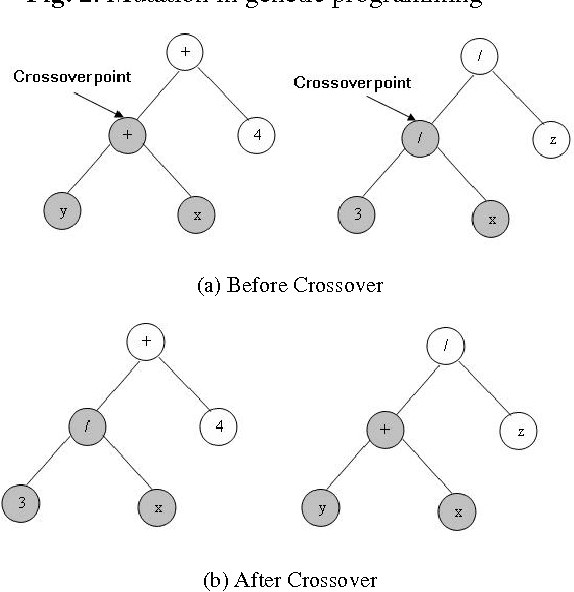
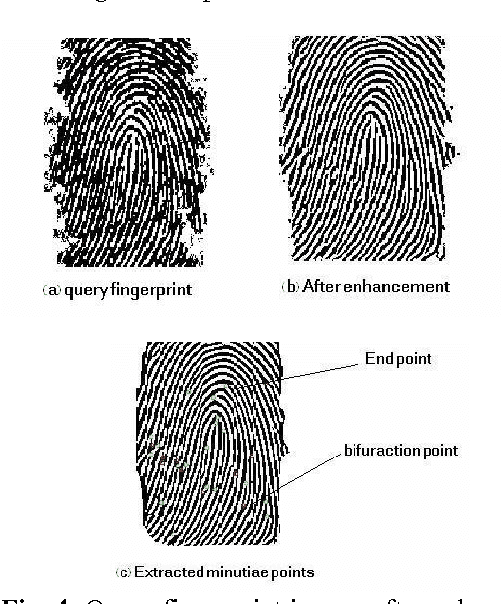
Abstract:A fingerprint matching is a very difficult problem. Minutiae based matching is the most popular and widely used technique for fingerprint matching. The minutiae points considered in automatic identification systems are based normally on termination and bifurcation points. In this paper we propose a new technique for fingerprint matching using minutiae points and genetic programming. The goal of this paper is extracting the mathematical formula that defines the minutiae points.
* 6 pages IEEE format, International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security, IJCSIS November 2009, ISSN 1947 5500, http://sites.google.com/site/ijcsis/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge