Iliana Ferrer
Socially assistive robots' deployment in healthcare settings: a global perspective
Oct 14, 2021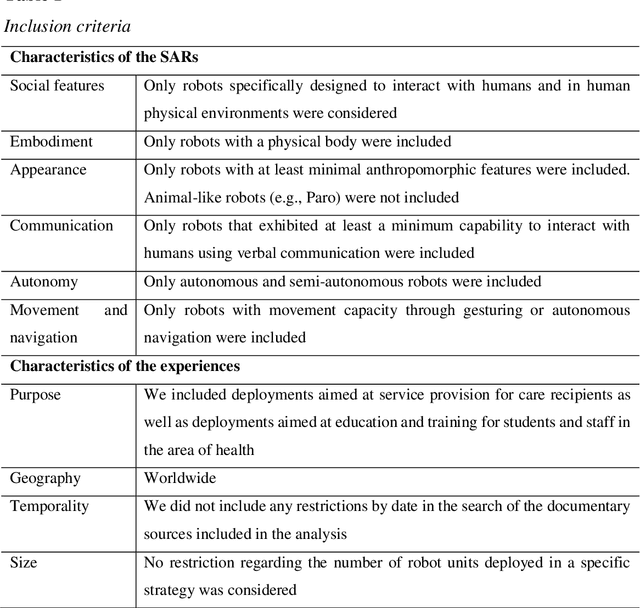
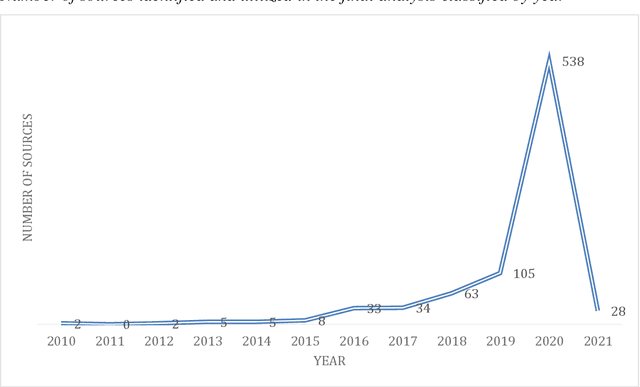
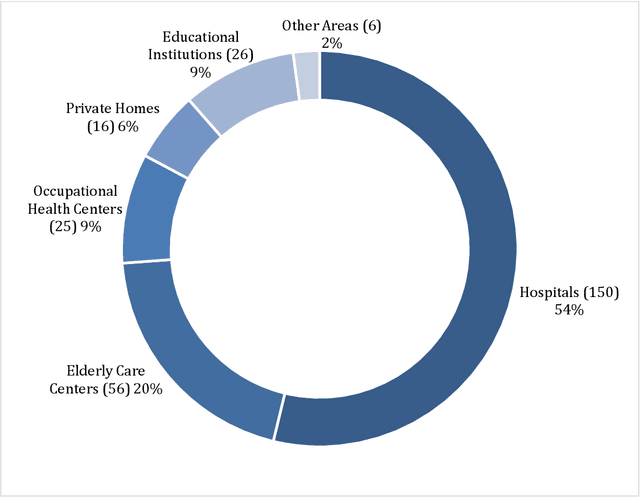
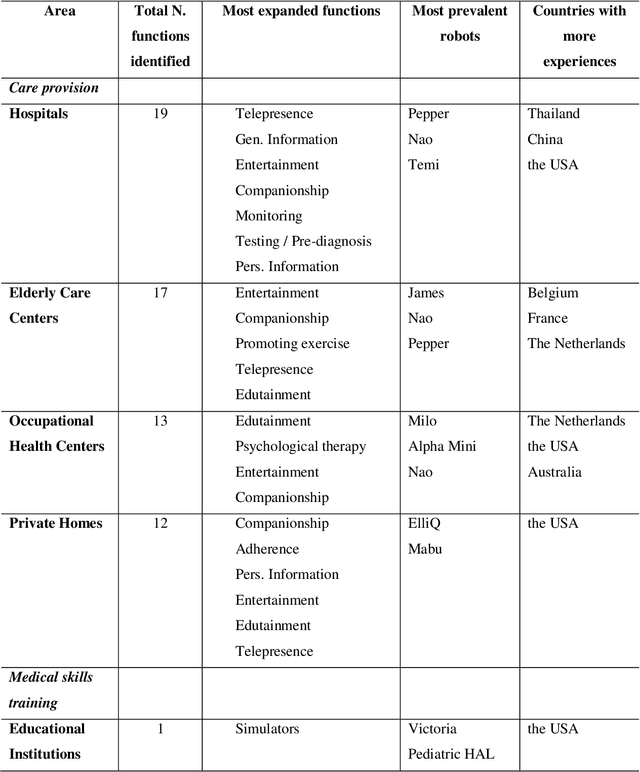
Abstract:One of the major areas where social robots are finding their place in society is for healthcare-related applications. Yet, very little research has mapped the deployment of socially assistive robots (SARs) in real settings. Using a documentary research method, we were able to trace back 279 experiences of SARs deployments in hospitals, elderly care centers, occupational health centers, private homes, and educational institutions worldwide from 33 different countries, and involving 52 different robot models. We retrieved, analyzed, and classified the functions that SARs develop in these experiences, the areas in which they are deployed, the principal manufacturers, and the robot models that are being adopted. The functions we identified for SARs are entertainment, companionship, telepresence, edutainment, providing general and personalized information or advice, monitoring, promotion of physical exercise and rehabilitation, testing and pre-diagnosis, delivering supplies, patient registration, giving location indications, patient simulator, protective measure enforcement, medication and well-being adherence, translating and having conversations in multiple languages, psychological therapy, patrolling, interacting with digital devices, and disinfection. Our work provides an in-depth picture of the current state of the art of SARs' deployment in real scenarios for healthcare-related applications and contributes to understanding better the role of these machines in the healthcare sector.
The implementation of social robots during the COVID-19 pandemic
Jul 08, 2020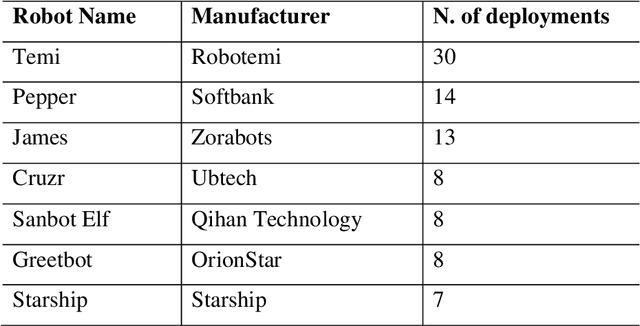
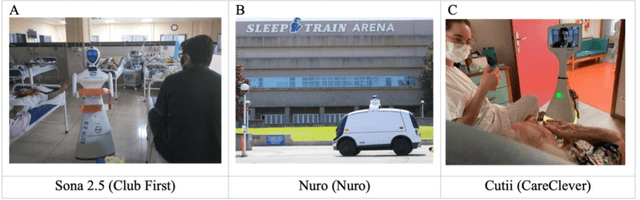
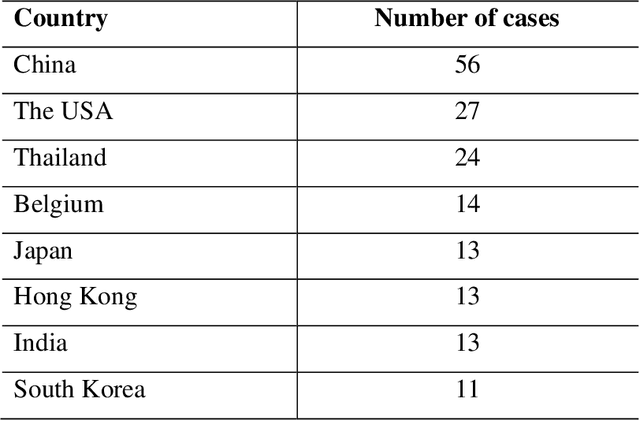

Abstract:The present study examines the implementation of social robots in real settings during the COVID-19 pandemic. In particular, we analyze the areas in which social robots are being adopted, the roles and tasks being fulfilled, and the robot models being implemented. For that, we traced back and analyzed 195 experiences with 66 different social robots worldwide that have been adopted during the coronavirus outbreak. We identified a clear resurgence and expansion of social robots during the crisis. The social robots' capacity to perform the roles of liaison in tasks that require human-human interaction, to act as a safeguard to ensure contagion risk-free environments, and to act as well-being coaches by providing therapeutic and entertaining functions for quarantined patients, which are directly associated with the needs of facilitating physical distance and palliate the effects of isolation, have been key to the renaissance of these robots during the pandemic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge